|
Empty Weight
The empty weight of a vehicle is based on its weight without any payload (cargo, passengers, usable fuel, etc.). Aviation Many different empty weight definitions exist. Here are some of the more common ones used. GAMA standardization In 1975 (or 1976 per FAA-H-8083-1B) the General Aviation Manufacturers Association (GAMA) standardized the definition of empty weight terms for Pilot Operating Handbooks as follows: Standard Empty Weight includes the following: * Empty weight of the airplane * Full Hydraulic Fluid * Unusable Fuel * Full Oil Optional Equipment includes the following: * All equipment installed beyond standard Non-GAMA usage Previously (Regarding aircraft certified under CAR Part 3) the following were commonly used to define empty weights: In this definition Empty Weight includes the following: * Empty weight of the airplane * Undrainable Oil * Full Hydraulic Fluid Note that weight of oil must be added to Licensed Empty Weight for it to be equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
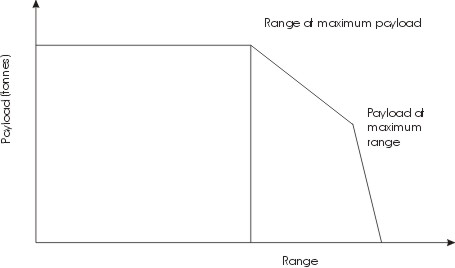
Payload
Payload is the object or the entity which is being carried by an aircraft or launch vehicle. Sometimes payload also refers to the carrying capacity of an aircraft or launch vehicle, usually measured in terms of weight. Depending on the nature of the flight or mission, the payload of a vehicle may include cargo, passengers, flight crew, munitions, scientific instruments or experiments, or other equipment. Extra fuel, when optionally carried, is also considered part of the payload. In a commercial context (i.e., an airline or air freight carrier), payload may refer only to revenue-generating cargo or paying passengers. A payload of ordnance carried by a combat aircraft is sometimes alternatively referred to as the aircraft's warload. For a rocket, the payload can be a satellite, space probe, or spacecraft carrying humans, animals, or cargo. For a ballistic missile, the payload is one or more warheads and related systems; their total weight is referred to as the throw-weight. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aviation Manufacturers Association
The General Aviation Manufacturer's Association (GAMA) is the industry trade association representing general aviation (non-military & non-airliner) aircraft manufacturers and related enterprises, chiefly in the United States.General Aviation Manufacturers' Assn. websiteStaffretrieved May 18, 2013. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., with an office in Brussels, Belgium. History Light aircraft manufacturers in the United States were typically members of the Aerospace Industries Association (originally called the Aeronautical Chamber of Commerce), which represented all aircraft manufacturers in the U.S. catering to military aviation, commercial aviation and general aviation. Increasing division of interests and priorities, and the disproportionate power of the military and commercial aircraft manufacturers, led to the establishment of a new organization to represent general aviation aircraft manufacturers. The organization was established as the Utility Aircraft Council, until i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Flight Manual
An aircraft flight manual (AFM) is a paper book or electronic information set containing information required to operate an aircraft of certain type or particular aircraft of that type (each AFM is tailored for a specific aircraft, though aircraft of the same type naturally have very similar AFMs). The information within an AFM is also referred to a Technical Airworthiness Data (TAWD). A typical flight manual will contain the following: operating limitations, Normal/Abnormal/Emergency operating procedures, performance data and loading information. An AFM will often include: * V speeds * Aircraft gross weight * Maximum ramp weight * Maximum takeoff weight * Manufacturer's empty weight * Operating empty weight * Centre of gravity limitations * Zero-fuel weight * Takeoff distance * Landing distance Originally, an AFM would follow whichever format and order the manufacturer felt appropriate. Eventually, the General Aviation Manufacturers Association came to an agreement to standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Fluid
A hydraulic fluid or hydraulic liquid is the medium by which power is transferred in hydraulic machinery. Common hydraulic fluids are based on mineral oil or water. Examples of equipment that might use hydraulic fluids are excavators and backhoes, hydraulic brakes, power steering systems, automatic transmissions, garbage trucks, aircraft flight control systems, lifts, and industrial machinery. Hydraulic systems like the ones mentioned above will work most efficiently if the hydraulic fluid used has zero compressibility. Functions and properties The primary function of a hydraulic fluid is to convey power. In use, however, there are other important functions of hydraulic fluid such as protection of the hydraulic machine components. The table below lists the major functions of a hydraulic fluid and the properties of a fluid that affect its ability to perform that function: Composition Base stock The original hydraulics fluid, dating back to the time of ancient Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usable Fuel
In aviation, usable fuel is the fuel on board an aircraft that can actually be used by its engines. The opposite of usable fuel is unusable fuel.Websters dictionary oUnusable fuel visited 19 March, 2012 The unusable fuel figure is calculated for an aircraft fuel tank in "the most adverse fuel feed condition occurring under each intended operation and flight maneuver involving that tank".Cornell Law online library https://www.law.cornell.edu/cfr/text/14/23.959, accessed 24 November 2017 The figure usable fuel is used when calculating or defining other key figures of an aircraft such as MTOW, zero-fuel weight The zero-fuel weight (ZFW) of an aircraft is the total weight of the airplane and all its contents, minus the total weight of the usable fuel on board. Unusable fuel is included in ZFW. For many types of airplane, the airworthiness limitations incl ... etc. Usable fuel is the total amount of fuel in an aircraft minus the fuel that cannot be fed into the engine(s): fuel under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Vehicle Weight
Vehicle weight is a measurement of wheeled motor vehicles; either an actual measured weight of the vehicle under defined conditions or a gross weight rating for its weight carrying capacity. Curb or kerb weight Curb weight (U.S. English) or kerb weight (British English) is the total mass of a vehicle with standard equipment and all necessary operating consumables such as motor oil, transmission oil, brake fluid, coolant, air conditioning refrigerant, and sometimes a full tank of fuel, while not loaded with either passengers or cargo. The gross vehicle weight is larger and includes the maximum payload of passengers and cargo. This definition may differ from definitions used by governmental regulatory agencies or other organizations. For example, many European Union manufacturers include the weight of a driver and luggage to follow European Directive 95/48/EC. Organizations may also define curb weight with fixed levels of fuel and other variables to equalize the value for the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. The DOE oversees the U.S. nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and domestic energy production and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the Secretary of Energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current Secretary of Energy is Jennifer Granholm, who has served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Fuel Weight
The zero-fuel weight (ZFW) of an aircraft is the total weight of the airplane and all its contents, minus the total weight of the usable fuel on board. Unusable fuel is included in ZFW. For many types of airplane, the airworthiness limitations include a maximum zero-fuel weight. This limitation is specified to ensure bending moments on the wing roots are not excessive during flight. When the aircraft is loaded before flight, the zero-fuel weight must not exceed the maximum zero-fuel weight. Maximum zero fuel weight The maximum zero fuel weight (MZFW) is the maximum weight allowed before usable fuel and other specified usable agents (engine injection fluid, and other consumable propulsion agents) are loaded in defined sections of the aircraft as limited by strength and airworthiness requirements. It may include usable fuel in specified tanks when carried in lieu of payload. The addition of usable and consumable items to the zero fuel weight must be in accordance with the applicabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Takeoff Weight
The maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) or maximum gross takeoff weight (MGTOW) or maximum takeoff mass (MTOM) of an aircraft is the maximum weight at which the pilot is allowed to attempt to take off, due to structural or other limits. The analogous term for rockets is gross lift-off mass, or GLOW. MTOW is usually specified in units of kilograms or pounds. MTOW is the heaviest weight at which the aircraft has been shown to meet all the airworthiness requirements applicable to it. MTOW of an aircraft is fixed and does not vary with altitude, air temperature, or the length of the runway to be used for takeoff or landing. Maximum permissible takeoff weight or "regulated takeoff weight", varies according to flap setting, altitude, air temperature, length of runway and other factors. It is different from one takeoff to the next, but can never be higher than the MTOW. Certification standards Certification standards applicable to the airworthiness of an aircraft contain many requirements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Weight Measurements
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air. It counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, helicopters, airships (including blimps), gliders, paramotors, and hot air balloons. The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard pilot, but unmanned aerial vehicles may be remotely controlled or self-controlled by onboard computers. Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, aircraft propulsion, usage and others. History Flying model craft and stories of manned flight go back many centuries; however, the first manned ascent — and safe descent — in modern times took place by larger hot-air ball ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Law
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), watercraft (ships, boats, underwater vehicles), amphibious vehicles (screw-propelled vehicles, hovercraft), aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, aerostats) and spacecraft.Halsey, William D. (Editorial Director): ''MacMillan Contemporary Dictionary'', page 1106. MacMillan Publishing, 1979. Land vehicles are classified broadly by what is used to apply steering and drive forces against the ground: wheeled, tracked, railed or skied. ISO 3833-1977 is the standard, also internationally used in legislation, for road vehicles types, terms and definitions. History * The oldest boats found by archaeological excavation are logboats, with the oldest logboat found, the Pesse canoe found in a bog in the Netherlands, being carbon dated to 8040 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |