|
Elections In Croatia
Regular elections in Croatia are mandated by the Constitution and legislation enacted by Parliament. The presidency, Parliament, county prefects and assemblies, city and town mayors, and city and municipal councils are all elective offices. Since 1990, seven presidential elections have been held. During the same period, ten parliamentary elections (with two for the upper house when the parliament was bicameral) were also held. In addition, there were nine nationwide local elections. Croatia has also held three elections to elect members of the European Parliament following its accession to the EU on 1 July 2013. The President of Croatia is elected for a five-year term by a direct vote of all citizens in a majority system, requiring runoff elections if no candidate wins more than 50 percent of votes in the first round. Members of Parliament are elected for a four-year term in ten multi-seat constituencies, with additional members elected in special constituencies reserved for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Croatia
The Constitution of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Ustav Republike Hrvatske) is promulgated by the Croatian Parliament. History While it was part of the socialist Yugoslavia, the Socialist Republic of Croatia had its own Constitution under the Constitution of Yugoslavia. Following the first multi-party parliamentary elections held in April 1990, the Parliament made various constitutional changes. On December 22, 1990, they rejected the communist one-party system and adopted a liberal-democratic Constitution of Croatia as the Republic of Croatia. The document is sometimes known as the Christmas Constitution (). The Constitution was amended in early 1998. The Constitution of 1990 used the semi-presidential model of the French Fifth Republic, with broad Presidential executive powers shared with the Government. In 2000, and again in 2001, the Croatian Parliament amended the Constitution changing bicameral parliament back into historic unicameral and reducing the Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian People's Party – Liberal Democrats
The Croatian People's Party – Liberal Democrats ( hr, Hrvatska narodna stranka – Liberalni demokrati or HNS – LD) is a social- liberal political party in Croatia. As of April 2015 HNS forms a parliamentary club with 5 members in the Croatian Parliament, making them the fourth largest party in Croatia in terms of parliament representation. HNS is a full member of the Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe Party. Since 17 December 2017, the party's leader has been Ivan Vrdoljak. Origins The People's Party in Croatia was originally formed in 1841, during the period of Croatian romantic nationalism. The Croatian People's Party describes the events of the Illyrian movement since 1835 as its history.. After 1861 the People's Party was known as the People's Liberal Party, its main splinter party was the Independent People's Party (1880–1903) which became more pro-autonomist, while the "old" People's Party developed into "party of the Settlement" having collaborated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabor
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor is composed of 151 members elected to a four-year term on the basis of direct, universal and equal suffrage by secret ballot. Seats are allocated according to the Croatian Parliament electoral districts: 140 members of the parliament are elected in multi-seat constituencies. An additional three seats are reserved for the diaspora and Croats in Bosnia and Herzegovina, while national minorities have eight places reserved in parliament. The Sabor is presided over by a Speaker, who is assisted by at least one deputy speaker (usually four or five deputies). The Sabor's powers are defined by the Constitution and they include: defining economic, legal and political relations in Croatia, preservation and use of its heritage and entering int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Croatian Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on 25 November 2007 and for overseas voters on 24 and 25 November.President announces elections The political campaign, campaign officially started on 3 November. The President of Croatia announced elections on 17 October and 14 days were allowed for candidate lists to be submitted. Elections were held in Croatian Parliament electoral districts, 10 electoral districts inside Croatia (each providing 14 members of parliament),Law defining electorates /ref> one electoral district for Croatian citizens living abroad (with a maximum 12 members of parliament), and one electoral district for national minorities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Amendment
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions ( codicils), thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document. Most constitutions require that amendments cannot be enacted unless they have passed a special procedure that is more stringent than that required of ordinary legislation. Examples of such special procedures include supermajorities in the legislature, or direct approval by the electorate in a referendum, or even a combination of two or more different special procedures. A referendum to amend the constitution may also be triggered in some jurisdictions by popular initiative. Australia and Ireland provide examples of constitutions requiring that all amendments are first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Croatian Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Croatia on Sunday, 4 December 2011 to elect 151 members to the Croatian Parliament. They were the sixth parliamentary election in Croatia since independence. Elections were held in 10 electoral districts inside Croatia (each electing 14 members of parliament), one electoral district for Croatian citizens living abroad (3 members of parliament), and one electoral district for national minorities (8 members of parliament). Candidate lists have to win more than 5% of the votes in an electoral district in order to be represented in Parliament. The previous elections were a close race between the two major political alliances and resulted with Ivo Sanader winning a second term as Prime Minister. After his sudden and unexpected resignation in mid-2009, Jadranka Kosor succeeded him as head of the governing party (Croatian Democratic Union, HDZ) and formed a new Government. Zoran Milanović, despite losing a close race four years ago, was again chos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Croatian Parliament
The Croatian Parliament ( hr, Hrvatski sabor) or the Sabor is the unicameral legislature of the Republic of Croatia. Under the terms of the Croatian Constitution, the Sabor represents the people and is vested with legislative power. The Sabor is composed of 151 members elected to a four-year term on the basis of direct, universal and equal suffrage by secret ballot. Seats are allocated according to the Croatian Parliament electoral districts: 140 members of the parliament are elected in multi-seat constituencies. An additional three seats are reserved for the diaspora and Croats in Bosnia and Herzegovina, while national minorities have eight places reserved in parliament. The Sabor is presided over by a Speaker, who is assisted by at least one deputy speaker (usually four or five deputies). The Sabor's powers are defined by the Constitution and they include: defining economic, legal and political relations in Croatia, preservation and use of its heritage and entering in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Court Of Croatia
The Constitutional Court of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Ustavni sud Republike Hrvatske) is an institution that acts as the interpreter and guardian of the Croatian Constitution and which monitors the conformity of laws with the Constitution as well as protection of human rights and freedoms of citizens that are guaranteed by the Constitution. It is considered to be ''de facto'' the highest judicial authority because it can overturn Supreme Court decisions on the basis of constitutional breaches. It is not considered as being part of the judicial branch of government, but rather a court '' sui generis'', and it is therefore often colloquially referred to as a "fourth branch of government", alongside the traditional model of tripartite separation of powers into the executive (Government/ President of the Republic), legislative (Parliament) and judicial (Supreme Court) branches. Powers and responsibilities According to the Articles 126-132 of the Croatian Constitution, Constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed List
Closed list describes the variant of party-list systems where voters can effectively only vote for political parties as a whole; thus they have no influence on the party-supplied order in which party candidates are elected. If voters had some influence, that would be called an open list. Closed list systems are still commonly used in party-list proportional representation, and most mixed electoral systems also use closed lists in their party list component. Many countries, however have changed their electoral systems to use open lists to incorporate personalised representation to their proportional systems. In closed list systems, each political party has pre-decided who will receive the seats allocated to that party in the elections, so that the candidates positioned highest on this list tend to always get a seat in the parliament while the candidates positioned very low on the closed list will not. However, the candidates "at the water mark" of a given party are in the positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportional Representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divisions (Political party, political parties) of the electorate. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast - or almost all votes cast - contribute to the result and are actually used to help elect someone—not just a Plurality (voting), plurality, or a bare majority—and that the system produces mixed, balanced representation reflecting how votes are cast. "Proportional" electoral systems mean proportional to ''vote share'' and ''not'' proportional to population size. For example, the United States House of Representatives, US House of Representatives has 435 districts which are drawn so roughly equal or "proportional" numbers of people live within each district, yet members of the House are elected in first-past-the-post e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
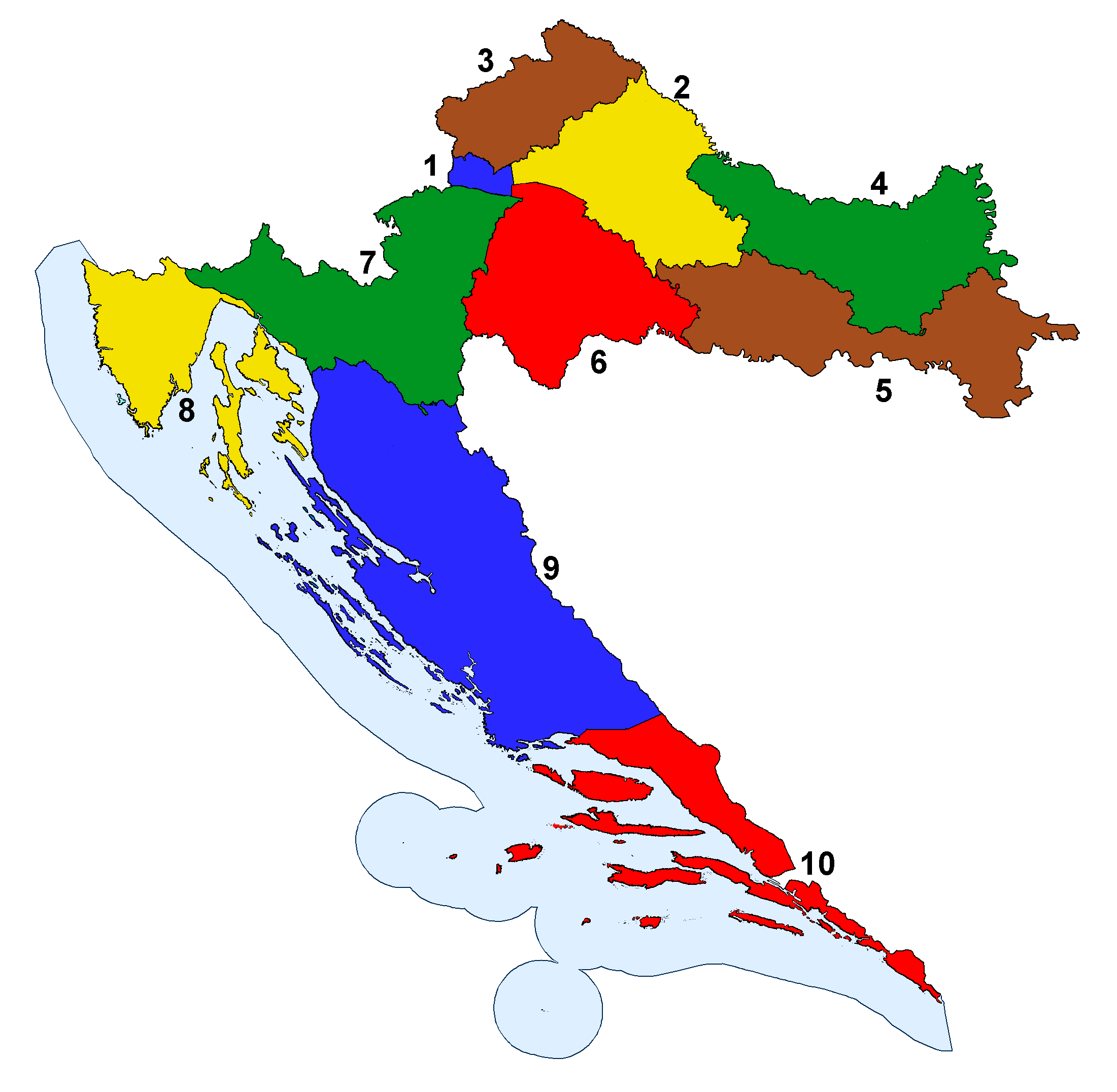
Administrative Divisions Of Croatia
The subdivisions of Croatia on the first level are the 20 counties (''županija'', pl. ''županije'') and one city-county ('' grad'', "city"). On the second level these are municipalities ('' općina'', pl. ''općine'') and cities (''grad'', pl. ''gradovi''). Both of these types of subdivisions encompass one or multiple settlements (''naselje'', pl. ''naselja'') which are not public or legal entities, the Croatian Bureau of Statistics consider them as non-administrative units – human settlements, similar to the United States census designated places. As parts of the cities or the (larger) municipalities they may form city districts (''gradski kotari'' or ''gradske četvrti'') or local committee areas (''mjesni odbori''). Small municipalities usually consist of only one settlement. Current (since 1992) Image:Croatia-counties-colorkey450px.png, left, 350px, alt=Map of present-day counties of Croatia, Counties of Croatia: poly 391 126 378 122 373 131 359 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefect
Prefect (from the Latin ''praefectus'', substantive adjectival form of ''praeficere'': "put in front", meaning in charge) is a magisterial title of varying definition, but essentially refers to the leader of an administrative area. A prefect's office, department, or area of control is called a prefecture, but in various post-Roman empire cases there is a prefect without a prefecture or ''vice versa''. The words "prefect" and "prefecture" are also used, more or less conventionally, to render analogous words in other languages, especially Romance languages. Ancient Rome ''Praefectus'' was the formal title of many, fairly low to high-ranking officials in ancient Rome, whose authority was not embodied in their person (as it was with elected Magistrates) but conferred by delegation from a higher authority. They did have some authority in their prefecture such as controlling prisons and in civil administration. Feudal times Especially in Medieval Latin, ''præfectus'' was used to r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |