|
Endocentric
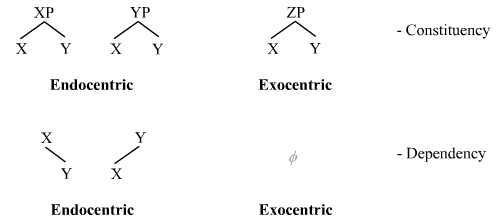
In theoretical linguistics, a distinction is made between endocentric and exocentric constructions. A grammatical construction (for instance, a phrase or compound) is said to be ''endocentric'' if it fulfils the same linguistic function as one of its parts, and ''exocentric'' if it does not. The distinction reaches back at least to Bloomfield's work of the 1930s, who based it on terms by Pāṇini and Patañjali in Sanskrit grammar. Such a distinction is possible only in phrase structure grammars (constituency grammars), since in dependency grammars all constructions are necessarily endocentric. Endocentric construction An endocentric construction consists of an obligatory head and one or more dependents, whose presence serves to modify the meaning of the head. For example: # NP_ A_big.html"_;"title="sub>NP_[A_big">sub>NP_[A_big[N_house.html" ;"title="sub>A_big.html" ;"title="sub>NP [A big">sub>NP [A big[N house">sub>A_big.html" ;"title="sub>NP [A big">sub>NP [A big[N house #[VP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound (linguistics)
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or sign) that consists of more than one stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make a longer word or sign. A compound that uses a space rather than a hyphen or concatenation is called an open compound or a spaced compound; the alternative is a closed compound. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stems of a compound may be of the same part of speech—as in the case of the English word ''footpath'', composed of the two nouns ''foot'' and ''path''—or they may belong to different parts of speech, as in the case of the English word ''blackbird'', composed of the adjective ''black'' and the noun ''bird''. With very few exceptions, English compound words are stressed on their first component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound (linguistics)
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme (less precisely, a word or sign) that consists of more than one stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. Compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make a longer word or sign. A compound that uses a space rather than a hyphen or concatenation is called an open compound or a spaced compound; the alternative is a closed compound. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stems of a compound may be of the same part of speech—as in the case of the English word ''footpath'', composed of the two nouns ''foot'' and ''path''—or they may belong to different parts of speech, as in the case of the English word ''blackbird'', composed of the adjective ''black'' and the noun ''bird''. With very few exceptions, English compound words are stressed on their first component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Bloomfield
Leonard Bloomfield (April 1, 1887 – April 18, 1949) was an American linguist who led the development of structural linguistics in the United States during the 1930s and the 1940s. He is considered to be the father of American distributionalism. His influential textbook ''Language'', published in 1933, presented a comprehensive description of American structural linguistics. He made significant contributions to Indo-European historical linguistics, the description of Austronesian languages, and description of languages of the Algonquian family. Bloomfield's approach to linguistics was characterized by its emphasis on the scientific basis of linguistics and emphasis on formal procedures for the analysis of linguistic data. The influence of Bloomfieldian structural linguistics declined in the late 1950s and 1960s as the theory of generative grammar developed by Noam Chomsky came to predominate. Early life and education Bloomfield was born in Chicago, Illinois, on April 1, 1887 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocentric Environment
In the field of user interfaces, an endocentric environment refers to a virtual reality or some other immersive environment which is introduced directly into the user's senses (for example by using VR goggles). Systems which display a virtual reality indirectly to the user (for example by placing the viewer in a room made up entirely of rear projection screens) do not qualify. See also * Exocentric environment In the field of user interfaces, an exocentric environment refers to a virtual reality or some other immersive environment which completely encompasses the user, e.g. by placing the viewer in a room made up entirely of rear projection screens. Sy ... Virtual reality {{Software-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
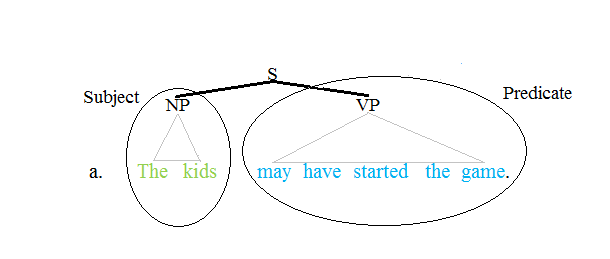
Predicate (grammar)
The term predicate is used in one of two ways in linguistics and its subfields. The first defines a predicate as everything in a standard declarative sentence except the subject, and the other views it as just the main content verb or associated predicative expression of a clause. Thus, by the first definition the predicate of the sentence ''Frank likes cake'' is ''likes cake''. By the second definition, the predicate of the same sentence is just the content verb ''likes'', whereby ''Frank'' and ''cake'' are the arguments of this predicate. Differences between these two definitions can lead to confusion. Syntax Traditional grammar The notion of a predicate in traditional grammar traces back to Aristotelian logic. A predicate is seen as a property that a subject has or is characterized by. A predicate is therefore an expression that can be ''true of'' something. Thus, the expression "is moving" is true of anything that is moving. This classical understanding of predicates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahuvrihi
A ''bahuvrihi'' compound (from sa, बहुव्रीहि, tr=bahuvrīhi, lit=much rice/having much rice, originally referring to fertile land but later denoting the quality of being wealthy or rich) is a type of compound word that denotes a referent by specifying a certain characteristic or quality the referent possesses. A bahuvrihi is exocentric, so that the compound is not a hyponym of its head. For instance, a sabretooth ('' smil-odon'') is neither a sabre nor a tooth, but a feline with sabre-like teeth. In Sanskrit bahuvrihis, the last constituent is a noun—more strictly, a nominal stem—while the whole compound is an adjective. In Vedic Sanskrit the accent is regularly on the first member ( ' "a king's son", but bahuvrihi ' "having kings as sons" ( lit. king-sons), viz. ', m., "father of kings", ', f., "mother of kings"), with the exception of a number of non-nominal prefixes such as the privative a; the word ' is itself likewise an exception to this rule. Bahu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warlpiri Language
The Warlpiri ( or ) ( wbp, Warlpiri > waɭbɪ̆ˌɻi language is spoken by about 3,000 of the Warlpiri people from the Tanami Desert, northwest of Alice Springs, Central Australia. It is one of the Ngarrkic languages of the large Pama–Nyungan family and is one of the largest Aboriginal languages in Australia in terms of number of speakers. One of the most well-known terms for The Dreaming (an Aboriginal spiritual belief), ''Jukurrpa'', derives from Warlpiri. Warnayaka (Wanayaga, Woneiga), Wawulya (Ngardilpa), and Ngalia are regarded as probable dialects of Warlpiri on the AUSTLANG database, although with potentially no data; while Ngardilypa is confirmed. Phonology In the following tables of the Warlpiri sound system, symbols in boldface give the practical alphabet used by the Warlpiri community. Phonemic values in IPA are shown in /slashes/ and phonetic values in quare brackets Vowels Warlpiri has a standard three-vowel system, similar to that of Classical Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
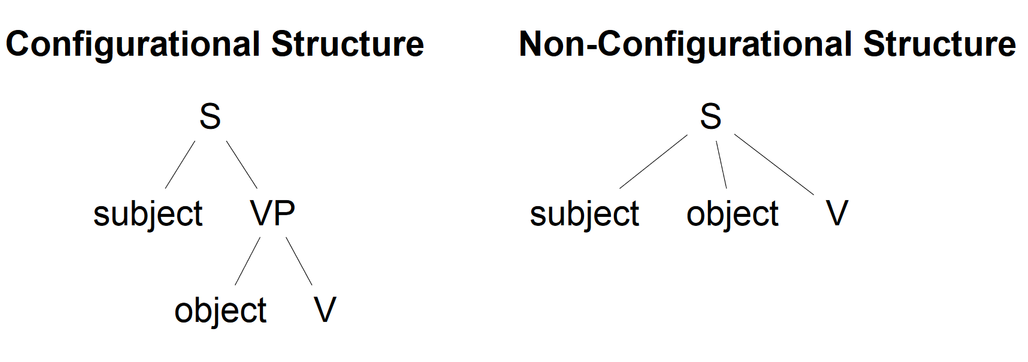
Non-configurational Language
In generative grammar, non-configurational languages are languages characterized by a flat phrase structure, which allows syntactically discontinuous expressions, and a relatively free word order. History of the concept of "non-configurationality" The concept of non-configurationality was developed by grammarians working within Noam Chomsky's generative framework. Some of these linguists observed that the Syntactic Universals proposed by Chomsky and which required a rigid phrase structure was challenged by the syntax of some of the world's languages that had a much less rigid syntax than that of the languages on which Chomsky had based his studies. The concept was invented by Ken Hale who described the syntax of Warlpiri as being non-configurational. However, the first to publish a description of non-configurationality was Chomsky himself in his 1981 lectures on Government and Binding, in which he referred to an unpublished paper by Hale. Chomsky made it a goal of the Government a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar Frameworks
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and theoretical grammar. Fluent speakers of a language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's native language(s) – are acquired not by conscious study or instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more explicit instruction. In this view, grammar is understood as the cognitive information underlying a specific instance of language production. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |