|
Enoch Moore (loyalist Turned Rebel)
Enoch Moore (April 16, 1779– August 1841), son of Samuel Moore U.E. and Rachel Stone, married Elizabeth Smith, daughter of James Smith and Hannah Hawksworth, on March 30, 1803, in Old Holy Trinity Church, Lower Middleton, Annapolis County, Nova Scotia. Elizabeth was born on April 18, 1784, in Wilmot Township, NS, died on March 3, 1871, and was buried in New Milford Cemetery, Winnebago County, Illinois. Enoch was a direct descendant of one of New Jersey's early colonial officials, Samuel Moore. Enoch's political alignment seemed to swing from one extreme to the other throughout his lifetime. He was born in a Loyalist refugee camp in New York City and was evacuated with his Quaker family, about 1784, to the Annapolis Valley, Nova Scotia where his father, Samuel Moore, became a leader in the Quaker community. He moved to Upper Canada about 1811, where he served as a dispatch rider in the Canadian militia during the War of 1812 against the Americans. His commanding off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enoch Moore's Honourable Discharge Certificate From The War Of 1812
Enoch () ''Henṓkh''; ar, أَخْنُوخ ', Qur'ān.html"_;"title="ommonly_in_Qur'ān">ommonly_in_Qur'ānic_literature__'_is_a_biblical_figure_and_Patriarchs_(Bible).html" "title="Qur'ānic_literature.html" ;"title="Qur'ān.html" ;"title="ommonly in Qur'ān">ommonly in Qur'ānic literature">Qur'ān.html" ;"title="ommonly in Qur'ān">ommonly in Qur'ānic literature ' is a biblical figure and Patriarchs (Bible)">patriarch prior to Noah's flood, and the son of Jared (biblical figure), Jared and father of Methuselah. He was of the Antediluvian period in the Hebrew Bible. The text of the Book of Genesis says Enoch lived 365 years before he was taken by God. The text reads that Enoch "walked with God: and he was no more; for God took him" (), which is interpreted as Enoch's entering heaven alive in some Jewish and Christian traditions, and interpreted differently in others. Enoch is the subject of many Jewish and Christian traditions. He was considered the author of the Book of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malahide, Ontario
Malahide (Canada 2016 Census population 9,292) is a Township (Canada), municipal township in Elgin County in Southwestern Ontario, southwestern Ontario, Canada. History Malahide Township was named for Malahide Castle in Malahide, Ireland, birthplace of land grant administrator Thomas Talbot (Upper Canada), Colonel Thomas Talbot in 1810. The village of Springfield was incorporated as a separate municipality in 1878. The current municipality was formed in 1998 through an amalgamation of the original Township of Malahide, the former Township of South Dorchester and the former Village of Springfield. The Ontario Police College is located in Malahide, at the site of the former RCAF Station Aylmer, Royal Canadian Air Force Station Aylmer, a training facility. Communities The township comprises the communities of Candyville, Crossley-Hunter, Copenhagen, Dunboyne, Fairview, Glencolin, Grovesend, Jaffa, Kingsmill, Lakeview, Little Aylmer, Luton, Lyons, Mile Corner, Mount Salem, Ontario, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elias Moore
Elias Moore (March 1, 1776 – October 13, 1847) was a Loyalist politician in Upper Canada. Born into a Quaker family in New Jersey just after the American Revolution began, he and his family eventually emigrated to Upper Canada. He later became a member of the Legislative Assembly of Upper Canada, and he is notable for being one of the first Quakers to take an elected seat in Canada. His family was traumatised "by the persecution Quakers suffered for their neutral stand during the American Revolution," and they soon moved to a Loyalist refugee camp in New York City. They then evacuated about 1784, to the Annapolis Valley in Nova Scotia where his father, Samuel, became a leader in the Quaker Community. As a young adult, Moore returned to his home state of New Jersey, and his family followed later. His family had deep roots there, an ancestor, Samuel Moore having held many offices in the early colony of East Jersey right after it had been settled in the 1660s. In 1811 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peace Bond
In Canadian law, a peace bond is an order from a criminal court that requires a person to keep the peace and be on good behaviour for a period of time. This essentially means that the person who signs a peace bond must not be charged with any additional criminal offences during its duration. Peace bonds often have other conditions as well, such as not having any weapons or staying away from a particular person or place. Peace bonds are similar to a civil court restraining order, and are also based on the lesser burden of proof of civil law. A peace bond can be issued by a criminal court judge or a Justice of the Peace. A peace bond is usually issued when the Crown Prosecutor is convinced that a strong case does not exist against the accused. A person does not plead guilty when they enter into a peace bond. Thus, there is no finding of guilt or conviction registered if a person agrees to sign a peace bond. One of the reasons why a person may agree to enter into a peace bond is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the jurisdiction. Pardons can be granted in many countries when individuals are deemed to have demonstrated that they have "paid their debt to society", or are otherwise considered to be deserving of them. In some jurisdictions of some nations, accepting a pardon may ''implicitly'' constitute an admission of guilt; the offer is refused in some cases. Cases of wrongful conviction are in recent times more often dealt with by appeal rather than by pardon; however, a pardon is sometimes offered when innocence is undisputed in order to avoid the costs that are associated with a retrial. Clemency plays a critical role when capital punishment exists in a jurisdiction. Pardons are sometimes seen as a mechanism for combating corruption, allowing a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
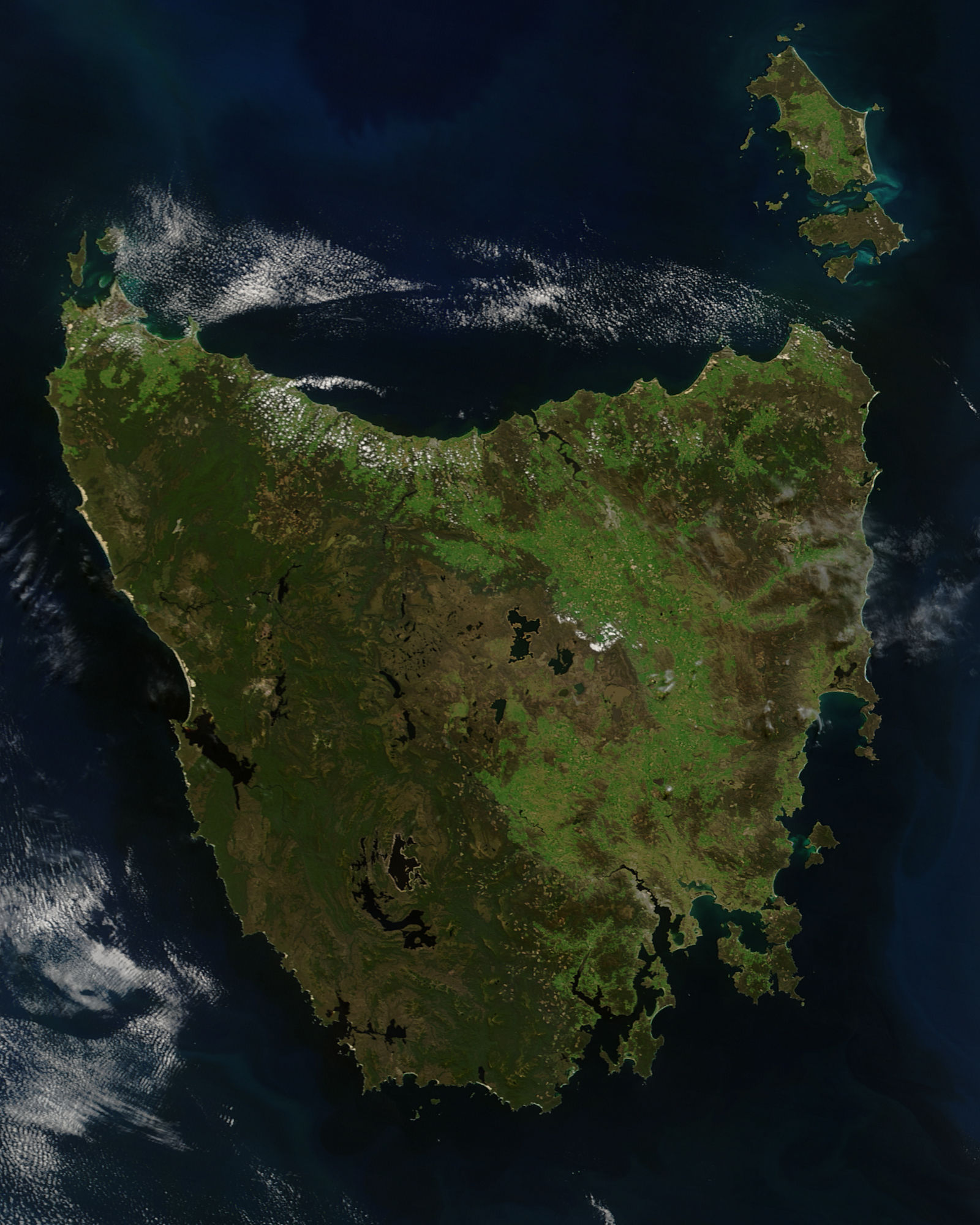
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
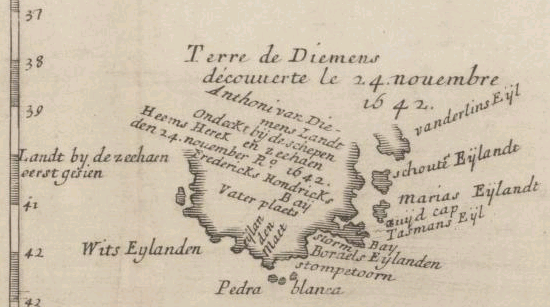
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer to a correctional facility located in a remote location, it is more commonly used to refer to communities of prisoners overseen by wardens or governors having absolute authority. Historically penal colonies have often been used for penal labour in an economically underdeveloped part of a state's (usually colonial) territories, and on a far larger scale than a prison farm. British Empire With the passage of the Transportation Act 1717, the British government initiated the penal transportation of indentured servants to Britain's colonies in the Americas. British merchants would be in charge of transporting the convicts across the Atlantic, where in the colonies their indentures would be auctioned off to planters. Many of the indentured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Transportation
Penal transportation or transportation was the relocation of convicted criminals, or other persons regarded as undesirable, to a distant place, often a colony, for a specified term; later, specifically established penal colonies became their destination. While the prisoners may have been released once the sentences were served, they generally did not have the resources to return home. Origin and implementation Banishment or forced exile from a polity or society has been used as a punishment since at least the 5th century BC in Ancient Greece. The practice of penal transportation reached its height in the British Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Transportation removed the offender from society, mostly permanently, but was seen as more merciful than capital punishment. This method was used for criminals, debtors, military prisoners, and political prisoners. Penal transportation was also used as a method of colonization. For example, from the earliest days of English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Moore House (Sparta, Ontario)
John Moore House is a pioneer home built in 1824 north of the village of Sparta, Ontario on land inherited from the builder's father, Samuel Moore U.E. It is considered a good example of pioneer architecture and construction in Elgin County, and a valuable relic of early settlement days in Southwestern Ontario, if not in the province. It is an example of Georgian architecture, a two-storey structure of stone and brick, it features a symmetrical five bay front façade with a central door and two sets of flanking windows on the main floor, and five on the second storey. Fieldstone chimneys rise from the end gables and connect to fireplaces on each floor. This house, "similar to many early Quaker homes in the Township of Norwich, was built into the side of a hill to accommodate a basement kitchen. This feature provided more space in an otherwise small home and was suitable for baking in the heat of the summer as well as the chill of winter." With the house built into the Sparta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pardon
A pardon is a government decision to allow a person to be relieved of some or all of the legal consequences resulting from a criminal conviction. A pardon may be granted before or after conviction for the crime, depending on the laws of the jurisdiction. Pardons can be granted in many countries when individuals are deemed to have demonstrated that they have "paid their debt to society", or are otherwise considered to be deserving of them. In some jurisdictions of some nations, accepting a pardon may ''implicitly'' constitute an admission of guilt; the offer is refused in some cases. Cases of wrongful conviction are in recent times more often dealt with by appeal rather than by pardon; however, a pardon is sometimes offered when innocence is undisputed in order to avoid the costs that are associated with a retrial. Clemency plays a critical role when capital punishment exists in a jurisdiction. Pardons are sometimes seen as a mechanism for combating corruption, allowing a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |