|
Eikoh Hosoe
is a Japanese photographer and filmmaker who emerged in the experimental arts movement of post-World War II Japan. Hosoe is best known for his dark, high contrast, black and white photographs of human bodies. His images are often psychologically charged, exploring subjects such as death, erotic obsession, and irrationality. Some of his photographs reference religion, philosophy and mythology, while others are nearly abstract, such as ''Man and Woman # 24'', from 1960. He was professionally and personally affiliated with the writer Yukio Mishima and experimental artists of the 1960s such as the dancer Tatsumi Hijikata, though his work extends to a diversity of subjects. His photography is not only notable for its artistic influence but for its wider contribution to the reputations of his subjects. Biography At birth Hosoe's name was "Toshihiro" (敏廣); he adopted the name "Eikoh" after World War II to symbolize a new Japan.Art2art Circulating ExhibitionsEikoh Hosoe: ukiyo-e p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eikoh Hosoe
is a Japanese photographer and filmmaker who emerged in the experimental arts movement of post-World War II Japan. Hosoe is best known for his dark, high contrast, black and white photographs of human bodies. His images are often psychologically charged, exploring subjects such as death, erotic obsession, and irrationality. Some of his photographs reference religion, philosophy and mythology, while others are nearly abstract, such as ''Man and Woman # 24'', from 1960. He was professionally and personally affiliated with the writer Yukio Mishima and experimental artists of the 1960s such as the dancer Tatsumi Hijikata, though his work extends to a diversity of subjects. His photography is not only notable for its artistic influence but for its wider contribution to the reputations of his subjects. Biography At birth Hosoe's name was "Toshihiro" (敏廣); he adopted the name "Eikoh" after World War II to symbolize a new Japan.Art2art Circulating ExhibitionsEikoh Hosoe: ukiyo-e p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbidden Colors
is a 1951 novel (禁色 Part 2 was published in 1953) by the Japanese writer Yukio Mishima, translated into English in 1968. The name ''kinjiki'' is a euphemism for same-sex love. The kanji 禁 means "forbidden" and 色 in this case means "erotic love", although it can also mean "color". The word "kinjiki" also means colors that were forbidden to be worn by people of various ranks in the Japanese court. It describes a marriage of a Gay man to a young woman. Like Mishima's earlier novel ''Confessions of a Mask'', it is generally considered somewhat autobiographical. Plot summary Aging, cynical Shunsuke is one of postwar Japan's most respected authors. While vacationing at an exclusive Japanese resort, he meets Yuichi, a stunningly gorgeous young man of limited means and intellect who is engaged to a prim, conventional young woman from a very well-to-do family. While he needs the marriage for financial reasons, Yuichi innocently confides to the older man that he feels no real phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiyosato, Yamanashi
is a locality in the cities of Japan, city of Hokuto, Yamanashi, Hokuto, Yamanashi Prefecture, Yamanashi, Japan. At over 1,200m in elevation with views south towards Mount Fuji, it is a popular highland resort area and location for second homes. After the opening of the Koumi Line in 1933, Kiyosato rose to prominence as a resort center and as the home of Camp Seisen Ryo, an Anglican youth mission center prior to the Second World War, rededicated in 1946 as the Kiyosato Educational Experiment Project (KEEP). Geography The KEEP farm with its focus on dairy farming, initially served as a local community and agricultural development center. Herds of Jersey cows are still a feature of the area, but KEEP is now better known as a year-round resort and conference center and as the home of the Paul Rusch Memorial Museum and the Japan, American Football Hall of Fame. The original farm property is the focus of the popular Yatsugatake County Fair and Paul Rusch Festival held each October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiyosato Museum Of Photographic Arts
The is a gallery of photography in the Kiyosato region of the city of Hokuto, Yamanashi (Japan). The gallery was founded in 1995; Eikoh Hosoe has been its director since its opening. The gallery, which also refers to itself as "K*MoPA", "embraces photographic art made in the affirmation of life"; ." this does not exclude harsh images. It attempts to acquire prints of archival quality, and is particularly keen to encourage younger photographers to submit their work for consideration. The work of young photographers that the gallery accepts is exhibited in an annual series of "Young Portfolio" exhibitions, perhaps inspired by a major opening exhibition in which twenty-five well-established Japanese photographers exhibited work that they had done while still in their twenties.''Works by 25 Photographers in their 20s''; the phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butoh
is a form of Japanese dance theatre that encompasses a diverse range of activities, techniques and motivations for dance, performance, or movement. Following World War II, butoh arose in 1959 through collaborations between its two key founders, Tatsumi Hijikata and Kazuo Ohno. The art form is known to "resist fixity" and is difficult to define; notably, founder Hijikata Tatsumi viewed the formalisation of butoh with "distress". Common features of the art form include playful and grotesque imagery, taboo topics, and extreme or absurd environments. It is traditionally performed in white body makeup with slow hyper-controlled motion. However, with time butoh groups are increasingly being formed around the world, with their various aesthetic ideals and intentions. History Butoh first appeared in post-World War II Japan in 1959, under the collaboration of Tatsumi Hijikata and Kazuo Ohno, "in the protective shadow of the 1950s and 1960s avant-garde". A key impetus of the art form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazuo Ohno
was a Japanese dancer who became a guru and inspirational figure in the dance form known as Butoh. He is the author of several books on Butoh, including ''The Palace Soars through the Sky'', ''Dessin'', ''Words of Workshop'', and ''Food for the Soul''. The latter two were published in English as ''Kazuo Ohno's World: From Without & Within'' (2004). Ohno once said of his work: "The best thing someone can say to me is that while watching my performance they began to cry. It is not important to understand what I am doing; perhaps it is better if they don't understand, but just respond to the dance."Childs, Martin"Kazuo Ohno: Dancer who co-founded the modern Butoh style and brought it to the world stage" ''The Independent'', July 7, 2010. Early life Ohno was born in Hakodate, Hokkaidō, Hakodate City, Hokkaido on October 27 in 1906. He demonstrated an aptitude for athletics in junior high school and graduated from an athletic college in 1929, teaching physical education at a Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seppuku
, sometimes referred to as hara-kiri (, , a native Japanese kun reading), is a form of Japanese ritual suicide by disembowelment. It was originally reserved for samurai in their code of honour but was also practised by other Japanese people during the Shōwa period (particularly officers near the end of World War II) to restore honour for themselves or for their families. As a samurai practice, ''seppuku'' was used voluntarily by samurai to die with honour rather than fall into the hands of their enemies (and likely be tortured), as a form of capital punishment for samurai who had committed serious offences, or performed because they had brought shame to themselves. The ceremonial disembowelment, which is usually part of a more elaborate ritual and performed in front of spectators, consists of plunging a short blade, traditionally a ''tantō'', into the belly and drawing the blade from left to right, slicing the belly open. If the cut is deep enough, it can sever the abdominal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
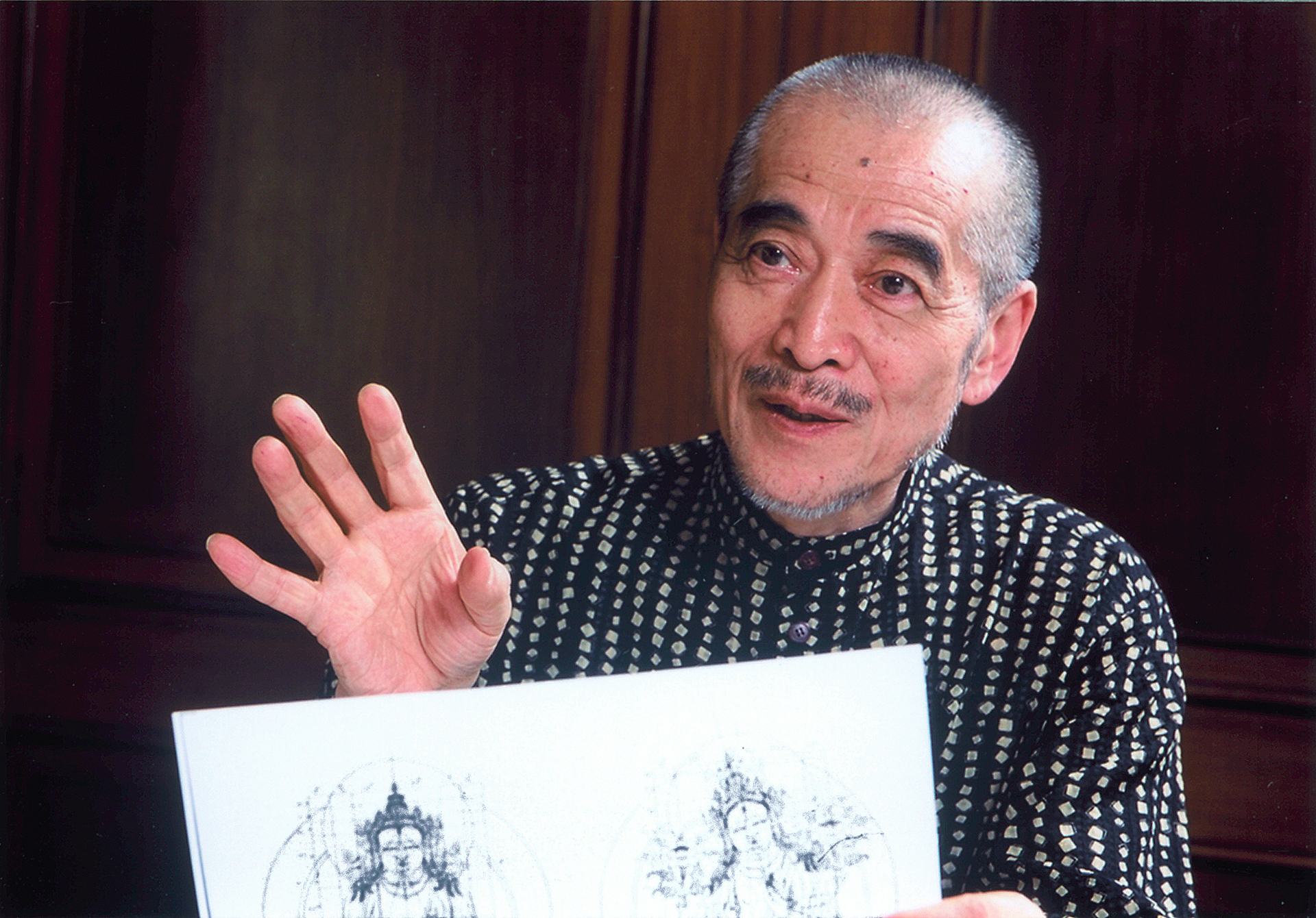
Kōhei Sugiura
is a Japanese graphic designer and researcher in Asian iconography. Throughout his career, Sugiura has been a pioneer within the design world using processes that enables the visualization of consciousness in his large body of work that ranges from record jackets and posters, to books, magazines, and exhibition catalogues, to diagrams, stamps, and more. He is also active in promoting the study of traditional Asian cultures through producing innovative catalogue designs and organizing exhibitions such as ''Mandala: now you see it, now you don't'' (1980) and ''Flower Cosmology: Traditions in Dyeing, Weaving, and Ornaments'' (1992), underscored by his prolific research on cosmologies and mandalas. Sugiura served as a visiting professor for the Ulm School of Design in Germany (1964-1967); professor at Kobe Design University (1987-2002); and is currently the director of the Asian Design Institute at Kobe Design University (from April 2010). He has received numerous awards in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodansha
is a Japanese privately-held publishing company headquartered in Bunkyō, Tokyo. Kodansha is the largest Japanese publishing company, and it produces the manga magazines ''Nakayoshi'', ''Afternoon'', ''Evening'', ''Weekly Shōnen Magazine'' and ''Bessatsu Shōnen Magazine'', as well as the more literary magazines ''Gunzō'', ''Shūkan Gendai'', and the Japanese dictionary ''Nihongo Daijiten''. Kodansha was founded by Seiji Noma in 1910, and members of his family continue as its owners either directly or through the Noma Cultural Foundation. History Seiji Noma founded Kodansha in 1910 as a spin-off of the ''Dai-Nippon Yūbenkai'' (, "Greater Japan Oratorical Society") and produced the literary magazine ''Yūben'' () as its first publication. The name ''Kodansha'' (taken from ''Kōdan Club'' (), a now-defunct magazine published by the company) originated in 1911 when the publisher formally merged with the ''Dai-Nippon Yūbenkai''. The company has used its current legal name since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giorgione
Giorgione (, , ; born Giorgio Barbarelli da Castelfranco; 1477–78 or 1473–74 – 17 September 1510) was an Italian painter of the Venetian school during the High Renaissance, who died in his thirties. He is known for the elusive poetic quality of his work, though only about six surviving paintings are firmly attributed to him. The uncertainty surrounding the identity and meaning of his work has made Giorgione one of the most mysterious figures in European art. Together with his younger contemporary Titian, he founded the Venetian school of Italian Renaissance painting, characterised by its use of colour and mood. The school is traditionally contrasted with Florentine painting, which relied on a more linear disegno-led style. Life What little is known of Giorgione's life is given in Giorgio Vasari's '' Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects''. He came from the small town of Castelfranco Veneto, 40 km inland from Venice. His name sometimes appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandro Botticelli
Alessandro di Mariano di Vanni Filipepi ( – May 17, 1510), known as Sandro Botticelli (, ), was an Italian Renaissance painting, Italian painter of the Early Renaissance. Botticelli's posthumous reputation suffered until the late 19th century, when he was rediscovered by the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood, Pre-Raphaelites who stimulated a reappraisal of his work. Since then, his paintings have been seen to represent the linear grace of late Italian Gothic and some Early Renaissance painting, even though they date from the latter half of the Italian Renaissance period. In addition to the mythological subjects for which he is best known today, Botticelli painted a wide range of religious subjects (including dozens of renditions of the ''Madonna and Child'', many in the round tondo (art), tondo shape) and also some portraits. His best-known works are ''The Birth of Venus'' and ''Primavera (painting), Primavera'', both in the Uffizi in Florence, which holds many of Botticelli’s w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

