|
Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma
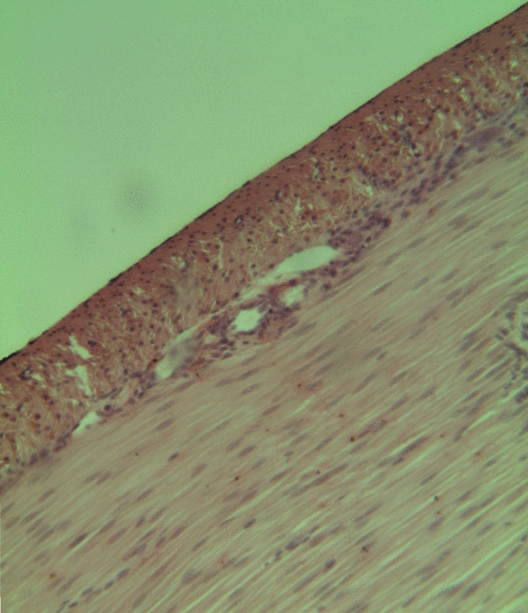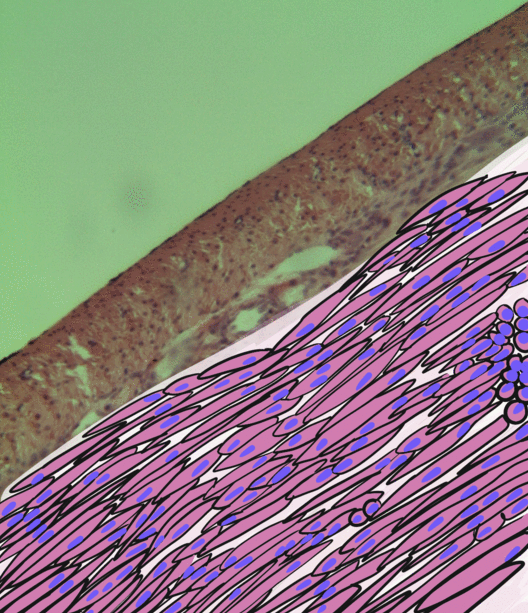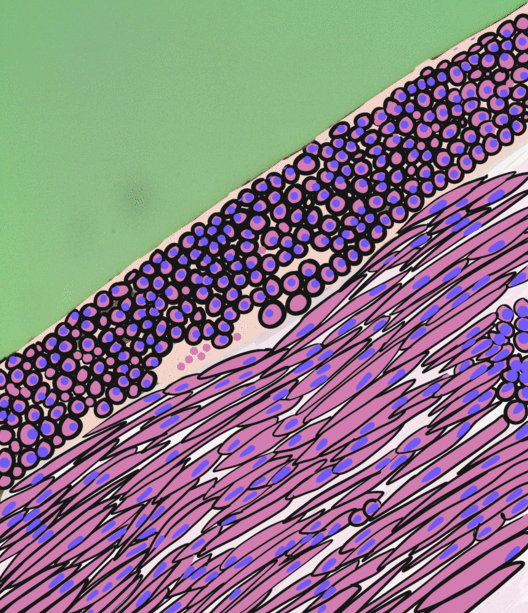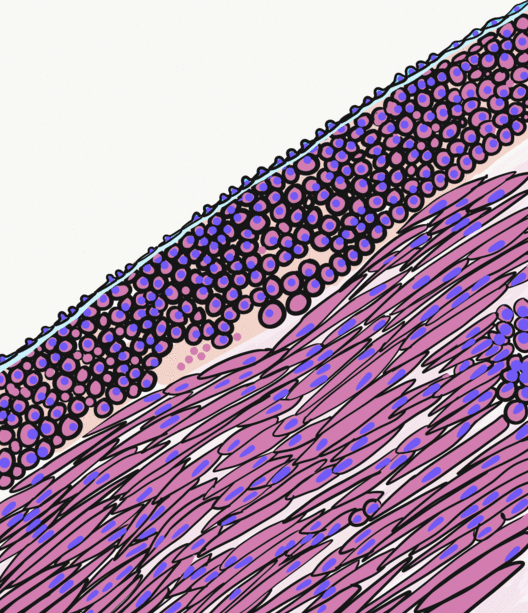
Endometrial stromal sarcoma is a malignant subtype of endometrial stromal tumor arising from the stroma (connective tissue) of the endometrium rather than the glands. There are three grades for endometrial stromal tumors, as follows. It was previously known as ''endolymphatic stromal myosis'' because of diffuse infiltration of myometrial tissue or the invasion of lymphatic channels. Low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma Low-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma consists of cells resembling normal proliferative phase endometrium, but with infiltration or vascular invasion. These behave less aggressively, sometimes metastasizing, with cancer stage the best predictor of survival. The cells express estrogen/progesterone-receptors. Undifferentiated uterine sarcoma Undifferentiated uterine sarcoma, or undifferentiated (high-grade) endometrial stromal sarcoma, does not resemble normal endometrial stroma and behaves much more aggressively, frequently metastasizing. The differential incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Ligament
The broad ligament of the uterus is the wide fold of peritoneum that connects the sides of the uterus to the walls and floor of the pelvis. Structure Subdivisions Contents The contents of the broad ligament include the following: * Reproductive ** uterine tubes (or Fallopian tube) ** ovary (some sources consider the ovary to be on the broad ligament, but not in it.) * vessels ** ovarian artery (in the suspensory ligament) ** uterine artery (in reality, travels in the cardinal ligament) * ligaments ** ovarian ligament ** round ligament of uterus ** suspensory ligament of the ovary (Some sources consider it a part of the broad ligament, while other sources just consider it a "termination" of the ligament.) Relations The peritoneum surrounds the uterus like a flat sheet that folds over its fundus (uterus), fundus, covering it anteriorly and posteriorly; on the sides of the uterus, this sheet of peritoneum comes in direct contact with itself, forming the double layer of perito ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAZF1
Juxtaposed with another zinc finger protein 1 (JAZF1) also known as TAK1-interacting protein 27 (TIP27) or zinc finger protein 802 (ZNF802) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JAZF1'' gene. Variants are associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer, an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and an increased height. Function This gene encodes a nuclear protein with three C2H2-type zinc fingers, and functions as a transcriptional repressor. Chromosomal aberrations involving this gene are associated with endometrial stromal tumor Endometrial stromal tumours are a type of mesenchymal tumor of the main body of the uterus. Types include endometrial stromal nodule, the distinct low and high-grade endometrial stromal sarcoma Endometrial stromal sarcoma is a malignant subtype o ...s. Alternatively spliced variants which encode different protein isoforms have been described; however, not all variants have been fully characterized References Further reading * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polycomb-group Proteins
Polycomb-group proteins (PcG proteins) are a family of protein complexes first discovered in fruit flies that can remodel chromatin such that epigenetic silencing of genes takes place. Polycomb-group proteins are well known for silencing Hox genes through modulation of chromatin structure during embryonic development in fruit flies (''Drosophila melanogaster''). They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles. In insects In ''Drosophila'', the Trithorax-group (trxG) and Polycomb-group (PcG) proteins (They derive their name from the fact that the first sign of a decrease in PcG function is often a homeotic transformation of posterior legs towards anterior legs, which have a characteristic comb-like set of bristles) act antagonistically and interact with chromosomal elements, termed Cellular Memory Modules (CMMs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Translocation
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes balanced and unbalanced translocation, with two main types: reciprocal-, and Robertsonian translocation. Reciprocal translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by exchange of parts between non-homologous chromosomes. Two detached fragments of two different chromosomes are switched. Robertsonian translocation occurs when two non-homologous chromosomes get attached, meaning that given two healthy pairs of chromosomes, one of each pair "sticks" and blends together homogeneously. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise-separated genes. It is detected on cytogenetics or a karyotype of affected cells. Translocations can be balanced (in an even exchange of material with no genetic information extra or missing, and ideally full functionality) or unbalanced (where the exchange of chromosome material is unequal resulting in extra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldesmon
Caldesmon is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CALD1'' gene. Caldesmon is a calmodulin binding protein. Like calponin, caldesmon tonically inhibits the ATPase activity of myosin in smooth muscle. This gene encodes a calmodulin- and actin-binding protein that plays an essential role in the regulation of smooth muscle and nonmuscle contraction. The conserved domain of this protein possesses the binding activities to Ca++-calmodulin, actin, tropomyosin, myosin, and phospholipids. This protein is a potent inhibitor of the actin-tropomyosin activated myosin MgATPase, and serves as a mediating factor for Ca++-dependent inhibition of smooth muscle contraction. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Immunochemistry In diagnostic immunochemistry, caldesmon is a marker for smooth muscle Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD117
Proto-oncogene c-KIT is the gene encoding the receptor tyrosine kinase protein known as tyrosine-protein kinase KIT, CD117 (cluster of differentiation 117) or mast/stem cell growth factor receptor (SCFR). Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. KIT was first described by the German biochemist Axel Ullrich in 1987 as the cellular homolog of the feline sarcoma viral oncogene v-kit. Function KIT is a cytokine receptor expressed on the surface of hematopoietic stem cells as well as other cell types. Altered forms of this receptor may be associated with some types of cancer. KIT is a receptor tyrosine kinase type III, which binds to stem cell factor , also known as "steel factor" or "c-kit ligand". When this receptor binds to stem cell factor (SCF) it forms a dimer that activates its intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity, that in turn phosphorylates and activates signal transduction molecules that propagate the signal in the cell. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmin
Desmin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DES'' gene. Desmin is a muscle-specific, type III intermediate filament that integrates the sarcolemma, Z disk, and nuclear membrane in sarcomeres and regulates sarcomere architecture. Structure Desmin is a 53.5 kD protein composed of 470 amino acids, encoded by the human ''DES'' gene located on the long arm of chromosome 2. There are three major domains to the desmin protein: a conserved alpha helix rod, a variable non alpha helix head, and a carboxy-terminal tail. Desmin, as all intermediate filaments, shows no polarity when assembled. The rod domain consists of 308 amino acids with parallel alpha helical coiled coil dimers and three linkers to disrupt it. The rod domain connects to the head domain. The head domain 84 amino acids with many arginine, serine, and aromatic residues is important in filament assembly and dimer-dimer interactions. The tail domain is responsible for the integration of filaments and interaction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smooth Muscle Actin
Smooth may refer to: Mathematics * Smooth function, a function that is infinitely differentiable; used in calculus and topology * Smooth manifold, a differentiable manifold for which all the transition maps are smooth functions * Smooth algebraic variety, an algebraic variety with no singular points * Smooth number, a number whose prime factors are all less than a certain value; used in applications of number theory * Smoothsort, a sorting algorithm Arts and entertainment Music * Smooth (singer), Juanita Stokes, American singer, rapper and actress * ''Smooth'' (album), by Smooth, 1995 * ''Smooth'', an album by Gerald Albright, 1994 * "Smooth" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2017 * "Smooth" (iiO song), 2004 * "Smooth" (Santana song), featuring Rob Thomas, 1999 * "Smooth", a mashup by Neil Cicierega from ''Mouth Moods'', 2017 Other media * ''Smooth'' (magazine), an American publication for young black men * Smooth Radio (other), UK radio station networks * smoothfm, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Specific Actin
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD10
Neprilysin (), also known as membrane metallo-endopeptidase (MME), neutral endopeptidase (NEP), cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MME'' gene. Neprilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves peptides at the amino side of hydrophobic residues and inactivates several peptide hormones including glucagon, enkephalins, substance P, neurotensin, oxytocin, and bradykinin. It also degrades the amyloid beta peptide whose abnormal folding and aggregation in neural tissue has been implicated as a cause of Alzheimer's disease. Synthesized as a membrane-bound protein, the neprilysin ectodomain is released into the extracellular domain after it has been transported from the Golgi apparatus to the cell surface. Neprilysin is expressed in a wide variety of tissues and is particularly abundant in kidney. It is also a common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen that is an importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |