|
Ehrlichia Minasensis
''Ehrlichia'' is a genus of Rickettsiales bacteria that are transmitted to vertebrates by ticks. These bacteria cause the disease ehrlichiosis, which is considered zoonotic, because the main reservoirs for the disease are animals. ''Ehrlichia'' species are obligately intracellular pathogens and are transported between cells through the host cell filopodia during initial stages of infection, whereas in the final stages of infection, the pathogen ruptures the host cell membrane. History The genus ''Ehrlichia'' is named after German microbiologist Paul Ehrlich. The first ehrlichial disease was recognized in South Africa during the 19th century. Its tick-borne nature was determined in 1900. The organism itself was demonstrated in 1925 when it was recognized to be a ''Rickettsia''. It was initially named ''Rickettsia ruminantium'', and is currently named ''Ehrlichia ruminantium''. In 1945, an "infection and treatment" method for livestock was developed. This is still the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrlichia Ewingii
''Ehrlichia ewingii'' is a species of rickettsiales bacteria. It has recently been associated with human infection, and can be detected via PCR serological testing. The name ''Ehrlichia ewingii'' was proposed in 1992. Taxonomy and characterization Taxonomy The current classification is Bacteria, Pseudomonadota, Alphaproteobacteria, Rickettsiales, Anaplasmataceae, ''Ehrlichia ewingii''. Classification of different members of the genus ''Ehrlichia'' has been disputed, however, it is generally agreed that close relatives of ''Ehrlichia ewingii'' are ''Ehrlichia chaffeensis'' and ''Ehrlichia canis''. It is also closely related to ''Wolbachia'', ''Anaplasma'', and '' Neorickettsia'' bacteria, with ''Rickettsia'' as a more distant genus. Characterization Species in the family Anaplasmataceae have unique characteristics that can help differentiate them from other families including: sensitivity to mechanical stress, changes in osmolarity, and thawing. &n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ixodes Scapularis
''Ixodes scapularis'' is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick (although some people reserve the latter term for ''Ixodes pacificus'', which is found on the west coast of the US), and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It was also named ''Ixodes dammini'' until it was shown to be the same species in 1993. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans (Lyme disease, babesiosis, anaplasmosis, Powassan virus disease, etc.) and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage. Description The image shown here—and in fact, most images of ''Ixodes scapularis'' that are commonly available—show an adult female that is unengorged, that is, an adult female that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralogs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
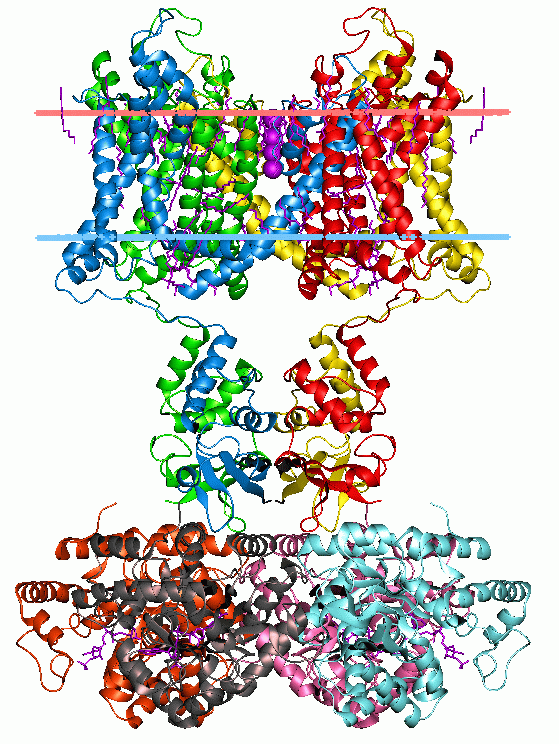
Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane ( integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct conformation of the protein in isolation from its native environment. Function Membrane proteins perform a variety of functions vital to the surv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness (biology)
Fitness (often denoted w or ω in population genetics models) is the Numerical data, quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the expected value, average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments. With asexual reproduction, it is sufficient to assign fitnesses to genotypes. With sexual reproduction, recombination scrambles alleles into different genotypes every generation; in this case, fitness values can be assigned to alleles by averaging over possible genetic backgrounds. Natural selection tends to make alleles with higher fitness more common ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Candidatus
In prokaryote nomenclature, ''Candidatus'' (Latin for candidate of Roman office) is used to name prokaryotic phyla that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S sequencing or metagenomics, provide much information about the analyzed organisms and thus allow to identify and characterize individual species. However, the majority of prokaryotic species remain uncultivable and hence inaccessible for further characterization in ''in vitro'' study. The recent discoveries of a multitude of candidate taxa has led to candidate phyla radiation expanding the tree of life through the new insights in bacterial diversity. Nomenclature History The initial International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes as well as early revisions did not account for the possibility of identifying prokaryotes which were not yet cultivable. Therefore, the term ''Candidatus'' was proposed in the context of a conference of the International Committee on Systemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriological Code
The International Code of Nomenclature of Prokaryotes (ICNP) formerly the International Code of Nomenclature of Bacteria (ICNB) or Bacteriological Code (BC) governs the scientific names for Bacteria and Archaea.P. H. A. Sneath, 2003. A short history of the Bacteriological CodURL It denotes the rules for naming taxa of bacteria, according to their relative rank. As such it is one of the nomenclature codes of biology. Originally the ''International Code of Botanical Nomenclature'' dealt with bacteria, and this kept references to bacteria until these were eliminated at the 1975 International Botanical Congress. An early Code for the nomenclature of bacteria was approved at the 4th International Congress for Microbiology in 1947, but was later discarded. The latest version to be printed in book form is the 1990 Revision, but the book does not represent the current rules. The 2008 Revision has been published in the '' International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrlichia Sennetsu
''Neorickettsia sennetsu'' is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes Sennetsu ehrlichiosis. See also *''Neorickettsia risticii ''Neorickettsia risticii'', formerly ''Ehrlichia risticii,'' is an obligate intracellular gram negative bacteria that typically lives as an endosymbiont to parasitic flatworms, specifically flukes. ''N. risticii'' is the known causative agent of ...'' References Rickettsiales Bacteria described in 2001 {{alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrlichia Risticii
''Ehrlichia'' is a genus of Rickettsiales bacteria that are transmitted to vertebrates by ticks. These bacteria cause the disease ehrlichiosis, which is considered zoonotic, because the main reservoirs for the disease are animals. ''Ehrlichia'' species are obligately intracellular pathogens and are transported between cells through the host cell filopodia during initial stages of infection, whereas in the final stages of infection, the pathogen ruptures the host cell membrane. History The genus ''Ehrlichia'' is named after German microbiologist Paul Ehrlich. The first ehrlichial disease was recognized in South Africa during the 19th century. Its tick-borne nature was determined in 1900. The organism itself was demonstrated in 1925 when it was recognized to be a ''Rickettsia''. It was initially named ''Rickettsia ruminantium'', and is currently named ''Ehrlichia ruminantium''. In 1945, an "infection and treatment" method for livestock was developed. This is still the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrlichia Muris
''Ehrlichia muris'' is a species of pathogenic bacteria first isolated from mice, with type strain AS145T. Its genome has been sequenced. References Further reading * * External linksLPSN*WISC entry Rickettsiales {{alphaproteobacteria-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehrlichia Minasensis
''Ehrlichia'' is a genus of Rickettsiales bacteria that are transmitted to vertebrates by ticks. These bacteria cause the disease ehrlichiosis, which is considered zoonotic, because the main reservoirs for the disease are animals. ''Ehrlichia'' species are obligately intracellular pathogens and are transported between cells through the host cell filopodia during initial stages of infection, whereas in the final stages of infection, the pathogen ruptures the host cell membrane. History The genus ''Ehrlichia'' is named after German microbiologist Paul Ehrlich. The first ehrlichial disease was recognized in South Africa during the 19th century. Its tick-borne nature was determined in 1900. The organism itself was demonstrated in 1925 when it was recognized to be a ''Rickettsia''. It was initially named ''Rickettsia ruminantium'', and is currently named ''Ehrlichia ruminantium''. In 1945, an "infection and treatment" method for livestock was developed. This is still the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |