|
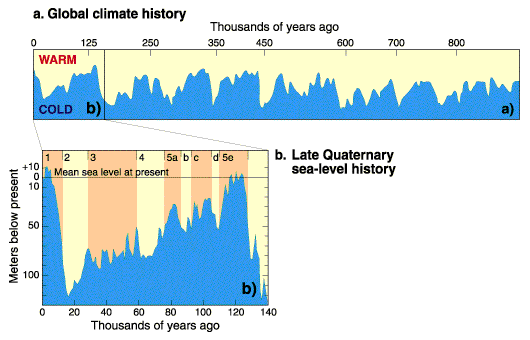
Eemian Sea
The Eemian Sea was a body of water located approximately where the Baltic Sea is now during the last interglacial, or Eemian Stage, Marine isotopic stage (MIS) 5e, roughly 130,000 to 115,000 years BP. Sea level was 5 to 7 metres higher globally than it is today, due to the release of glacial water in the early stage of the interglacial. Although “Eemian” rightly applies only to the northern European glacial system, some scientists use the term in a wider sense to mean any high-level body of water in the last interglacial. The early Eemian Sea connected with the White Sea along the line of the present White Sea-Baltic Canal. Karelia was inundated and Lakes Ladoga and Onega were mere depressions in the shallow eastern end of the Eemian sea. At the other end the sea connected to the North Sea more broadly than it presently does. Much of northern Europe was under shallow water. Scandinavia was an island. The salinity of the Eemian Sea was comparable to that of the Atlantic. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The " Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corylus
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . though some botanists split the hazels (with the hornbeams and allied genera) into a separate family Corylaceae. The fruit of the hazel is the hazelnut. Hazels have simple, rounded leaves with double-serrate margins. The flowers are produced very early in spring before the leaves, and are monoecious, with single-sex catkins. The male catkins are pale yellow and long, and the female ones are very small and largely concealed in the buds, with only the bright-red, 1-to-3 mm-long styles visible. The fruits are nuts long and 1–2 cm diameter, surrounded by an involucre (husk) which partly to fully encloses the nut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Littorina Sea
Littorina Sea (also Litorina Sea) is a geological brackish water stage of the Baltic Sea, which existed around 7500–4000 BP and followed the Mastogloia Sea, a transitional stage of the Ancylus Lake. This stage and form of the body of water is named after common periwinkle (''Littorina littorea''), then a prevailing mollusc in the waters, which indicates its salinity. A transgression of the Baltic approximately 4500 BP widened its ocean link, allowing it to reach a peak of salinity during the warmer Atlantic period of European climatology. At this peak, the sea bore twice the volume of water and covered 26.5% more land than it does today. As the period ended, the features of the modern coast appeared, including lagoons, spits, and dunes. Notable exceptions include steep terraces such as the Øresund where the recession of sea level exposes less dry land. During the period, temperate deciduous forest Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastogloia Sea
The Mastogloia Sea is one of the prehistoric stages of the Baltic Sea in its development after the last ice age. This took place 8000 years ago following the Ancylus Lake stage and preceding the Littorina Sea stage. Overview Towards its demise, the Ancylus Lake was falling, having partly eroded and scouring away at its new outlet at the Great Belt. It reached sea level 8500 years ago, making it the Mastogloia Sea. At this time global sea level was rising rapidly due to the melting of vast tracts of the great ice age ice sheets. As a result, some sea (salt) water started to penetrate into the basin through the Danish straits, mixing into the vast freshwater body. This led to the stage's slightly brackish conditions in the Baltic. This phase of the body of water takes its name from the brackish water-dwelling diatom genus ''Mastogloia'', the species of which are characteristic of the geological deposits of this stage. Continuing sea level rise during this stage deepened the stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancylus Lake
Ancylus Lake is a name given by geologists to a large freshwater lake that existed in northern Europe approximately from 9500 to 8000 years B.C being in effect one of various predecessors to the modern Baltic Sea. Origin, evolution and demise The Ancylus Lake replaced the Yoldia Sea after the latter had been severed from its saline intake across a seaway along the Central Swedish lowland, roughly between Gothenburg and Stockholm. The cutoff was the result of isostatic rise being faster than the concurrent post-glacial sea level rise. In the words of Svante Björck the Ancylus Lake "is perhaps the most enigmatic (and discussed) of the many Baltic stages". The lake's outlet and elevation relative to sea-level was for long time surrounded by controversy. It is now known that the lake was above sea level, included Lake Vänern, and drained westward through three outlets at Göta Älv, Uddevalla and Otteid. As result of the continued isostatic uplift of Sweden, the outlets in cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoldia Sea
Yoldia Sea is a name given by geologists to a variable brackish water stage in the Baltic Sea basin that prevailed after the Baltic Ice Lake was drained to sea level during the Weichselian glaciation. Dates for the Yoldia sea are obtained mainly by radiocarbon dating material from ancient sediments and shore lines and from clay-varve chronology. They tend to vary by as much as a thousand years, but a good estimate is 10,300 – 9500 radiocarbon years BC, equivalent to ca 11,700–10,700 calendar years BC. The sea ended gradually when isostatic rise of Scandinavia closed or nearly closed its effluents, altering the balance between saline and fresh water. The Yoldia Sea became Ancylus Lake. The Yoldia Sea stage had three phases of which only the middle phase had brackish water. The name of the sea is adapted from the obsolete name of the bivalve, ''Portlandia arctica'' (previously known as ''Yoldia arctica''), found around Stockholm. This bivalve requires cold saline water. It cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Ice Lake
The Baltic Ice Lake is a name given by geologists to a freshwater lake that evolved in the Baltic Sea basin as glaciers retreated from that region at the end of the last ice age. The lake existed between 12,600 and 10,300 years Before Present (BP). The Baltic Ice Lake is one of a number of water stages that eventually resulted in the modern Baltic Sea. After the Baltic Ice Lake came the Yoldia Sea (10,300–9,500 BP), the Ancylus Lake (9,500–8,000 BP), the Mastogloia Sea (8,000–7,500 BP), the Littorina Sea (7,500–4,000 BP) and finally the Baltic Sea (4,000 BP–present day). Phenomena related to ice lake and sea formation The term lake is used to mean a body of primarily fresh water. A sea is filled with brackish or salt water. In the history of the Baltic Sea, the distinction is not always clear. Salinity has varied with location, depth and time. The main factors are the advance or recession of the Scandinavian glacier and the isostatic sinking of the landforms due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Last Glacial Maximum, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered Northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. The present-day polar ice sheets are relatively young in geol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weichselian
The Weichselian glaciation was the last glacial period and its associated glaciation in northern parts of Europe. In the Alpine region it corresponds to the Würm glaciation. It was characterized by a large ice sheet (the Fenno-Scandian ice sheet) that spread out from the Scandinavian Mountains and extended as far as the east coast of Schleswig-Holstein, northern Poland and Northwest Russia. This glaciation is also known as the Weichselian ice age (german: Weichsel-Eiszeit), Vistulian glaciation, Weichsel or, less commonly, the Weichsel glaciation, Weichselian cold period (''Weichsel-Kaltzeit''), Weichselian glacial (''Weichsel-Glazial''), ''Weichselian Stage'' or, rarely, the Weichselian complex (''Weichsel-Komplex''). In Northern Europe it was the youngest of the glacials of the Pleistocene ice age. The preceding warm period in this region was the Eemian interglacial. The last cold period began about 115,000 years ago and ended 11,700 years ago. Its end corresponds with the end o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '' brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more often expressed as 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (‰), which is a specific grav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |