|
Edward Bonaventure
''Edward Bonaventure'' was an English ship under the command of Richard Chancellor that was forced to seek shelter in 1553 on the north coast of Russia near Nyonoksa due to weather conditions, leading to its crew coming into contact with the court of Ivan the Terrible, the forming of the Muscovy Company, and diplomatic contacts between Elizabeth I of England and Ivan of Russia. English trade with Russia In 1553, ''Edward'' was one of a fleet of three ships under the command of Sir Hugh Willoughby, the other two ships were the command ship ''Bona Esperanza'' with Willoughby on it and the ''Bona Confidentia'' with its captain Cornelius Durforth. The fleet was financed by London's Company of Merchant Adventurers to New Lands and it was organized by Sebastian Cabot with the purpose of finding the northeastern passage to the Far East and left London on 10 May 1553. Richard Chancellor was the pilot for the voyage. The opening of the northeastern passage from England to India was desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Chancellor
Richard Chancellor (died 10 November 1556) was an English explorer and navigator; the first to penetrate to the White Sea and establish relations with the Tsardom of Russia. Life Chancellor, a native of Bristol, was brought up in the household of Sir Henry Sidney, an influential English gentleman. In 1550 Chancellor sailed as an apprentice pilot to the eastern Mediterranean in the bark ''Aucher'' commanded by Roger Bodenham.McDermott 2004 Hakluyt ''Voyages'' He acquired additional geographical and maritime proficiency from the explorer Sebastian Cabot and the geographer John Dee. Cabot had always been interested in making a voyage to Asia through the Arctic, and for this purpose an association of London merchants chartered the Company of Merchant Adventurers in 1552–1553, with the Duke of Northumberland as principal patron. They hoped not only to discover a north-east passage but also to find a market for English woolen cloth.Evans 2014 Sir Hugh Willoughby was given three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Production
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantities in seawater. The open ocean has about of solids per liter of sea water, a salinity of 3.5%. Salt is essential for life in general, and saltiness is one of the basic human tastes. Salt is one of the oldest and most ubiquitous food seasonings, and is known to uniformly improve the taste perception of food, including otherwise unpalatable food. Salting, brining, and pickling are also ancient and important methods of food preservation. Some of the earliest evidence of salt processing dates to around 6,000 BC, when people living in the area of present-day Romania boiled spring water to extract salts; a salt-works in China dates to approximately the same period. Salt was also prized by the ancient Hebrews, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Of England
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
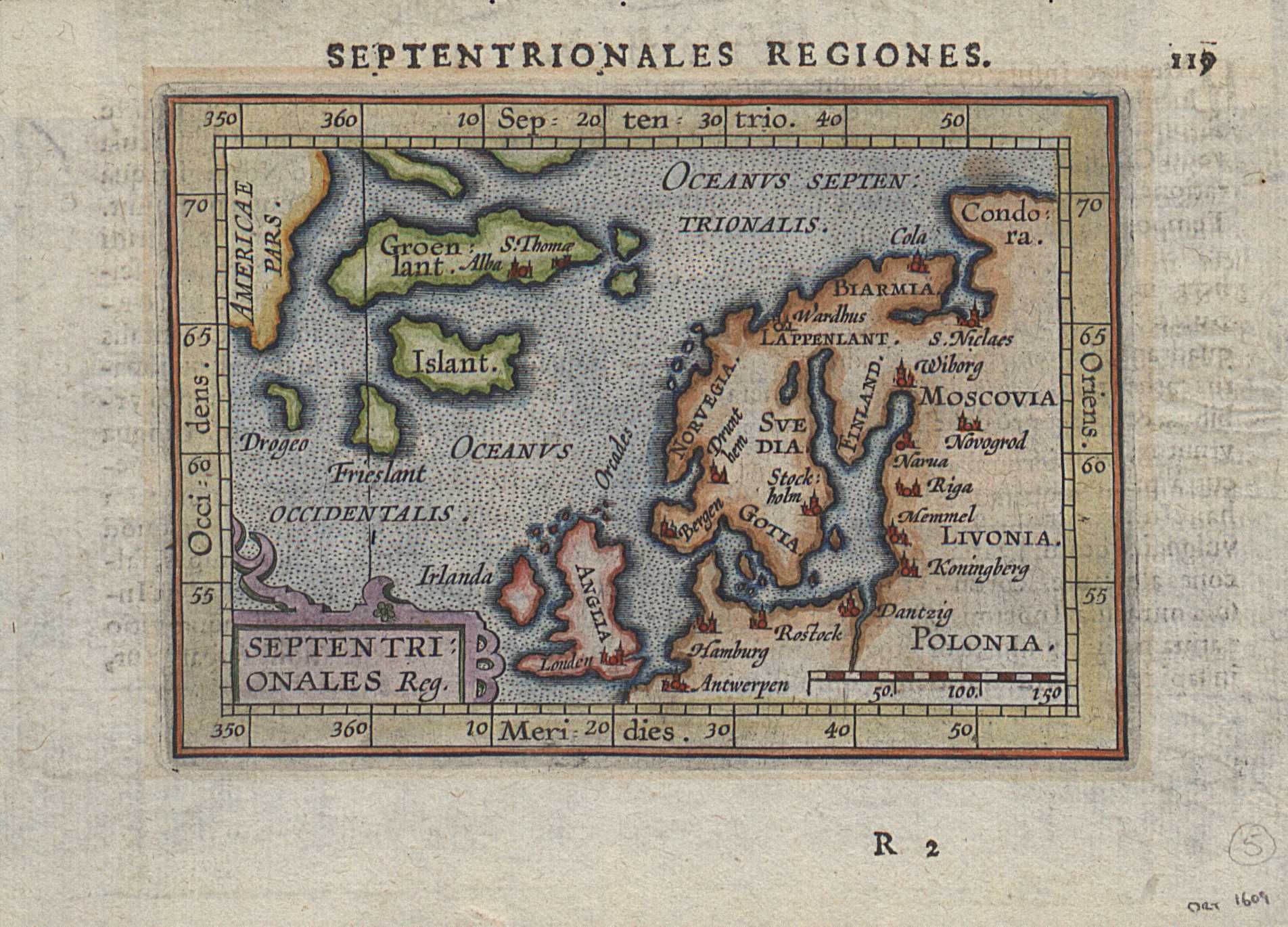
Arkhangelsk
Arkhangelsk (, ; rus, Арха́нгельск, p=ɐrˈxanɡʲɪlʲsk), also known in English as Archangel and Archangelsk, is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina near its mouth into the White Sea. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river and numerous islands of its river delta, delta. Arkhangelsk was the chief seaport of medieval and early modern Russia until 1703, when it was replaced by the newly-founded Saint Petersburg. A Northern Railway (Russia), railway runs from Arkhangelsk to Moscow via Vologda and Yaroslavl, and air travel is served by the Talagi Airport and the smaller Vaskovo Airport. As of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census, the city's population was 301,199. Coat of arms The arms of the city display the Michael (archangel), Archangel Michael in the act of defeating the Devil. Legend states that this victory took place near where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kola, Russia
Kola (russian: Ко́ла; se, Guoládat; sms, Kuâlõk) is a town and the administrative center of Kolsky District of Murmansk Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Kola and Tuloma Rivers, south of Murmansk and southwest of Severomorsk. It is the oldest town of the Kola Peninsula. Population: 11,060 ( 2002 Census); History The district of Kolo was first attested in Russian chronicles in 1264. The first documented mention of the town itself dates to 1565—''Administrative-Territorial Division of Murmansk Oblast'', pp. 18–19 the area was settled by the Pomors, who built the fort of Kola also called ''Malmus'' (russian: Мальмус). Over time, Sweden extracted the Kola Peninsula from both Russia and Denmark-Norway in a series of wars and resulting treaties.''A Short History of Finland'', pp. 36–37 However, in the later Treaty of Teusina in 1595, Sweden acknowledged Russian rights in Kola. Claims from Denmark-Norway remained, however, and in 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Jenkinson
Anthony Jenkinson (1529 – 1610/1611) was born at Market Harborough, Leicestershire. He was one of the first Englishmen to explore Muscovy and present-day Russia. Jenkinson was a traveller and explorer on behalf of the Muscovy Company and the English crown. He also met Ivan the Terrible several times during his trips to Moscow and Russia. He detailed the accounts of his travel through several written works over his life. Family life Anthony Jenkinson's father, William Jenkinson, was a man of great property and wealth. Anthony Jenkinson was thus trained in his earlier years for a mercantile career. By the year 1568, Jenkinson had become a pivotal researcher for the Muscovy Company. On 26 January 1568 Jenkinson married his wife Judith Marshe, daughter of John Marshe and his wife Alice. Marshe had extensive business ties, including being one of the founding members of the Company. Jenkinson thus benefited greatly through these financial ties. Jenkinson and his wife h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, and was the fourth largest urban area. Trondheim lies on the south shore of Trondheim Fjord at the mouth of the River Nidelva. Among the major technology-oriented institutions headquartered in Trondheim are the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU), the Foundation for Scientific and Industrial Research (SINTEF), and St. Olavs University Hospital. The settlement was founded in 997 as a trading post, and it served as the capital of Norway during the Viking Age until 1217. From 1152 to 1537, the city was the seat of the Catholic Archdiocese of Nidaros; it then became, and has remained, the seat of the Lutheran Diocese of Nidaros, and the site of the Nidaros Cathedral. It was incorporated in 1838. The current municipalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosehearty
Rosehearty ( gd, Ros Abhartaich) is a settlement on the Moray Firth coast, four miles west of the town Fraserburgh, in the historical county of Aberdeenshire in Scotland. The burgh has a population of approximately 1,300 with about 25 per cent of pensionable age. Etymology The name ''Rosehearty'' was documented in 1508 as Rossawarty and is derived from Gaelic ''ros'', meaning "cape, headland", and the personal name ''Abhartach''. History The settlement which is now Rosehearty was founded by a group of shipwrecked Danes in the 14th century.''Ordnance Gazetteer of Scotland: A Graphic and Accurate Description of Every Place in Scotland'' Frances Hindes Groome (1901), p. 1383 In 1424 the Fraser family built |
Pechenga Monastery
The Pechenga Monastery (russian: Печенгский монастырь; fi, Petsamon luostari) was for many centuries the northernmost monastery in the world. It was founded in 1533 at the influx of the Pechenga River into the Barents Sea, 135 km west of modern Murmansk, by St. Tryphon, a monk from Novgorod. Inspired by the model of the Solovki, Tryphon wished to convert the local Skolts to Christianity and to demonstrate how faith could flourish in the most inhospitable lands. His example was eagerly followed by other Russian monks. By 1572, the Pechenga Monastery counted about 50 brethren and 200 lay followers. Six years after St. Tryphon's death in 1583, the wooden monastery was raided and burnt down by the Swedes on December 25, 1589. It is said that the raid claimed the lives of 51 monks and 65 lay brothers, bringing the history of Tryphon's establishment to an end. This revenge raid, and was part of the Russo-Swedish War of 1590–1595, is said to have been carried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwood Publishing Group
Greenwood Publishing Group, Inc. (GPG), also known as ABC-Clio/Greenwood (stylized ABC-CLIO/Greenwood), is an educational and academic publisher (middle school through university level) which is today part of ABC-Clio. Established in 1967 as Greenwood Press, Inc. and based in Westport, Connecticut, GPG publishes reference works under its Greenwood Press imprint, and scholarly, professional, and general interest books under its related imprint, Praeger Publishers (). Also part of GPG is Libraries Unlimited, which publishes professional works for librarians and teachers. History 1967–1999 The company was founded as Greenwood Press, Inc. in 1967 by Harold Mason, a librarian and antiquarian bookseller, and Harold Schwartz who had a background in trade publishing. Based in Greenwood, New York, the company initially focused on reprinting out-of-print works, particularly titles listed in the American Library Association's first edition of ''Books for College Libraries'' (1967), unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
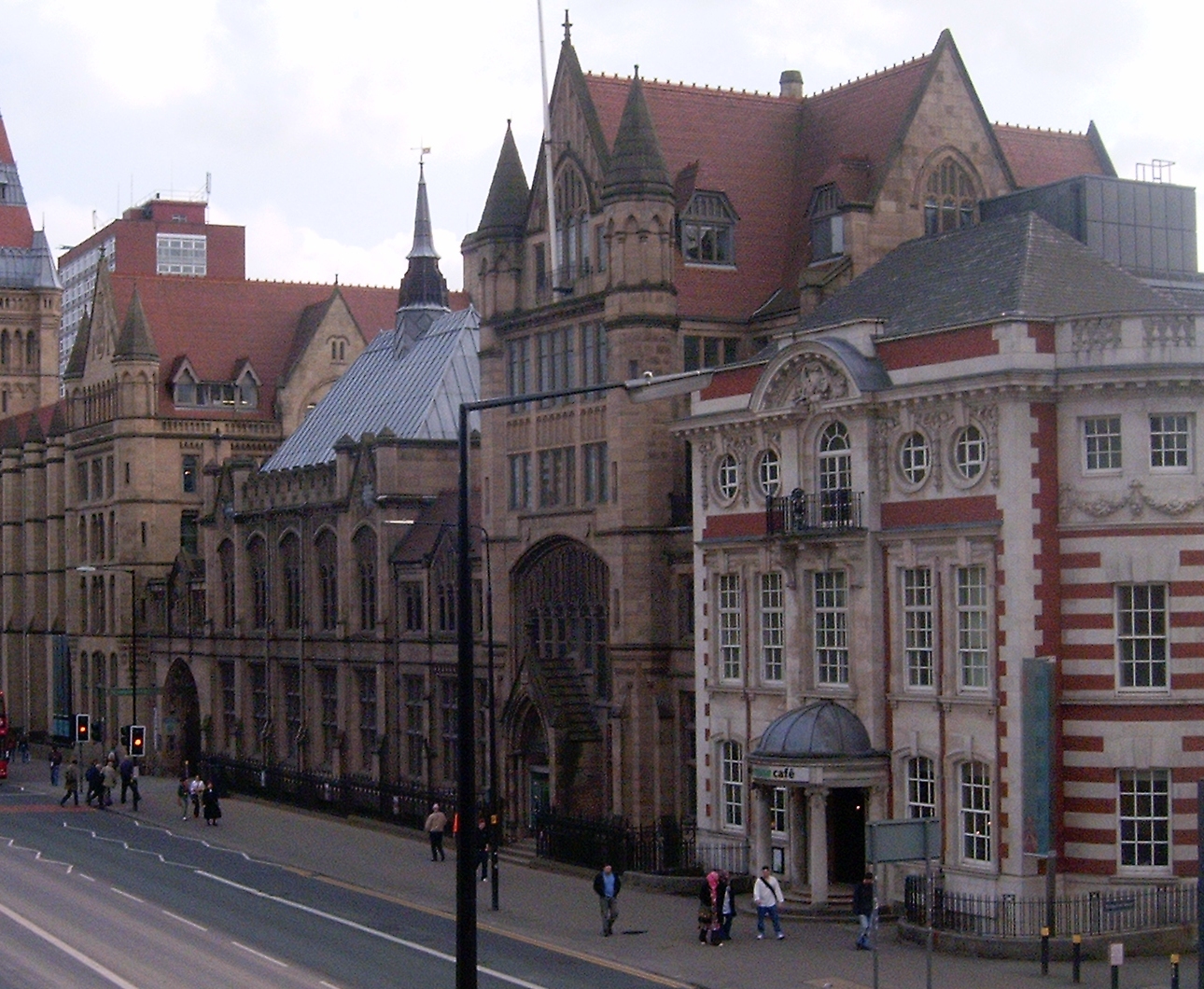
Manchester University Press
Manchester University Press is the university press of the University of Manchester, England and a publisher of academic books and journals. Manchester University Press has developed into an international publisher. It maintains its links with the University. Publishing Manchester University Press publishes monographs and textbooks for academic teaching in higher education. In 2012 it was producing about 145 new books annually and managed a number of journals. Areas of expertise are history, politics and international law, literature and theatre studies, and visual culture. MUP books are marketed and distributed by Oxford University Press in the United States and Canada, and in Australia by Footprint Books; all other global territories are covered from Manchester itself. Some of the press's books were formerly published in the US by Barnes & Noble, Inc., New York. Later the press established an American office in Dover, New Hampshire. Open access Manchester University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |