|
Edo Clan
The Edo clan were a minor offshoot of the Taira clan, and first fortified the settlement known as Edo, which would later become Tokyo. The Imperial Palace now stands at this location.Time Out Tokyo edited by Cathy Phillips, page 11 During the Azuchi‚ÄďMomoyama period, the clan was renamed the Kitami clan. History The clan originated in Chichibu in Musashi Province (now Saitama Prefecture). In the late 12th century, Edo Shigetsugu moved south and fortified the little hill at Edo, located where the Sumida River enters Tokyo Bay. This area later became the Honmaru and Ninomaru portions of Edo Castle. There, the Edo grew in military strength under the second patriarch, Edo Shigenaga. In August 1180, Shigenaga attacked Muira Yoshizumi, an ally of the rival Minamoto clan. Three months later, he switched sides just as Minamoto no Yoritomo entered Musashi. Shigenaga assisted the Minamoto in overthrowing the Taira clan in Kyoto. In return, Yoritomo granted Shigenaga seven new es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taira Clan
The Taira was one of the four most important clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian, Kamakura and Muromachi Periods of Japanese history ‚Äď the others being the Fujiwara, the Tachibana, and the Minamoto. The clan is divided into four major groups, named after the emperor they descended from: Kanmu Heishi, NinmyŇć Heishi, Montoku Heishi, and KŇćkŇć Heishi. The clan is commonly referred to as or , using the character's On'yomi for ''Taira'', while means " clan", and is used as a suffix for "extended family". History Along with the Minamoto, Taira was one of the honorary surnames given by the emperors of the Heian Period (794‚Äď1185 CE) to their children and grandchildren who were not considered eligible for the throne. The clan was founded when the Imperial Court grew too large, and the emperor ordered that the descendants of previous emperors from several generations ago would no longer be princes, but would instead be given noble surnames and ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minamoto
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were excluded from the line of succession and demoted into the ranks of the nobility from 1192 to 1333. The practice was most prevalent during the Heian period (794‚Äď1185 AD), although its last occurrence was during the Sengoku period. The Taira were another such offshoot of the imperial dynasty, making both clans distant relatives. The Minamoto clan is also called the , or less frequently, the , using the on'yomi reading for Minamoto. The Minamoto were one of four great clans that dominated Japanese politics during the Heian period‚ÄĒthe other three were the Fujiwara, the Taira, and the Tachibana. History The first emperor to grant the surname Minamoto was Minamoto no Makoto, seventh son of Emperor Saga. The most prominent of the several Minamoto families, the Seiwa Genji, descended from Minamoto no Tsunemoto (897‚Äď961), a grandson of Emperor Seiwa. Tsunemoto went to the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
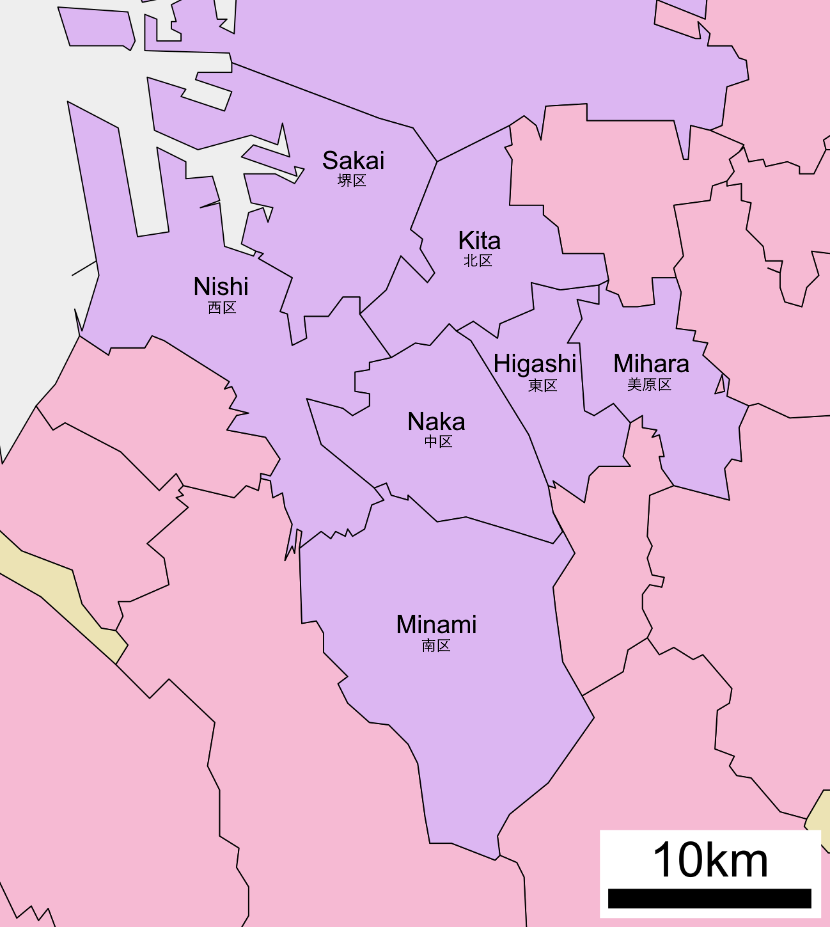
Sakai, Osaka
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its keyhole-shaped burial mounds, or kofun, which date from the fifth century and include Daisen Kofun, the largest grave in the world by area. Once known for swords, Sakai is now famous for the quality of its cutlery. , the city had an estimated population of 819,965, making it the fourteenth most populous city in Japan (excluding Tokyo). Geography Sakai is located in southern Osaka Prefecture, on the edge of Osaka Bay and directly south of the city of Osaka. Neighboring municipalities Osaka Prefecture *Osaka * Matsubara *Habikino *ŇĆsakasayama *Kawachinagano * Izumi * Takaishi Climate Sakai has a Humid subtropical climate (K√∂ppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sakai is . The average annual rainfall is with June as the wettest month ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese Śĺ≥Ś∑ĚŚĻēŚļú ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Fr√©d√©ric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 978.Nussbaum"''Edo-jidai''"at p. 167. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shŇćgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyŇć'' lords of the ''samurai'' class.Nussbaum"Tokugawa"at p. 976. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of ''Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyŇć'' administering a ''han'' (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitami
is a Cities of Japan, city in Okhotsk Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the most populous city and the commercial center in the subprefecture, although the subprefecture capital is Abashiri, Hokkaido, Abashiri. Kitami is physically in the middle of Okhotsk Subprefecture. The Kitami Mountains are nearby and are the main reason behind the city's name. The city is the result of the merger of Kitami, Tanno, Hokkaido, Tanno, Tokoro, Hokkaido, Tokoro and Rubeshibe, Hokkaido, Rubeshibe towns in 2006 administrative reform. Kitami developed mainly in commerce and industry/service industries, Tanno in agriculture, Tokoro in fishery and agriculture, and Rubeshibe in forestry and tourism on hot springs. Due to the characteristics of the region, Kitami has the highest onion and white flower bean production in Japan. Scallop fishing also flourishes, which makes it the "birthplace of scallop farming" in the country. In addition, the region is home to historical and tourist places like t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Katsutada
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo. Edo, formerly a ''jŇćkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of Japan from 1603 as the seat of the Tokugawa shogunate. Edo grew to become one of the largest cities in the world under the Tokugawa. After the Meiji Restoration in 1868 the Meiji government renamed Edo as ''Tokyo'' (, "Eastern Capital") and relocated the Emperor from the historic capital of Kyoto to the city. The era of Tokugawa rule in Japan from 1603 to 1868 is known eponymously as the Edo period. History Before Tokugawa Before the 10th century, there is no mention of Edo in historical records, but for a few settlements in the area. Edo first appears in the Azuma Kagami chronicles, that name for the area being probably used since the second half of the Heian period. Its development started in late 11th century with a branch of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shŇćgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fellow Oda subordinate Toyotomi Hideyoshi. The son of a minor daimyo, Ieyasu once lived as a hostage under daimyo Imagawa Yoshimoto on behalf of his father. He later succeeded as daimyo after his father's death, serving as a vassal and general of the Oda clan, and building up his strength under Oda Nobunaga. After Oda Nobunaga's death, Ieyasu was briefly a rival of Toyotomi Hideyoshi, before declaring his allegiance and fighting on his behalf. Under Toyotomi, Ieyasu was relocated to the Kanto plains in eastern Japan, away from the Toyotomi power base in Osaka. He built his castle in the fishing village of Edo (now Tokyo). He became the most powerful daimyo and the most senior officer under the Toyotomi regime. Ieyasu preserved his strength i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashikaga Clan
The was a prominent Japanese samurai clan which established the Muromachi shogunate and ruled Japan from roughly 1333 to 1573. The Ashikaga were descended from a branch of the Minamoto clan, deriving originally from the town of Ashikaga in Shimotsuke Province (modern-day Tochigi Prefecture). For about a century the clan was divided in two rival branches, the KantŇć Ashikaga, who ruled from Kamakura, and the KyŇćto Ashikaga, rulers of Japan. The rivalry ended with the defeat of the first in 1439. The clan had many notable branch clans, including the Hosokawa, Imagawa, Hatakeyama (after 1205), Kira , Shiba, and Hachisuka clans. After the head family of the Minamoto clan died out during the early Kamakura period, the Ashikaga came to style themselves as the head of the Minamoto, co-opting the prestige which came with that name. Another Ashikaga clan, not related by blood, and derived instead from the Fujiwara clan, also existed. History Emperor Go-Daigo ŚĺĆťÜćťÜźŚ§©Áöá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanrei
or, more rarely, ''kanryŇć'', was a high political post in feudal Japan; it is usually translated as ''shŇćguns deputy''. After 1349, there were actually two ''Kanrei'', the ''Kyoto Kanrei'' and the ''KantŇć Kanrei''. Originally, from 1219 until 1333, the post was synonymous with the ''Rokuhara Tandai'', and was based in Kyoto. The HŇćjŇć clan monopolized this post, and there were during this period two Deputies ‚Äď a southern chief, and a northern chief. From 1336 to 1367, the Deputy was called . The first to hold this title was KŇć no Moronao. In 1367, Hosokawa Yoriyuki was chosen by a council to become Deputy (Kyoto ''Kanrei''). In order to ensure the loyalty of his colleagues, the Hatakeyama and Shiba clans, he proposed that three families share the position of ''Kanrei'', alternating between them every time a new appointment was needed. Thus was born the ''San-Kan'' or Three ''Kanrei''. However, in 1379, Yoriyuki's actions attracted the resentment of certain powerful lords, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uesugi Sadamasa
Uesugi (sometimes written ''Uyesugi'') is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: People *Uesugi clan, a Japanese samurai clan **Uesugi Akisada, (1454‚Äď1510), a samurai of the Uesugi clan **Uesugi Harunori (1751‚Äď1822), a Japanese daimyŇć **Uesugi Kagekatsu (1556‚Äď1623), a daimyŇć during the Sengoku and Edo periods of Japanese history **Uesugi Kagenobu (?‚Äď1578), a samurai and relative of Uesugi Kenshin in the Sengoku period of Japan **Uesugi Kagetora (1552‚Äď1579), the seventh son of HŇćjŇć Ujiyasu and adopted son of Uesugi Kenshin **Uesugi Kenshin (1530‚Äď1578), a daimyŇć who ruled Echigo province in the Sengoku period of Japan ** Uesugi Mochinori (1844‚Äď1919), a Japanese samurai of the late Edo period **Uesugi Narinori, (1820‚Äď1889), a Japanese daimyŇć of the Edo period **Uesugi Norimasa (1523‚Äď1579), a daimyŇć of feudal Japan **Uesugi Norizane, (1410‚Äď1466), a Japanese samurai of the Uesugi clan **Uesugi Tomooki, (1488‚Äď1537), a lord of Edo Castle an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uesugi Clan
The is a Japanese samurai clan which was at its peak one of the most powerful during the Muromachi and Sengoku periods (14th to 17th centuries). Appert, Georges. (1888) ''Ancien Japon,'' p. 79./ref> At its height, the clan had three main branches: the ŇĆgigayatsu, Inukake, and Yamanouchi. Its most well-known member is the warlord Uesugi Kenshin (1530‚Äď1578). During the Edo period, the Uesugi were a '' tozama'' or outsider clan, in contrast with the '' fudai'' or insider ''daimyŇć'' clans which had been hereditary vassals or allies of the Tokugawa clan. History The clan claims descent from the Fujiwara clan, specifically Fujiwara no Yoshikado, Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de g√©ographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003).html" ;"title="DF 71 of 80)">"Uesugi", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 67 [PDF 71 of 80)/nowiki>">DF 71 of 80)">"Uesugi", ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 67 [PDF 71 of 80)/nowiki> retrieved 2013-5-11. who was a ''daijŇć-daijin'' during t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇĆta DŇćkan
, also known as ŇĆta Sukenaga (Ś§™ÁĒį Ť≥áťē∑) or ŇĆta DŇćkan Sukenaga, was a Japanese ''samurai'' warrior-poet, military tactician and Buddhist monk. ŇĆta Sukenaga took the tonsure (bald scalp) as a Buddhist priest in 1478, and he also adopted the Buddhist name, DŇćkan, by which he is known today.Time Out Magazine, Ltd. (2005 ''Time Out Tokyo,'' p. 11./ref> DŇćkan is best known as the architect and builder of Edo Castle (now the Imperial Palace) in what is today modern Tokyo; and he is considered the founder of the castle town which grew up around that ''ŇĆnin'' era fortress. ŇĆta clan genealogy The ŇĆta clan originated in 15th-century Musashi Province.Appert, Georges ''et al.'' (1888) ''Ancien Japon'', p. 76./ref> They claimed descent from Minamoto no Yorimasa, and through that branch of the Minamoto they claimed kinship with the Seiwa-Genji. Papinot, Edmund. (2003)''Nobiliare du Japon'' -- ŇĆta, pp. 48 Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d'histoire et de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |