|
Edward Marshall Hall
Sir Edward Marshall Hall, (16 September 1858 – 24 February 1927) was an English barrister who had a formidable reputation as an orator. He successfully defended many people accused of notorious murders and became known as "The Great Defender". Marshall Hall practised as a barrister in the late Victorian and Edwardian eras, when the public took a great interest in the sensational court cases of the day. Big criminal and civil trials were widely reported on by the popular press on a daily basis. As a consequence, he and other successful barristers of the day became very famous. The widespread belief that he was a much better orator than a lawyer may explain his failure to achieve elevation to the High Court Bench, which was a source of great disappointment to him. Personal life Born in Brighton, the son of the eminent physician Alfred Hall, Marshall Hall was educated at Rugby School and St John's College, Cambridge. Unusually, he left Cambridge after his fourth term to emb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstantial Evidence
Circumstantial evidence is evidence that relies on an inference to connect it to a conclusion of fact—such as a fingerprint at the scene of a crime. By contrast, direct evidence supports the truth of an assertion directly—i.e., without need for any additional evidence or inference. Overview On its own, circumstantial evidence allows for more than one explanation. Different pieces of circumstantial evidence may be required, so that each corroborates the conclusions drawn from the others. Together, they may more strongly support one particular inference over another. An explanation involving circumstantial evidence becomes more likely once alternative explanations have been ruled out. Circumstantial evidence allows a trier of fact to infer that a fact exists. In criminal law, the inference is made by the trier of fact to support the truth of an assertion (of guilt or absence of guilt). Reasonable doubt is tied into circumstantial evidence as that evidence relies on inferen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crumbles Murders
The Crumbles Murders are two separate and unrelated crimes which occurred on a shingle beach located between Eastbourne and Pevensey Bay, England—locally referred to as "the Crumbles"—in the 1920s. The first of these two murders is the 1920 bludgeoning murder of 17-year-old Irene Munro, committed by two men: Jack Field and William Gray. The second murder to occur upon the Crumbles is the 1924 murder of 38-year-old Emily Kaye, who was murdered by her lover, Patrick Mahon. The three perpetrators of the two "Crumbles Murders" were all tried at Lewes assizes before Mr Justice Avory. All three were executed by hanging at Wandsworth Prison. The executioner of all three men was Thomas Pierrepoint. Murder of Irene Munro Background Irene Violet Munro was a 17-year-old typist, employed by a firm of chartered accountants based in Oxford Street, London. In August 1920, Munro informed her mother, Flora, of her intentions to vacation alone in the seaside resort of Eastbourne rathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Sparrow
Gerald Sparrow (1903–1988) was a British lawyer, judge and travel writer. He served on the International Court in Bangkok, Thailand, for over 20 years. He was the president of the Club of Ten, a pro-apartheid organization, and the author of over 40 books. Early life Gerald Sparrow was born in 1903 in Chapel-en-le-Frith, Derbyshire. He attended Sherborne School in Dorset, then Trinity Hall, Cambridge, Trinity Hall, University of Cambridge, where he was the president of the Cambridge Union Society. Career Sparrow practised as a barrister in Manchester in the mid-1920s, then (invited by the Crown Prince) emigrated to Siam (now Thailand), where he was appointed, in 1930 and aged only 26 or 27, as a judge on the International Court (which tried cases involving non-Thais) in Bangkok. He served on the court "for two decades". He was also the author of "over 40 books, mostly about travel". Sparrow was the president of the Club of Ten, a pro-apartheid organization whose members included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Greenwood (solicitor)
Harold Greenwood (1874 – 17 January 1929) was an English solicitor who was accused and acquitted of murdering his wife by arsenic poisoning. He was tried at Carmarthen Assizes in 1920 and defended by Edward Marshall Hall; his case is a rare example of a legal professional being charged with murder. Facts Harold Greenwood, a Yorkshire solicitor, moved to Wales in 1898 where he, his wife Mabel (née Bowater) and their four children lived comfortably with domestic staff, in Kidwelly, Carmarthenshire. Mabel was not in good health and on 16 June 1919, complained of stomach pains after eating a gooseberry pie for lunch; "it always disagrees with me", she said. Greenwood gave her brandy, which caused her to vomit, and Dr Griffiths was summoned and dispensed medication. By the early hours of the 17th, however, she had died and the cause of death was certified by Griffiths as heart disease. Within a few months of her funeral, Greenwood married Gladys Jones, who was much younger th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solicitor
A solicitor is a legal practitioner who traditionally deals with most of the legal matters in some jurisdictions. A person must have legally-defined qualifications, which vary from one jurisdiction to another, to be described as a solicitor and enabled to practise there as such. For example, in England and Wales a solicitor is admitted to practise under the provisions of the Solicitors Act 1974. With some exceptions, practising solicitors must possess a practising certificate. There are many more solicitors than barristers in England; they undertake the general aspects of giving legal advice and conducting legal proceedings. In the jurisdictions of England and Wales and in Northern Ireland, in the Australian states of New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland, Hong Kong, South Africa (where they are called '' attorneys'') and the Republic of Ireland, the legal profession is split between solicitors and barristers (called ''advocates'' in some countries, for example Scotlan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Bernard Spilsbury
Sir Bernard Henry Spilsbury (16 May 1877 – 17 December 1947) was a British pathologist. His cases include Hawley Crippen, the Seddon case, the Major Armstrong poisoning, the "Brides in the Bath" murders by George Joseph Smith, the Crumbles murders, the Podmore case, the Sidney Harry Fox matricide, the Vera Page case, and the murder trials of Louis Voisin, Jean-Pierre Vaquier, Norman Thorne, Donald Merrett, Alfred Rouse, Elvira Barney, Toni Mancini, and Gordon Cummins. Spilsbury's courtroom appearances became legendary for his demeanour of effortless dominance. He also played a crucial role in the development of Operation Mincemeat, a deception operation during the Second World War which saved thousands of lives of Allied service personnel. Spilsbury died by suicide in 1947. Personal life Spilsbury was born on 16 May 1877 at 35 Bath Street, Leamington Spa, Warwickshire. He was the eldest of the four children of James Spilsbury, a manufacturing chemist, and his wife, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Joseph Smith
George Joseph Smith (11 January 1872 – 13 August 1915) was an English serial killer and bigamist who was convicted and subsequently hanged for the murders of three women in 1915, the case becoming known as the Brides in the Bath Murders. As well as being widely reported in the media, the case was significant in the history of forensic pathology and detection. It was also one of the first cases in which similarities between connected crimes were used to prove deliberation, a technique used in subsequent prosecutions. Early life and marriages The son of an insurance agent, George Joseph Smith was born in Bethnal Green, London. He was sent to a reformatory at Gravesend, Kent, at age 9 and later served time for swindling and theft. In 1896, Smith was imprisoned for twelve months for persuading a woman to steal from her employers. He used the proceeds to open a baker's shop in Leicester. In 1898, under the alias George Oliver Love, Smith married Caroline Beatrice Thornhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but only the gray form, which has a metallic appearance, is important to industry. The primary use of arsenic is in alloys of lead (for example, in car batteries and ammunition). Arsenic is a common n-type dopant in semiconductor electronic devices. It is also a component of the III-V compound semiconductor gallium arsenide. Arsenic and its compounds, especially the trioxide, are used in the production of pesticides, treated wood products, herbicides, and insecticides. These applications are declining with the increasing recognition of the toxicity of arsenic and its compounds. A few species of bacteria are able to use arsenic compounds as respiratory metabolites. Trace quantities of arsenic are an essential dietary element in r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense. Whether something is considered a poison may change depending on the amount, the circumstances, and what living things are present. Poisoning could be accidental or deliberate, and if the cause can be identified there may be ways to neutralise the effects or minimise the symptoms. In biology, a poison is a chemical substance causing death, injury or harm to organisms or their parts. In medicine, poisons are a kind of toxin that are delivered passively, not actively. In industry the term may be negative, something to be removed to make a thing safe, or positive, an agent to limit unwanted pests. In ecological terms, poisons introduced into the environment can later cause unwanted effects elsewhere, or in other parts of the food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Seddon
Frederick Henry Seddon (sometimes spelled Sedden) (21 January 1872 – 18 April 1912) was a British murderer hanging, hanged in 1912 for the arsenic poisoning murder of his lodger Eliza Mary Barrow. Background Frederick Seddon was born in Liverpool to William Seddon and Mary Ann (Married and maiden names, née Kennen) on 21 January 1872. He married Margaret Ann (''née'' Jones) (1878–1946) on 31 December 1893, and had five children with her: William James Seddon (b. 1894); Margaret Seddon (b. 1896); Frederick Henry Seddon Jr (b. 1897); Ada Seddon (b. 1905), and Lilian Louisa Agnes Emma Seddon (b. 1911). His father also lived with him. The names of William and Frederick Seddon appear in the visitors' book for the Metropolitan Police Black Museum, Crime Museum on 1 December 1905; the museum was not open to the general public and the reason for their visit is unknown. At one time Seddon had been a Freemasonry, Freemason, being initiated into Liverpool's Stanley Lodge No. 1325 in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
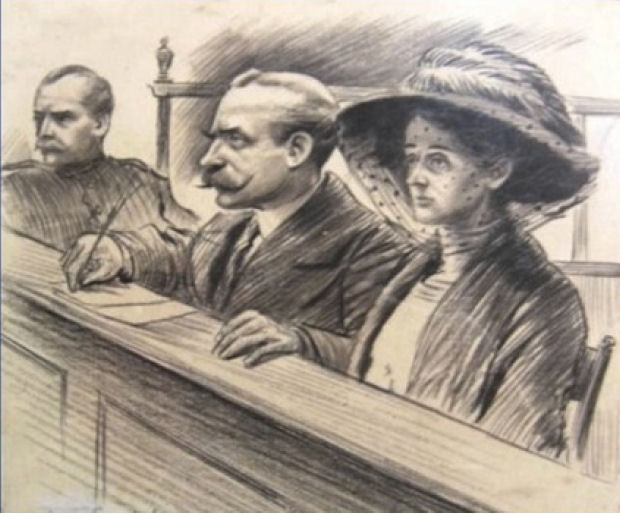
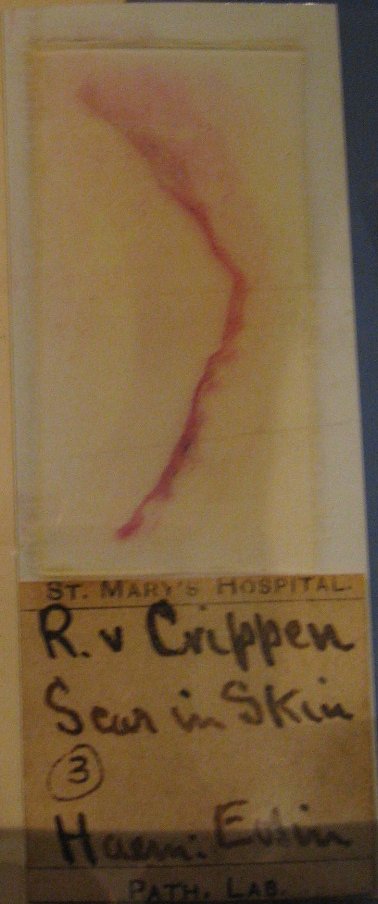
Dr Crippen
Hawley Harvey Crippen (September 11, 1862 – November 23, 1910), usually known as Dr. Crippen, was an American homeopath, ear and eye specialist and medicine dispenser. He was hanged in Pentonville Prison in London for the murder of his wife Cora Henrietta Crippen. Crippen was one of the first criminals to be captured with the aid of wireless telegraphy. Early life and career Crippen was born in Coldwater, Michigan, to Andresse Skinner (1835-1909) and Myron Augustus Crippen (1835-1910), a merchant."Hawley Harvey Crippen"''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography''/ref> Crippen studied first at the University of Michigan Homeopathic Medical School and graduated from the Cleveland Homeopathic Medical College in 1884. Crippen's first wife, Charlotte, died of a stroke in 1892, and Crippen entrusted his parents, living in California, with the care of his son, Hawley Otto (1889-1974). Having qualified as a homeopath, Crippen started to practice in New York, where in 1894 he married h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |