|
EnerGuide For Houses
EnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products. The EnerGuide's efficiency percent is calculated by dividing the power output by power input. EnerGuide labelling exists for appliances, heating and cooling equipment, houses and vehicles. EnerGuide includes a house energy evaluation, including tests to find air leakage and the energy efficiency of its heating. It was designed to help Canadians reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and to save energy. To accomplish the same goals for new home construction the EnerGuide for New Houses program was initiated in 2006. The new Saskatchewan EnerGuide for Houses program is active from April 1, 2011 to October 31, 2013. EnerGuide for New Houses The EnerGuide for New Houses program, a sister program of EnerGuide for Houses, helps Canadians plan and build new homes that are cost-effective and energy efficient, that lower greenhous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Canada
The government of Canada (french: gouvernement du Canada) is the body responsible for the federal administration of Canada. A constitutional monarchy, the Crown is the corporation sole, assuming distinct roles: the executive, as the ''Crown-in-Council''; the legislature A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make law Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its p ..., as the ''Crown-in-Parliament''; and the courts, as the ''Crown-on-the-Bench''. Three institutions—the Privy Council ( conventionally, the Cabinet); the Parliament of Canada; and the Judiciary of Canada, judiciary, respectively—exercise the powers of the Crown. The term "Government of Canada" (french: Gouvernement du Canada, links=no) more commonly refers specifically to the executive—Minister of the Crown, ministers of the Crown (the Cabinet) and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively (using less energy for continuous service) or changing one's behavior to use less service (for example, by driving less). Energy conservation can be achieved through energy efficiency, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, a smaller carbon footprint, and cost, water, and energy savings. Energy conservation is an essential factor in building design and construction. It has increased in importance since the 1970s, as 40% of energy use in the U.S. is in buildings. Recently, concern over the effects of climate change and global warming has emphasized the importance of energy conservation. Energy can only be transformed from one form to another, such as when heat energy is converted into vehicle motive power or when water flow's kinetic energy is converted into electricity in hydroelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and large oil and gas companies, many state-owned by OPEC and Russia. Human-caused emissions have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but it was consistent among all greenhouse gases (GHG). Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than ever before. Electricity generation and transport are major emitters; the largest single source, according to the United States Environmental Protection Agency, is transportation, accounting for 27% of all USA greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation and other changes in land use also emit carbon dioxide and methane. The largest source of anthropogenic methane emissions is agriculture, closely followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EnerGuide For New Houses
EnerGuide is the official Government of Canada mark associated with the labelling and rating of the energy consumption or energy efficiency of specific products. The EnerGuide's efficiency percent is calculated by dividing the power output by power input. EnerGuide labelling exists for appliances, heating and cooling equipment, houses and vehicles. EnerGuide includes a house energy evaluation, including tests to find air leakage and the energy efficiency of its heating. It was designed to help Canadians reduce their greenhouse gas emissions and to save energy. To accomplish the same goals for new home construction the EnerGuide for New Houses program was initiated in 2006. The new Saskatchewan EnerGuide for Houses program is active from April 1, 2011 to October 31, 2013. EnerGuide for New Houses The EnerGuide for New Houses program, a sister program of EnerGuide for Houses, helps Canadians plan and build new homes that are cost-effective and energy efficient, that lower greenhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R-2000 Program
R-2000 is a Natural Resources Canada (NRCan) program that was developed in partnership with the Canadian Home Builders' Association in 1981, and formalized as a standard in 1982. Notably, the R-2000 standard is a voluntary standard to exceed building code requirements for energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and environmental responsibility. The R-2000 program is managed by NRCan's Office of Energy Efficiency and comprises: * R-2000 standard - technical specifications * quality assurance * certification * training and licensing of builders and service providers * consumer information In May 2008, the CHBA published an internal discussion paper proposing changes to the R-2000 standard so it would remain at the forefront as the reference model that influences other programs or initiatives. See also * Canada Green Building Council * EnerGuide * Energy Star Energy Star (trademarked ''ENERGY STAR'') is a program run by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and U.S. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
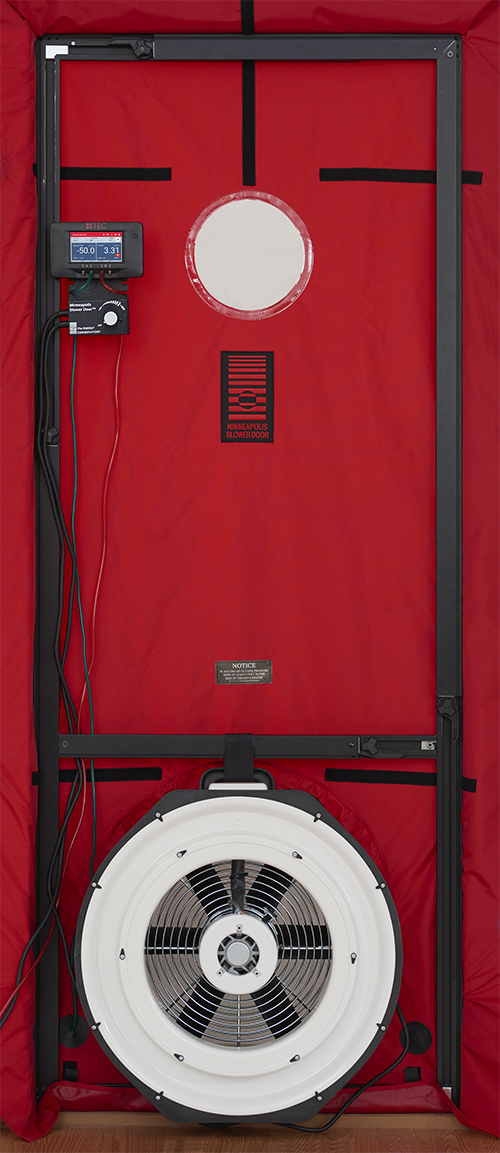
Blower Door
A blower door is a machine used to measure the airtightness of buildings. It can also be used to measure airflow between building zones, to test ductwork airtightness and to help physically locate air leakage sites in the building envelope. There are three primary components to a blower door: (1) a calibrated, variable-speed blower or fan, capable of inducing a range of airflows sufficient to pressurize and depressurize a variety of building sizes, (2) a pressure measurement instrument, called a manometer, to simultaneously measure the pressure differential induced across the face of the fan and across the building envelope, as a result of fan airflow, and (3) a mounting system, used to mount the fan in a building opening, such as a door or a window. Air tightness testing is usually thought of in residential settings. It is becoming more common in commercial settings. The General Services Administration (GSA) requires testing of new US federal government buildings. A variety o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Audit
An energy audit is an inspection survey and an analysis of energy flows for energy conservation in a building. It may include a process or system to reduce the amount of energy input into the system without negatively affecting the output. In commercial and industrial real estate, an energy audit is the first step in identifying opportunities to reduce energy expense and carbon footprint. Principle When the object of study is an occupied building then reducing energy consumption while maintaining or improving human comfort, health and safety are of primary concern. Beyond simply identifying the sources of energy use, an energy audit seeks to prioritize the energy uses according to the greatest to least cost-effective opportunities for energy savings. Home energy audit A ''home energy audit'' is a service where the energy efficiency of a house is evaluated by a person using professional equipment (such as blower doors and infrared cameras), with the aim to suggest the best ways to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Conservation In Canada
Canada has access to all main sources of energy including Oil and Gas, oil and gas, coal, hydropower, biomass, Solar power, solar, Geothermal energy, geothermal, Wind power, wind, Marine energy, marine and Nuclear power, nuclear. It is the world's second largest producer of uranium, third largest producer of hydro-electricity, fourth largest natural gas producer, and the fifth largest producer of crude oil. In 2006, only Russia, the People's Republic of China, the United States and Saudi Arabia produce more total energy than Canada. The United States is Canada's major trade market for energy products and services. Canada sent around 98% of its total energy exports to the United States in 2015, meaning that Canada is the largest supplier of energy exports to the world's largest economy. Canada also exports significant amounts of uranium and coal to Asia, Europe and Latin America. Despite being a net energy exporter, Canada also imports energy products. $24.5 billion of energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)