|
Effective Schools
"Effective Schools" is both an educational movement and body of research which examines school-based factors which positively influence learning outcomes in K-12 schools. Effective schools research has been widely adopted by school districts worldwide. History Early research into the essential qualities of successful schools emerged in North America as a response to the controversial 1966 Coleman Report, which concluded that family background and socio-economics were the major determinants of student achievement. Research published by Christopher Jencks in 1972 contributed to Coleman's findings, suggesting that "school quality has little effect on achievement." The Coleman Report prompted U.S. policymakers to focus on "compensatory programs" which focused on changing the behavior of less advantaged students. The report also stimulated vigorous reaction from educational researchers who believed, to the contrary, that schools ''could'' make a significant difference on student achie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
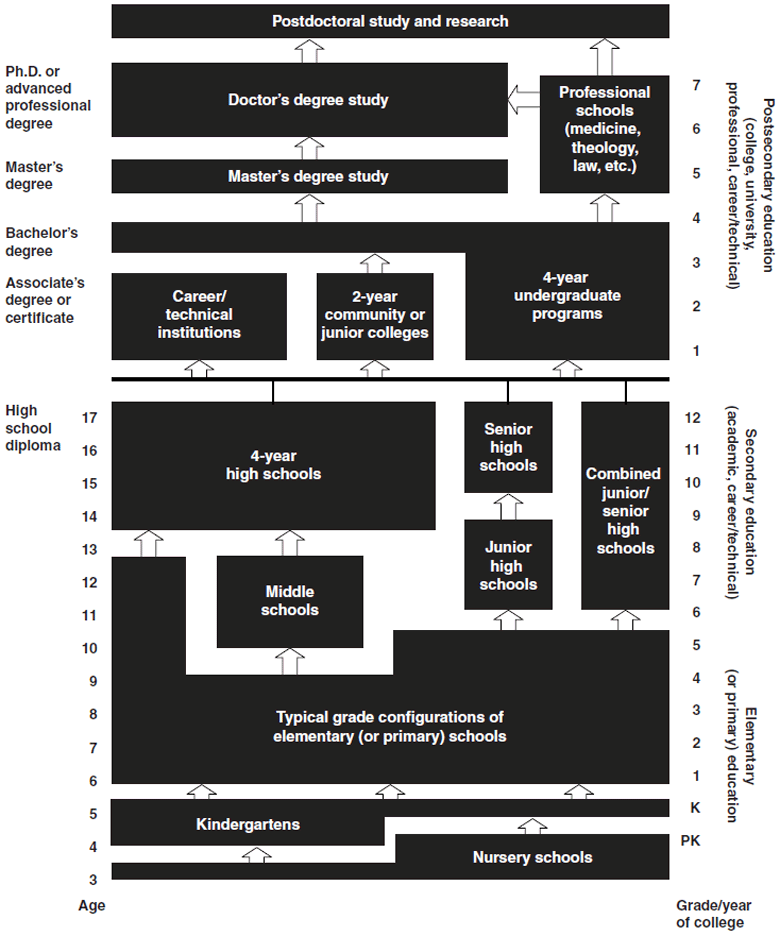
K–12 (education)
K–12, from kindergarten to 12th grade, is an American English expression that indicates the range of years of publicly supported primary and secondary education found in the United States, which is similar to publicly supported school grades before college in several other countries, such as Afghanistan, Australia, Canada, China, Ecuador, Egypt, India, Iran, the Philippines, South Korea, and Turkey. History U.S. public education was conceived of in the late 18th century. In 1790, Pennsylvania became the first state to require some form of free education for everyone regardless of whether they could afford it. New York passed similar legislation in 1805. In 1820, Massachusetts became the first state to create a tuition-free high school, Boston English. The first K–12 public school systems appeared in the early 19th century. In the 1830s and 1840s, Ohioans were taking a significant interest in the idea of public education. At that point in time, schools were commonly opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Samuel Coleman
James Samuel Coleman (May 12, 1926 – March 25, 1995) was an American sociologist, theorist, and empirical researcher, based chiefly at the University of Chicago. He was elected president of the American Sociological Association in 1991. He studied the sociology of education and public policy, and was one of the earliest users of the term social capital. He may be considered one of the original neoconservatives in sociology. His work ''Foundations of Social Theory'' (1990) influenced countless sociological theories, and his works ''The Adolescent Society'' (1961) and "Coleman Report" (''Equality of Educational Opportunity'', 1966) were two of the most cited books in educational sociology. The landmark Coleman Report helped transform educational theory, reshape national education policies, and it influenced public and scholarly opinion regarding the role of schooling in determining equality and productivity in the United States. Early life As the son of James and Maurine Coleman, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Jencks
Christopher Sandy Jencks (born October 22, 1936) is an American social scientist. Career Jencks is currently the Malcolm Wiener Professor of Social Policy in the Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University. He graduated from Phillips Exeter Academy in 1954 and was president of the school's newspaper, the Exonian, as a senior. After Exeter, he received an A.B. in English literature from Harvard in 1958, followed by a M.Ed. in Harvard Graduate School of Education. During the year 1960-1961 he studied sociology at the London School of Economics. He has previously held positions at Northwestern University, the University of Chicago and the University of California at Santa Barbara. His interests are in the study of education, social stratification, social mobility, poverty and the poor. His recent research concerns changes in family structure over the past generation, the costs and benefits of economic inequality, the extent to which economic advantages are inherited an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larry Lezotte
Lawrence W. "Larry" Lezotte is an American educational researcher, consultant, and speaker, notable for his expertise on creating effective K-12 schools. Education and career Lezotte earned his bachelor's and master's degrees at Western Michigan University, and his doctorate at Michigan State University (MSU) in 1969. He joined the MSU faculty and taught there for 18 years. Lezotte went on to found Effective Schools Products, a consulting and publishing firm in Okemos, Michigan. He has written widely on effective schools, and speaks across North America. Research Lezotte's early research was in response to the controversial 1966 Coleman Report, which concluded that family background was the major determinant of student achievement. Between 1974 and 1976, Lezotte and Wilbur B. Brookover conducted studies at eight Michigan elementary schools, identifying characteristics of schools that were improving or declining. A notable finding was that "staff in the declining schools had low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ronald Edmonds
Ronald R. Edmonds (May 24, 1935 – July 15, 1983) was an American educator, author, and pioneer of effective schools research. Early life and career Edmonds was born in Ypsilanti, Michigan. He received a B.A. in American history from the University of Michigan, an M.A. in American history from Eastern Michigan University, and a certificate of advanced study from Harvard Graduate School of Education. Edmonds began his career as a teacher at Pioneer High School in Ann Arbor, Michigan in 1964. He was a faculty member at the University of Michigan's Labor School from 1968–1970, and Director of the Center for Urban Studies in Harvard’s graduate education program from 1973–1977. From 1981 until his death in 1983, Edmonds was a professor in the Department of Teacher Education at Michigan State University. Edmonds served as assistant superintendent with the Michigan Department of Public Instruction from 1970–1972, and senior assistant for instruction with New York City Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
District Of Columbia Public Schools
The District of Columbia Public Schools (DCPS) is the local public school system for the District of Columbia, in the United States. It is distinct from the District of Columbia Public Charter Schools (DCPCS), which governs public charter schools in the city. Composition and enrollment It is the sole public school district in the District of Columbia. As of 2013, the District of Columbia Public Schools (DCPS) consisted of 111 of the 238 public elementary and secondary schools and learning centers in Washington, D.C. These schools span prekindergarten to twelfth grade. As of 2000, kindergarten students entered at 5 years old. School is compulsory for DCPS students between the ages of 5 and 18. DCPS schools typically start the last Monday in August. The school day generally lasts for about six hours. The ethnic breakdown of students enrolled in 2014 was 67% Black, 17% Hispanic (of any race), 12% non-Hispanic White, and 4% of other races. As of 2014, the District itself ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Research
Educational research refers to the systematic collection and analysis of data related to the field of education. Research may involve a variety of methods and various aspects of education including student learning, teaching methods, teacher training, and classroom dynamics. Educational researchers generally agree that research should be rigorous and systematic. However, there is less agreement about specific standards, criteria and research procedures. As a result, the value and quality of educational research has been questioned. Educational researchers may draw upon a variety of disciplines including psychology, economics, sociology, anthropology, and philosophy. Methods may be drawn from a range of disciplines. Conclusions drawn from an individual research study may be limited by the characteristics of the participants who were studied and the conditions under which the study was conducted. General characteristics Gary Anderson outlined ten aspects of educational research: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |