|
Entelognathus Primordialis
''Entelognathus primordialis'' (“primordial complete jaw”) is a maxillate placoderm from the late Silurian (Ludlow epoch) of Qujing, Yunnan, 419 million years ago. A team led by Min Zhu of the Academy of Sciences' Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology in Beijing discovered the intact, articulated fossil in rock formations at Xiaoxiang reservoir. Specimen and taxonomy The holotype of ''E. primordialis'' is the uncrushed and mostly intact anterior half of an individual with the articulating head and trunk armor preserved in three dimensions. The holotype is about long, and the live animal is estimated to have been over long. In overall form, the animal resembles primitive arthrodires, but the anatomy of the jaws strongly suggests the anatomies of bony fish and tetrapods. Specifically, this is the first stem gnathostome with dermal marginal jaw bones. These bones are the premaxilla, maxilla, and dentary. Most known placoderms had simple beak-like jaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptyctodont
The ptyctodontids ("folded-teeth") are placoderms of the order Ptyctodontida, containing the family Ptyctodontidae. With their big heads, big eyes, reduced armor and long bodies, the ptyctodontids bore a superficial resemblance to modern day chimaeras (Holocephali). Their armor was reduced to a pattern of small plates around the head and neck. Like the extinct and related acanthothoracids, and the living and unrelated holocephalians, most of the ptyctodontids are thought to have lived near the sea bottom and preyed on shellfish. On account of their radically reduced armor, some paleontologists have suggested that the Ptyctodontida were not actually placoderms, but actual holocephalians, some primitive group of elasmobranch fish, or even were the ancestors of the holocephalians, including the chimaeras. Thorough anatomical examinations of whole fossil specimens reveal that the profound similarities between these two groups are actually very superficial. The major differences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Fossils
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors. In 1859, when Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as "the most obvious and gravest objection which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Animals Of China
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placodermi Enigmatic Taxa
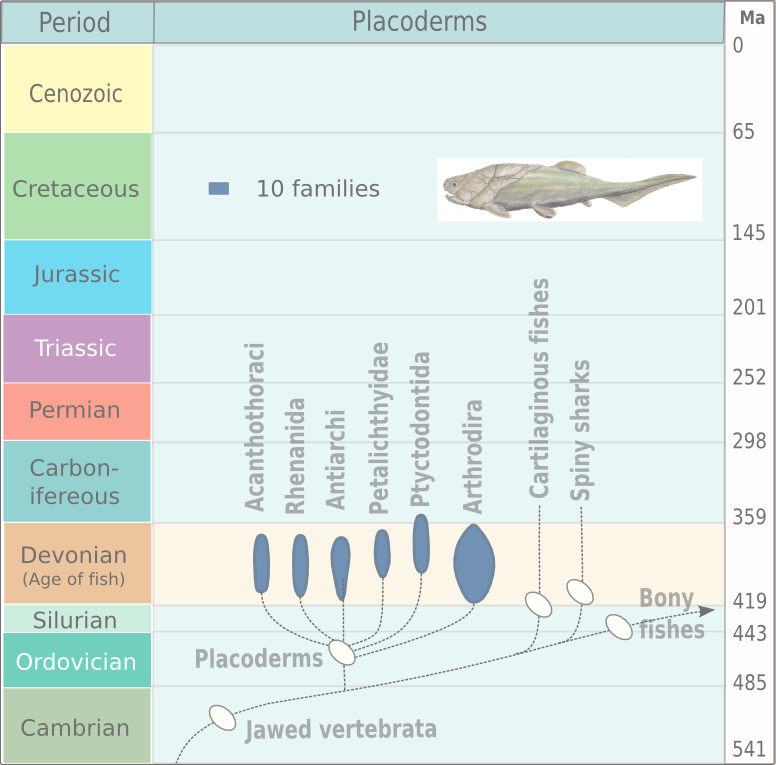
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian Fish Of Asia
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of Asia
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally ' plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurolepis
''Silurolepis platydorsalis'' is an extinct species of Silurian-aged "maxillate" placoderm that has been described from (mostly) articulated remains. Although it has been known for several years, it was finally described by Zhang, et al., in 2010. The earliest described placoderm is the yunnanolepid antiarch, ''Shimenolepis'', from Llandovery Hunan. In contrast to ''S. platydorsalis'', ''Shimenolepis'' is known only from distinctively ornamented thoracic armor plates that bear anatomic features unique to yunnanolepids. ''S. platydorsalis'' was previously considered a basal antiarch, but a 2019 study instead recovers it as a maxillate placoderm most closely related to ''Qilinyu ''Qilinyu rostrata'' is a "maxillate" placoderm from the late Ludlow epoch of Qujing, Yunnan, 419 million years ago.Zhu, Min, et al. "A Silurian maxillate placoderm illuminates jaw evolution." Science 354.6310 (2016): 334-336/ref> Specimens and ...''. ''S. platydorsalis'' is known from thoracic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qilinyu
''Qilinyu rostrata'' is a "maxillate" placoderm from the late Ludlow epoch of Qujing, Yunnan, 419 million years ago.Zhu, Min, et al. "A Silurian maxillate placoderm illuminates jaw evolution." Science 354.6310 (2016): 334-336/ref> Specimens and taxonomy The holotype and paratype of ''Q. rostrata'' are two exquisitely preserved specimens both featuring a domed cranium and a curved rostrum presenting a "dolphin-like profile." The researchers' cladistic diagram shows ''Q. rostrata'' as the sister taxon of ''Entelognathus'', ''Janusiscus'' and the crown gnathostomes (i.e., bony and cartilaginous fishes and their descendants). Evolutionary significance ''Qilinyu rostrata'', together with ''Entelognathus'', demonstrates additional evidence that modern gnathostomes evolved from placoderms.Long, John A. "The first jaws." Science 354.6310 (2016): 280-281. See also * ''Entelognathus'' * ''Bianchengichthys'' * ''Silurolepis ''Silurolepis platydorsalis'' is an extinct species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bianchengichthys
''Bianchengichthys'' is an extinct genus of maxillate placoderm fish from the late Silurian Period. Its fossils have been recovered from Yunnan Province, China, and it is represented by only one species: ''Bianchengichthys micros''. Description ''Bianchengichthys'' is a small, somewhat dorsoventrally compressed placoderm fish. The mandible (made from dermal bone) of this genus differs from ''Entelognathus'' and ''Qilinyu''—two other maxillate placoderms from late Silurian China−in that the oral lamina is broad and carries a row of tooth-like denticles, though the marginal flange is toothless. The pectoral fin, preceded by two small spines on its thoracic shield, is lobate in shape and situated along by a 'fringe' of scales similar to those of ''Lepidotrichia'' in bony fishes. Similarly to other maxillate placoderms, its eyes are anteriorly orientated and very close to its mouth. Evolutionary significance ''Bianchengichthys mandible bears physical resemblance to both its r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Restoration Of Sparalepis Tingi
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy transformation, and reproduction. Various forms of life exist, such as plants, animals, fungi, protists, archaea, and bacteria. Biology is the science that studies life. The gene is the unit of heredity, whereas the cell is the structural and functional unit of life. There are two kinds of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, both of which consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane and contain many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Cells reproduce through a process of cell division, in which the parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells and passes its genes onto a new generation, sometimes producing genetic variation. Organisms, or the individual entities of life, are generally thought to be open systems that maint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |