|
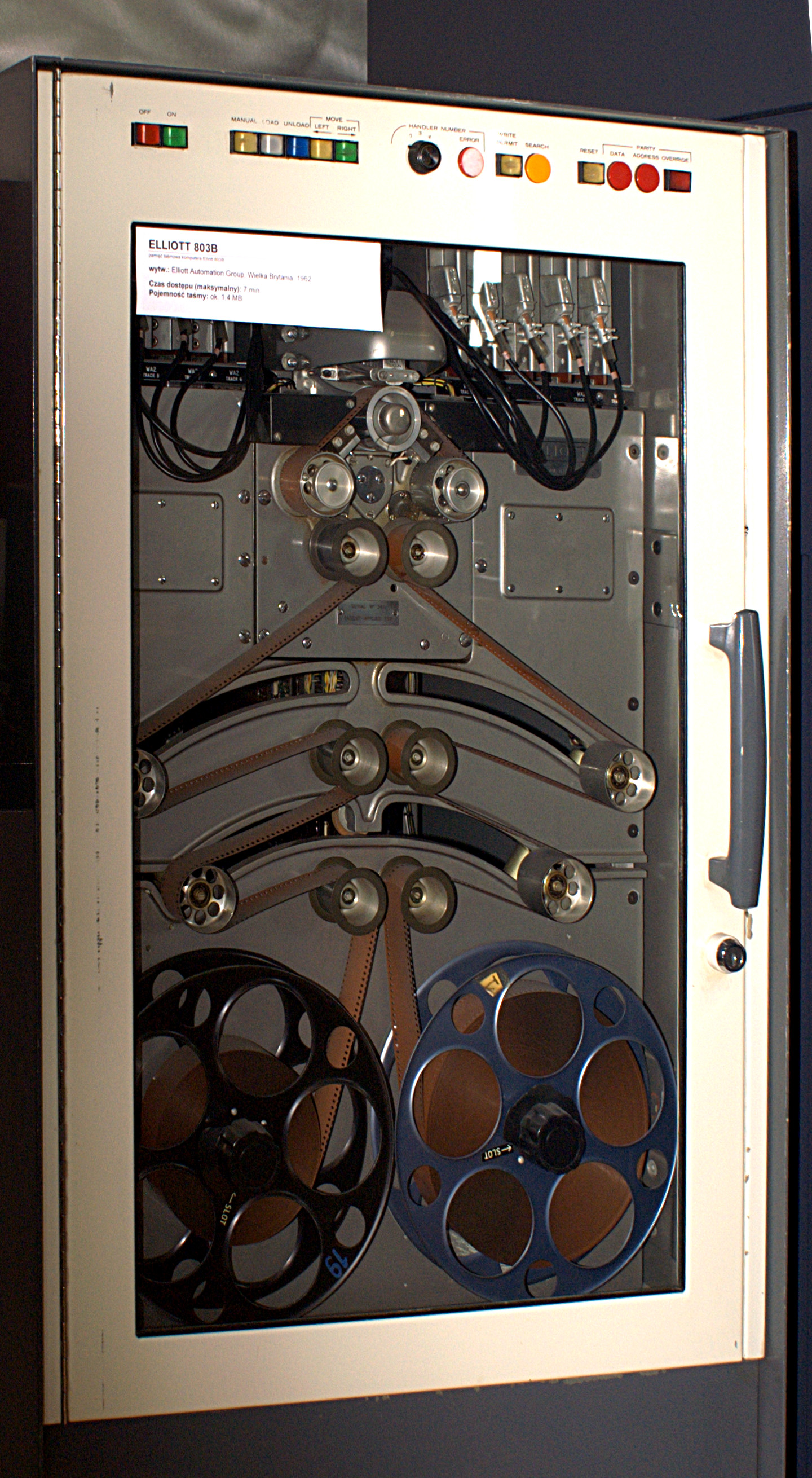
Elliott 803
The Elliott 803 is a small, medium-speed transistor digital computer which was manufactured by the British company Elliott Brothers in the 1960s. About 211 were built. History The 800 series began with the 801, a one-off test machine built in 1957. The 802 was a production model but only seven were sold between 1958 and 1961. The short-lived 803A was built in 1959 and first delivered in 1960; the 803B was built in 1960 and first delivered in 1961. Over 200 Elliott 803 computers were delivered to customers, at a unit price of about £29,000 in 1960 (roughly ). Most sales were of the 803B version with more parallel paths internally, larger memory and hardware floating-point operations. The Elliott 803 was the computer used in the ISI-609, the world's first process or industrial control system, wherein the 803 was a data logger. It was used for this purpose at the US's first dual-purpose nuclear reactor, the N-Reactor. A significant number of British universities had an Ellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliott 803
The Elliott 803 is a small, medium-speed transistor digital computer which was manufactured by the British company Elliott Brothers in the 1960s. About 211 were built. History The 800 series began with the 801, a one-off test machine built in 1957. The 802 was a production model but only seven were sold between 1958 and 1961. The short-lived 803A was built in 1959 and first delivered in 1960; the 803B was built in 1960 and first delivered in 1961. Over 200 Elliott 803 computers were delivered to customers, at a unit price of about £29,000 in 1960 (roughly ). Most sales were of the 803B version with more parallel paths internally, larger memory and hardware floating-point operations. The Elliott 803 was the computer used in the ISI-609, the world's first process or industrial control system, wherein the 803 was a data logger. It was used for this purpose at the US's first dual-purpose nuclear reactor, the N-Reactor. A significant number of British universities had an Ellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printed Circuit Boards
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers: each of the conductive layers is designed with an artwork pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) etched from one or more sheet layers of copper laminated onto and/or between sheet layers of a non-conductive substrate. Electrical components may be fixed to conductive pads on the outer layers in the shape designed to accept the component's terminals, generally by means of soldering, to both electrically connect and mechanically fasten them to it. Another manufacturing process adds vias: plated-through holes that allow interconnections between layers. Printed circuit boards are used in nearly all electronic products. Alternatives to PCBs include wire wrap a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Film Stock
Film stock is an analog medium that is used for recording motion pictures or animation. It is recorded on by a movie camera, developed, edited, and projected onto a screen using a movie projector. It is a strip or sheet of transparent plastic film base coated on one side with a gelatin emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast and resolution of the film.Karlheinz Keller et al. "Photography" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
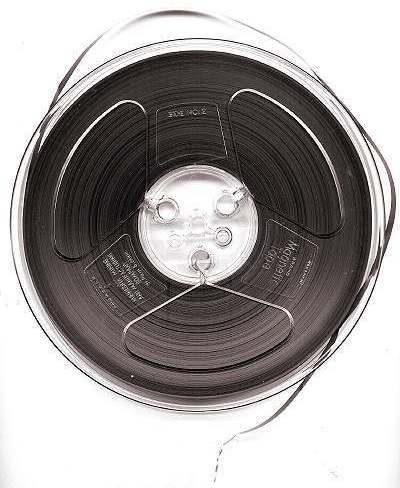
Magnetic Tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magnetic tape could with relative ease record and playback audio, visual, and binary computer data. Magnetic tape revolutionized sound recording and reproduction and broadcasting. It allowed radio, which had always been broadcast live, to be recorded for later or repeated airing. Since the early 1950s, magnetic tape has been used with computers to store large quantities of data and is still used for backup purposes. Magnetic tape begins to degrade after 10–20 years and therefore is not an ideal medium for long-term archival storage. Durability While good for short-term use, magnetic tape is highly prone to disintegration. Depending on the environment, this process may begin after 10–20 years. Over time, magnetic tape made in the 197 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling the humidity of internal air. Air conditioning can be achieved using a mechanical 'air conditioner' or alternatively a variety of other methods, including passive cooling or ventilative cooling. Air conditioning is a member of a family of systems and techniques that provide heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Heat pumps are similar in many ways to air conditioners, but use a reversing valve to allow them to both heat and also cool an enclosed space. Air conditioners, which typically use vapor-compression refrigeration, range in size from small units used within vehicles or single rooms to massive units that can cool large buildings. Air source heat pumps, which can be used for heating as well as cooling, are becoming incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Register
In computing, the instruction register (IR) or current instruction register (CIR) is the part of a CPU's control unit that holds the instruction currently being executed or decoded. In simple processors, each instruction to be executed is loaded into the instruction register, which holds it while it is decoded, prepared and ultimately executed, which can take several steps. Some of the complicated processors use a pipeline of instruction registers where each stage of the pipeline does part of the decoding, preparation or execution and then passes it to the next stage for its step. Modern processors can even do some of the steps out of order as decoding on several instructions is done in parallel. Decoding the op-code in the instruction register includes determining the instruction, determining where its operands are in memory, retrieving the operands from memory, allocating processor resources to execute the command (in super scalar processors), etc. The output of the IR is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baudot Code
The Baudot code is an early character encoding for telegraphy invented by Émile Baudot in the 1870s. It was the predecessor to the International Telegraph Alphabet No. 2 (ITA2), the most common teleprinter code in use until the advent of ASCII. Each character in the alphabet is represented by a series of five bits, sent over a communication channel such as a telegraph wire or a radio signal by asynchronous serial communication. The symbol rate measurement is known as baud, and is derived from the same name. History Baudot code (ITA1) In the below table, Columns I, II, III, IV, and V show the code; the Let. and Fig. columns show the letters and numbers for the Continental and UK versions; and the sort keys present the table in the order: alphabetical, Gray and UK Baudot developed his first multiplexed telegraph in 1872 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by a interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depends on perspective. Mice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punched Tape
Five- and eight-hole punched paper tape Paper tape reader on the Harwell computer with a small piece of five-hole tape connected in a circle – creating a physical program loop Punched tape or perforated paper tape is a form of data storage that consists of a long strip of paper in which holes are punched. It developed from and was subsequently used alongside punched cards, differing in that the tape is continuous. Punched cards, and chains of punched cards, were used for control of looms in the 18th century. Use for telegraphy systems started in 1842. Punched tape was used throughout the 19th and for much of the 20th centuries for programmable looms, teleprinter communication, for input to computers of the 1950s and 1960s, and later as a storage medium for minicomputers and CNC machine tools. During the Second World War, high-speed punched tape systems using optical readout methods were used in code breaking systems. Punched tape was used to transmit data for manufacture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Initially they were used in telegraphy, which developed in the late 1830s and 1840s as the first use of electrical engineering, though teleprinters were not used for telegraphy until 1887 at the earliest. The machines were adapted to provide a user interface to early mainframe computers and minicomputers, sending typed data to the computer and printing the response. Some models could also be used to create punched tape for data storage (either from typed input or from data received from a remote source) and to read back such tape for local printing or transmission. Teleprinters could use a variety of different communication media. These included a simple pair of wires; dedicated non-switched telephone circuits (leased lines); switched network ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creed & Company
Creed & Company was a British telecommunications company founded by Frederick George Creed which was an important pioneer in the field of teleprinter machines. It was merged into the International Telephone and Telegraph Corporation (ITT) in 1928. History The company was founded by Frederick George Creed and Danish telegraph engineer Harald Bille, and was first incorporated in 1912 as "Creed, Bille & Company Limited". After Bille's death in a railway accident in 1916, his name was dropped from the company's title and it became simply Creed & Company. The Company spent most of World War I producing high-quality instruments, manufacturing facilities for which were very limited at that time in the UK. Among the items produced were amplifiers, spark-gap transmitters, aircraft compasses, high-voltage generators, bomb release apparatus, and fuses for artillery shells and bombs. In 1924 Creed entered the teleprinter field with their Model 1P, which was soon superseded by the improv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |