|
Enragés
The ''Enragés'' (French for "enraged ones") commonly known as the Ultra-radicals (french: Ultra-radicaux) were a small number of firebrands known for defending the lower class and expressing the demands of the extreme radical sans-culottes during the French Revolution.Jeremy D. Popkin (2015). ''A Short History of the French Revolution''. Hoboken, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc. p. 68. They played an active role in the 31 May – 2 June 1793 Paris uprisings that forced the expulsion of the Girondins from the National Convention, allowing the Montagnards to assume full control. The Enragés became associated with this term for their angry rhetoric appealing to the National Convention to take more measures that would benefit the poor. Jacques Roux, Jean-François Varlet, Jean Théophile Victor Leclerc and Claire Lacombe, the primary leaders of the Enragés, were strident critics of the National Convention for failing to carry out the promises of the French Revolution. The Enragés were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Roux
Jacques Roux (, 21 August 1752 – 10 February 1794) was a radical Roman Catholic priest who took an active role in politics during the French Revolution. He skillfully expounded the ideals of popular democracy and classless society to crowds of Parisian sans-culottes, working class wage earners and shopkeepers, radicalizing them into a revolutionary force. He became a leader of a popular far-left. Radical revolutionary In 1791 Roux was elected to the Paris Commune. When the French First Republic started in 1792, Roux became aligned with the political faction dubbed by their enemies as the Enragés () (French for ''The Enraged Ones'' but also a "madman"). He was considered the most extreme spokesman on the left for the interests of the Parisian ''sans-culottes''. Roux consistently fought for an economically equal society, turning the crowds of sans-culottes against the bourgeois torpor of the Jacobins. He demanded that food be made available to every member of society, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-François Varlet
Jean-François Varlet (14 July 1764 – 4 October 1837) was a leader of the Enragés faction during the French Revolution. He was important in the History of France#Bloodbath in Paris and the Republic established (September 1792), fall of the monarchy and the Insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793. Life Born in Paris on 14 July 1764 into a family of the petite bourgeoisie, petty bourgeoisie, Jean-François Varlet studied at the Lycée Saint-Louis, Collège d'Harcourt. He welcomed the Revolution with enthusiasm and wrote patriotic songs. However, at 21 Varlet was too young to be eligible for an elected position, so he turned to popular agitation instead. He was an early supporter of the radical Jacques Hébert. Varlet first rose to prominence through his History of France#Bloodbath in Paris and the Republic established (September 1792), opposition to the monarchy. When Louis XVI Flight to Varennes, attempted to flee Paris, Varlet circulated petitions in the National Assembly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Théophile Victor Leclerc
Jean Théophile Victor Leclerc, a.k.a. Jean-Theophilus Leclerc and Theophilus Leclerc d'Oze (1771 – 1820), was a radical French revolutionary, publicist, and soldier. After Jean-Paul Marat was assassinated, Leclerc assumed his mantle. Leclerc was the son of a civil engineer and joined the National Guard in Clermont-Ferrand at the outbreak of revolution in 1789. He then went to Martinique as a merchant's agent. However, his militant pro-revolutionary stance brought him into conflict with the planter aristocracy, who soon expelled him for revolutionary propaganda in 1791. He returned to metropolitan France and joined the 1st battalion of Morbihan in which he served until February 1792, when he left for Paris to defend seventeen grenadiers accused, in Martinique, of being revolutionaries. He successfully defended them in front of the Jacobin Club and the revolutionary national assembly. On April first that year he made a speech before the Jacobin Club calling for the execution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sans-culottes
The (, 'without breeches') were the common people of the lower classes in late 18th-century France, a great many of whom became radical and militant partisans of the French Revolution in response to their poor quality of life under the . The word , which is opposed to "aristocrat", seems to have been used for the first time on 28 February 1791 by Jean-Bernard Gauthier de Murnan in a derogatory sense, speaking about a " army". The word came into vogue during the demonstration of 20 June 1792. The name refers to their clothing, and through that to their lower-class status: were the fashionable silk knee-breeches of the 18th-century nobility and bourgeoisie, and the working class wore ''pantaloons'', or long trousers, instead.Chisholm, Hugh (1911). "Sans-culottes". ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' (11th ed.), 1911. This saying meant "ordinary patriots without fine clothes", and referred to the fancy clothes that famous patriots wore. They wore pants with cuffed, rolled up bottoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
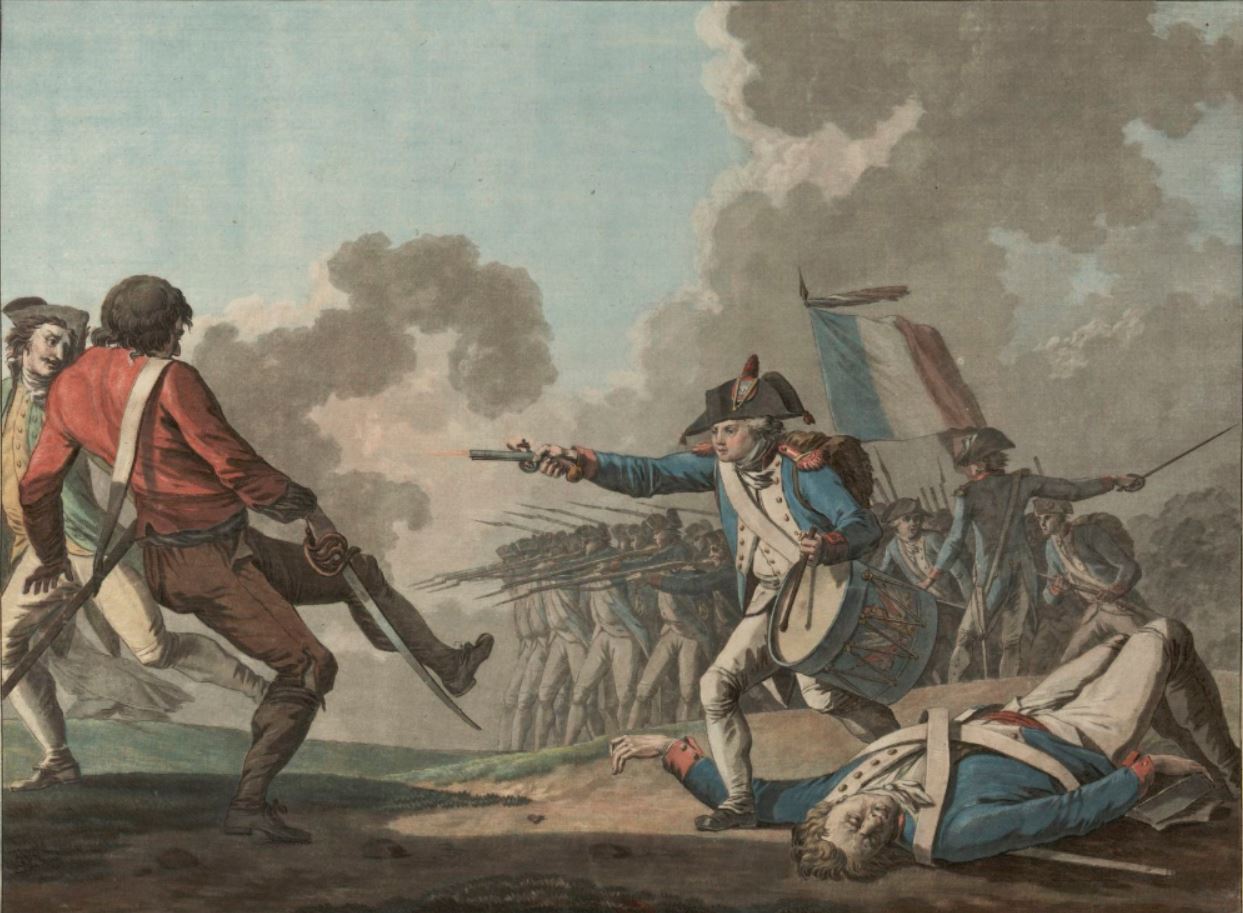
Insurrection Of 31 May – 2 June 1793
), during the French Revolution, started after the Paris commune demanded that 22 Girondin deputies and members of the Commission of Twelve should be brought before the Revolutionary Tribunal. Jean-Paul Marat led the attack on the representatives in the National Convention, who in January had voted against the execution of the King and since then had paralyzed the Convention. It ended after thousands of armed citizens surrounded the Convention to force the deputies to deliver the deputies denounced by the Commune. The result was the fall of the 29 Girondins and two Ministers under pressure of the ''sans-culottes'', Jacobins of the clubs, and Montagnards. By its impact and importance, this insurrection stands as one of the three great popular insurrections of the French Revolution, following those of 14 July 1789 and 10 August 1792. The principal conspirators were the Enragés Dobsen and Varlet; Pache and Chaumette would lead the march on the Convention. Background During t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mountain
The Mountain (french: La Montagne) was a political group during the French Revolution. Its members, called the Montagnards (), sat on the highest benches in the National Convention. They were the most radical group and opposed the Girondins. The term, first used during a session of the Legislative Assembly, came into general use in 1793. By the summer of 1793, that pair of opposed minority groups divided the National Convention. That year, the Montagnards were influential in what is commonly known as the Reign of Terror. The Mountain was composed mainly of members of the middle class, but represented the constituencies of Paris. As such, the Mountain was sensitive to the motivations of the city and responded strongly to demands from the working class sans-culottes. The Mountain operated on the belief that what was best for Paris would be best for all of France. Although they attempted some rural land reform, most of it was never enacted and they generally focused on the needs o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not necessarily limited to, governments, nation states, and capitalism. Anarchism advocates for the replacement of the state with stateless societies or other forms of free associations. As a historically left-wing movement, usually placed on the farthest left of the political spectrum, it is usually described alongside communalism and libertarian Marxism as the libertarian wing (libertarian socialism) of the socialist movement. Humans lived in societies without formal hierarchies long before the establishment of formal states, realms, or empires. With the rise of organised hierarchical bodies, scepticism toward authority also rose. Although traces of anarchist thought are found throughout history, modern anarchism emerged from the Enlightenment. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claire Lacombe
Claire Lacombe (4 August 1765-2 May 1826) was a French actress and revolutionary. She is best known for her contributions during the French Revolution. Though it was only for a few years, Lacombe was a revolutionary and a founding member of the Society of Revolutionary Republican Women. Early life Lacombe was born in the provincial town of Pamiers in southwestern France. She became an actress at a young age and appeared in theatrical productions in the provinces before arriving in Paris in 1792. She was not an outstanding success in the theater, and she was not entirely happy with her life. The acting company that Lacombe worked for moved from town to town and sometimes went to castles and the country houses of aristocrats. This probably had an influence in her decision to quit the company to become a revolutionary. Revolutionary career In Paris during the insurrection of 10 August 1792, Lacombe fought with the rebels during the storming of the Tuileries. She was shot through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
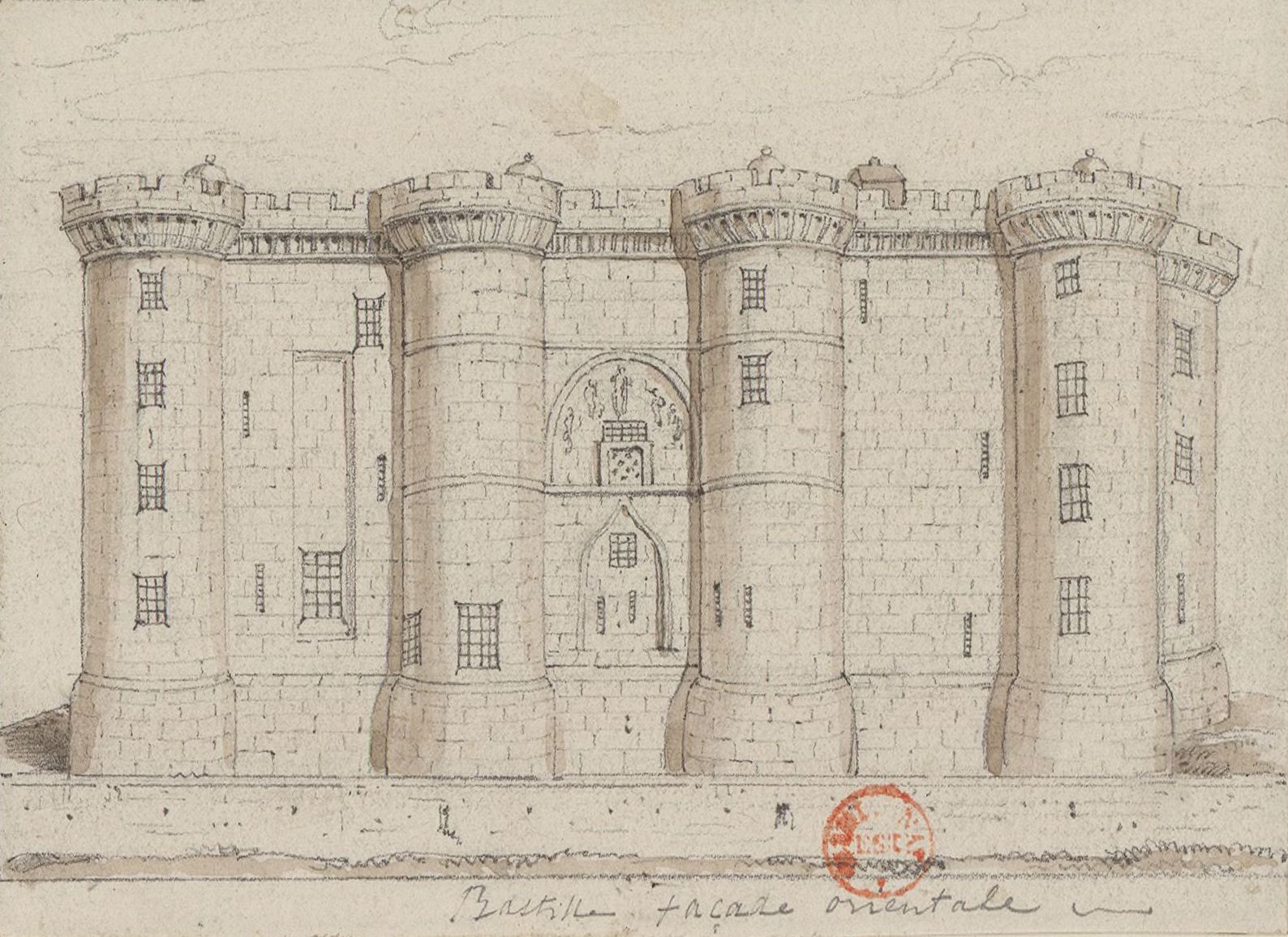
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterrevolutionary
A counter-revolutionary or an anti-revolutionary is anyone who opposes or resists a revolution, particularly one who acts after a revolution in order to try to overturn it or reverse its course, in full or in part. The adjective "counter-revolutionary" pertains to movements that would restore the state of affairs, or the principles, that prevailed during a prerevolutionary era. Definition A counter-revolution is opposition or resistance to a revolutionary movement. It can refer to attempts to defeat a revolutionary movement before it takes power, as well as attempts to restore the old regime after a successful revolution. Europe France The word "counter-revolutionary" originally referred to thinkers who opposed themselves to the 1789 French Revolution, such as Joseph de Maistre, Louis de Bonald or, later, Charles Maurras, the founder of the ''Action française'' monarchist movement. More recently, it has been used in France to describe political movements that reject the lega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitability asse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, good (economics), goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline in value.) Many speculators pay little attention to the fundamental value of a security and instead focus purely on price movements. In principle, speculation can involve any tradable good or financial instrument. Speculators are particularly common in the markets for stocks, bond (finance), bonds, commodity futures, currency, currencies, fine art, collectibles, real estate, and derivative (finance), derivatives. Speculators play one of four primary roles in financial markets, along with hedge (finance), hedgers, who engage in transactions to offset some other pre-existing risk, arbitrageus who seek to profit from situations where Fungibility, fungible instruments trade at different prices in different market segments, and investors who s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)