|
Electra (star)
Electra , designated 17 Tauri, is a blue-white giant star in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. It is the third-brightest star in the Pleiades Open cluster, open star cluster (Messier object, M45); the most visible stars in this group are named for the Pleiades (Greek mythology), Seven Sisters of Greek mythology. Properties The star has an apparent brightness of 3.72, the third-brightest of the stars in the group. Electra belongs to the spectral class B6 IIIe and is approximately 400 light-years from the Sun. The Pleiades cluster is thought to be 444 light-years away. The stellar rotation, projected rotational velocity of this star is 181 km/s, making it a fast rotator. This is the velocity component of the star's equatorial rotation along the line of sight to the Earth. The estimated inclination of the star's pole is , giving it a true equatorial rotational velocity of . The rapid rotation rate of this star flattens the poles and stretch the equa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taurus (constellation)
Taurus (Latin for "the Bull") is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the northern celestial hemisphere. Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the Northern Hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to the Early Bronze Age at least, when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Its importance to the agricultural calendar influenced various bull figures in the mythologies of Ancient Sumer, Akkad, Assyria, Babylon, Egypt, Greece, and Rome. Its old astronomical symbol is (♉︎), which resembles a bull's head. A number of features exist that are of interest to astronomers. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth, the Pleiades and the Hyades, both of which are visible to the naked eye. At first magnitude, the red giant Aldebaran is the brightest star in the constellation. In the northeast part of Taurus is Messier 1, more commonly known as the Crab Nebula, a supernova remnant co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleiades (Greek Mythology)
The Pleiades (; grc-gre, Πλειάδες, Ancient Greek pronunciation: ), were the seven sister-nymph, nymphs, companions of Artemis, the goddess of the hunt. Together with their seven sisters, the Hyades (mythology), Hyades, they were called the Atlantides, Dodonides, or Nysiads, Nysiades, nursemaids and teachers of the infant Dionysus. The Pleiades were thought to have been translated to the night sky as a cluster of stars, the Pleiades, and were associated with rain. Etymology The name Pleiades ostensibly derived from the name of their mother, Pleione, effectively meaning "daughters of Pleione". However, the name of the star-cluster likely came first, and Pleione was invented to explain it. According to another suggestion ''Pleiades'' derived from πλεῖν (''plein'' , "to sail") because of the cluster's importance in delimiting the sailing season in the Mediterranean Sea: "the season of navigation began with their heliacal rising". Family The Pleiades' parents were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler Space Telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit. The principal investigator was William J. Borucki. After nine and a half years of operation, the telescope's reaction control system fuel was depleted, and NASA announced its retirement on October 30, 2018. Designed to survey a portion of Earth's region of the Milky Way to discover Earth-size exoplanets in or near habitable zones and estimate how many of the billions of stars in the Milky Way have such planets, Kepler's sole scientific instrument is a photometer that continually monitored the brightness of approximately 150,000 main sequence stars in a fixed field of view. These data were transmitted to Earth, then analyzed to detect periodic dimming caused by exoplanets that cross in front of their host star. Only planets whose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that travel in different optical paths, which are then combined again to produce interfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopic Binary
A binary star is a system of two star, stars that are gravity, gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in which case they are called ''visual binaries''. Many visual binaries have long orbital periods of several centuries or millennia and therefore have orbits which are uncertain or poorly known. They may also be detected by indirect techniques, such as spectroscopy (''spectroscopic binaries'') or astrometry (''astrometric binaries''). If a binary star happens to orbit in a plane along our line of sight, its components will eclipse and transit (astronomy), transit each other; these pairs are called ''eclipsing binaries'', or, together with other binaries that change brightness as they orbit, ''photometric binaries''. If components in binary star systems are close enough they can gravitationally distort their mutual outer stella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the temporal rate of change, rate of change of the distance or Slant range, range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection of the target-observer relative velocity onto the relative direction (geometry), relative direction connecting the two points. In astronomy, the point is usually taken to be the observer on Earth, so the radial velocity then denotes the speed with which the object moves away from the Earth (or approaches it, for a negative radial velocity). Formulation Given a differentiable vector \mathbf \in \mathbb^3 defining the instantaneous position of a target relative to an observer. Let with \mathbf \in \mathbb^3, the instantaneous velocity of the target with respect to the observer. The magnitude of the position vector \mathbf is defined as The quantity range rate is the time derivative of the magnitud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Be Star
Be stars are a heterogeneous set of stars with B spectral types and emission lines. A narrower definition, sometimes referred to as ''classical Be stars'', is a non-supergiant B star whose spectrum has, or had at some time, one or more Balmer emission lines. Definition and classification Many stars have B-type spectra and show hydrogen emission lines, including many supergiants, Herbig Ae/Be stars, mass-transferring binary systems, and B stars. It is preferred to restrict usage of the term Be star to non-supergiant stars showing one or more Balmer series lines in emission. These are sometimes referred to as classical Be stars. The emission lines may be present only at certain times. Although the Be type spectrum is most strongly produced in class B stars, it is also detected in O and A shell stars, and these are sometimes included under the "Be star" banner. Be stars are primarily considered to be main sequence stars, but a number of subgiants and giant stars are also inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Darkening
Gravity darkening, also referred to as gravity brightening, is an astronomical phenomenon where the poles of a star are brighter than the equator, due to rapid rotation and oblate shape. When a star is oblate, it has a larger radius at its equator than it does at its poles. As a result, the poles have a higher surface gravity, and thus higher temperature and pressure is needed to maintain hydrostatic equilibrium. Thus, the poles are "gravity brightened", and the equator "gravity darkened". The star becomes oblate (and hence gravity darkening occurs) because the centrifugal force resulting from rotation creates additional outward pressure on the star. The centrifugal force is expressed mathematically as : F_\text = m \Omega^2 \rho, where m is mass (in this case of a small volume element of the star), \Omega is the angular velocity, and \rho is the radial distance from the axis of rotation. In the case of a star, the value of \rho is largest at the equator and smallest at the poles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
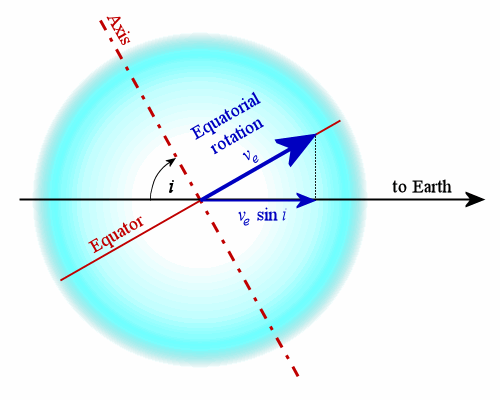
Stellar Rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. The magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its rate of angular velocity slows. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star is being observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |