|
Ensemble De Lancement Vega
ELA-1, short for Ensemble de Lancement Ariane 1 (French for Ariane Launch Area 1), now named Ensemble de Lancement Vega (short ELV), is a launch pad at the Centre Spatial Guyanais in French Guiana. It has been used to support launches of the Europa rocket, Ariane 1, Ariane 3, and is currently used to launch Vega rockets. History Europa (BEC) ELA-1, at the time designated Base Équatoriale du CECLES (BEC) was constructed as an equatorial launch site for the Europa-II rocket which was being built as part of the ELDO programme. The first launch occurred on 5 November 1971. This was the only flight of the Europa-II, which ended in failure due to a guidance problem. The launch site was mothballed, and later demolished. Ariane (ELA) When the Ariane 1 programme was started, to replace the failed ELDO programme, a new launch site was built on the site of the former CECLES pad. This was designated Ensemble de Lancement Ariane (ELA). The first Ariane 1 launch occurred on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiana Space Centre
The Guiana Space Centre (french: links=no, Centre spatial guyanais; CSG), also called Europe's Spaceport, is a European spaceport to the northwest of Kourou in French Guiana, a region of France in South America. Kourou is located approximately north of the equator, at a latitude of 5°. In operation since 1968, it is suitable as a location for a spaceport, because of its equatorial location and open sea to the east. The European Space Agency (ESA), the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), the French space agency CNES (National Centre for Space Studies), the Space Agency of the Republic of Azerbaijan (Azercosmos) and the commercial company Arianespace conduct launches from Kourou. It was used by the ESA to send supplies to the International Space Station using the Automated Transfer Vehicle. History In 1964 Guiana was selected to become the spaceport of France, replacing France's first launch site Centre interarmées d'essais d'engins spéciaux in Hammag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
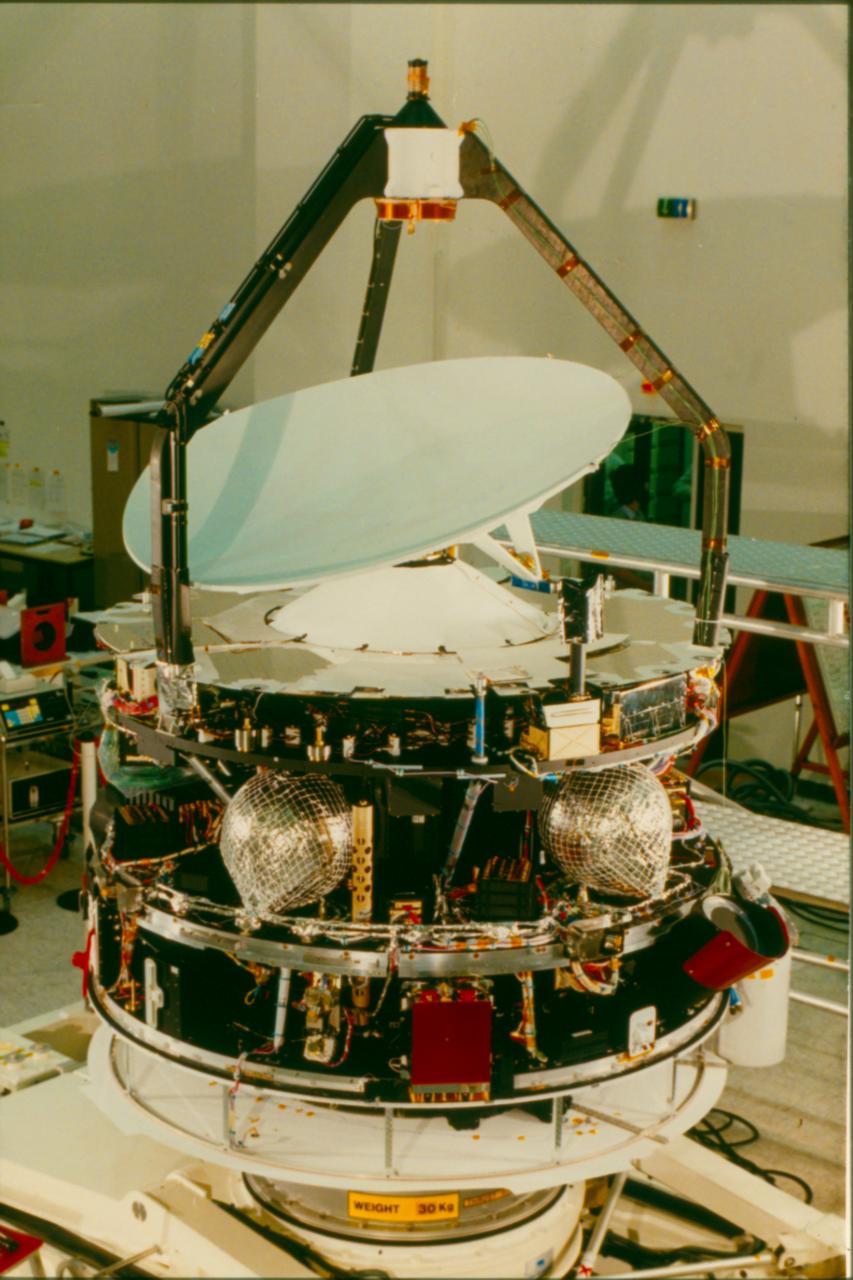
Meteosat
The Meteosat series of satellites are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program. The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over. __TOC__ First generation The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provided continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. Meteosat-1 to -7 have all now retired. When operational, the Meteosat First Generation provided images every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water Vapour, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager (MVIRI) instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tele-X
Tele-X was the first communications satellite serving the Nordic countries. It was launched with an Ariane 2 launch vehicle from Kourou, French Guiana, on 2 April 1989. On 16 January 1998, its fuel was exhausted and it was moved into graveyard orbit. The project was managed and operated by the Swedish Space Corporation (SCC), but it was built by Aérospatiale and Saab Ericsson Space, based on the Spacebus 300 series. Some of the TV channels it broadcast was TV4 Sweden, Kanal 5 Sweden, NRK and Filmnet. In addition, it broadcast radio for TT, The Voice Danmark, Radio Sweden, Rix FM, Mix Megapol and NRJ. It was also used for Internet communication for universities in Eastern Europe Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ .... References External links Tele-X Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INSAT-1C
INSAT-1C was the third in the first generation INSAT series of satellites (termed as INSAT-1) built by Ford Aerospace to satisfy the domestic communication requirement of India. The Govt. agencies using its services were All India Radio, Doordarshan, Department of Space and Indian Meteorological Department Launch INSAT-1C was launched from Guiana Space Centre in Kourou using Ariane 3 rocket on July 21, 1988. At launch, it had a mass of , and an expected operational lifespan of seven years. The satellite was positioned at 93.5° East longitude in geostationary orbit Payloads INSAT-1C carried 3 payloads on board to provide communication services to Indian Meteorological Department, Department of Telecommunications The Department of Telecommunications, abbreviated to DoT, is a department of the Ministry of Communications of the executive branch of the Government of India. History Telecom services have been recognized the world-over as an important tool f ... and Department o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelsat VA F-13
Intelsat VA F-13 or Intelsat 513, then named 'NSS-513', was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat and which was later sold to New Satellite Skies. Launched in 1988, it was the thirteenth of fifteen Intelsat V satellites to be launched. The Intelsat V series was constructed by Ford Aerospace, based on the Intelsat VA satellite bus. Intelsat VA F-13 was part of an advanced series of satellites designed to provide greater telecommunications capacity for Intelsat's global network. Satellite The satellite was box-shaped, measuring 1.66 by 2.1 by 1.77 metres; solar arrays spanned 15.9 metres tip to tip. The arrays, supplemented by nickel-hydrogen batteries during eclipse, provided 1800 watts of power at mission onset, approximately 1280 watts at the end of its seven-year design life. The payload housed 26 C-band and 6 Ku-band transponders. It could accommodate 15,000 two-way voice circuits and two TV channels simultaneously. It also provided maritime communications for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optus (satellite)
This is a list of the satellites operated by Optus, an Australian telecommunications company. The satellite communications facility is located at Belrose on Sydney's Northern Beaches. Optus' satellites are divided into 4 classes A, B, C and D. As of April 2014 it owns and operates Optus B3, Optus C1, Optus D1, Optus D2 and Optus D3. Optus A1, Optus A2, Optus A3 and Optus B1 satellites have been retired. Optus has the largest network of satellites in Australia and New Zealand. On February 2, 2014 NBN Co of Australia chose Optus for a five-year contract to operate two purpose-built satellites (the Sky Muster satellites) to deliver high speed broadband across rural and remote Australia. A-Class *Satellite Type: Hughes HS-376 *Design Life: 7 Years for A1 & A2 - 10 Years for A3 *Equipment: 15 Ku band transponders (including four 30W transponders and eleven 12W transponders) *Diameter: 2.2m *Height: 2.9m (stowed), 6.3m (deployed) The Aussat A-Class satellites were funded by the Gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelsat VA F-14
Intelsat VA F-14, was a communications satellite operated by Intelsat. Launched in 1986, it was the fourteenth of fifteen Intelsat V satellites to be launched. The Intelsat V series was constructed by Ford Aerospace, based on the Intelsat VA satellite bus. Intelsat VA F-14 was part of an advanced series of satellites designed to provide greater telecommunications capacity for Intelsat's global network. Satellite The satellite was box-shaped, measuring 1.66 by 2.1 by 1.77 metres; Photovoltaic system, solar arrays spanned 15.9 metres tip to tip. The arrays, supplemented by Nickel–hydrogen battery, nickel-hydrogen batteries during eclipse, provided 1800 watts of power at mission onset, approximately 1280 watts at the end of its seven-year design life. The payload housed 26 C band (IEEE), C-band and 6 Ku band, Ku-band transponders. It could accommodate 15,000 two-way voice circuits and two TV channels simultaneously. It also provided maritime communications for ships at sea. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking (satellite)
Viking was Sweden's first satellite. It was launched on an Ariane 1 rocket as a piggyback payload together with the French satellite SPOT 1, on February 22, 1986. Operations ended on May 12, 1987. Viking was used to explore plasma processes in the magnetosphere and the ionosphere. Spacecraft Space was limited underneath the SPOT 1 satellite, and Viking had to be quite sturdy in order to withstand the stress of launch. The basic shape of the Swedish satellite was a flat octagonal disc, 0.5 metres thick and 1.9 metres across. The mechanical interface of the payload adapter from the Ariane rocket was duplicated on top of Viking. This enabled it to be added to the launch with a minimum of redesign of the SPOT satellite. After SPOT had been released, Viking fired its own rocket engine and was sent into its proper polar orbit. Mission Once in orbit, 4 wire segments of 40 metre length each were spooled out in a radial direction from the edge of the spinning satellite disc. Also, 2 st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPOT (satellite)
SPOT (french: Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre, lit. "Satellite for observation of Earth") is a commercial high-resolution optical Earth imaging satellite system operating from space. It is run by Spot Image, based in Toulouse, France. It was initiated by the CNES (''Centre national d'études spatiales'' – the French space agency) in the 1970s and was developed in association with the SSTC (Belgian scientific, technical and cultural services) and the Swedish National Space Board (SNSB). It has been designed to improve the knowledge and management of the Earth by exploring the Earth's resources, detecting and forecasting phenomena involving climatology and oceanography, and monitoring human activities and natural phenomena. The SPOT system includes a series of satellites and ground control resources for satellite control and programming, image production, and distribution. Earlier satellites were launched using the European Space Agency's Ariane 2, 3, and 4 rocket ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giotto (spacecraft)
''Giotto'' was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency. The spacecraft flew by and studied Halley's Comet and in doing so became the first spacecraft to make close up observations of a comet. On 13 March 1986, the spacecraft succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers. It was named after the Early Italian Renaissance painter Giotto di Bondone. He had observed Halley's Comet in 1301 and was inspired to depict it as the star of Bethlehem in his painting ''Adoration of the Magi'' in the Scrovegni Chapel. Mission Originally a United States partner probe was planned that would accompany ''Giotto'', but this fell through due to budget cuts at NASA. There were plans to have observation equipment on board a Space Shuttle in low-Earth orbit around the time of ''Giotto''s fly-by, but they in turn fell through with the ''Challenger'' disaster. The plan then became a cooperative armada of five space probes including ''Giotto'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasilsat-A1
Brasilsat A1 was a Brazilian communications satellite which was operated by Embratel. It was constructed by the Spar Aerospace, and is based on the HS-376 satellite bus. The Brasilsat A1 was off duty in March 2002 and was transferred to the graveyard orbit. Specifications The satellite had the shape of a cylinder, where at its top was located a directional antenna that opened after the launching of the satellite. The satellite had a mass in orbit of 671 kg, had a rotation stabilized between 50 and 55 rpm, its propellers used as a propellant 136 kg of hydrazine and was powered by solar cells that supplied 982 Watts at the beginning of its phase of operation, using two NiCd batteries as power reserve. It carried 24 C-band transmitters with six spare transmitters. They provided an effective incident radiated power (EIRP) of 34 dBW for most of the Brazilian territory. * Lead contractor: Spar Aerospace * Model used: HS-376 * Mass at launch: 1,195 kg * Mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabsat-1A
Arabsat-1A ( ar, عربسات-A1) was a Saudi Arabian communications satellite which was operated by Arab Satellite Communications Organization. It was used to provide communication services to the Arab States. It was constructed by Aérospatiale, based on the Spacebus 100 satellite bus, and carries two NATO E/F-band (IEEE S band) and 25 NATO G/H-Band (IEEE C band) transponders. At launch, it had a mass of , and an expected operational lifespan of seven years. Arabsat-1A was launched by Arianespace using an Ariane 3 rocket flying from ELA-1 at Guiana Space Centre, Kourou. The launch took place at 23:22:00 UTC on 8 February 1985. It was the first Spacebus satellite to be launched. Immediately after launch, one of its solar panels failed to deploy, resulting in reduced performance. It was placed into a geosynchronous orbit at a longitude of 19.0° East. Following a series of gyroscope malfunctions, it was retired from active service, and remained operational as a backup. In Septembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |