|
Edda-Gesellschaft
Armanism and Ariosophy are esoteric ideological systems that were developed largely by Guido von List and Jörg Lanz von Liebenfels respectively, in Austria between 1890 and 1930. The term 'Ariosophy', which means the wisdom of the Aryans, was invented by Lanz von Liebenfels in 1915, and during the 1920s it became the name of his doctrine. For research of the topic, such as Nicholas Goodrick-Clarke's book ''The Occult Roots of Nazism'', the term 'Ariosophy' is used generically to describe the Aryan/esoteric theories of a subset of the ' Völkische Bewegung'. This broader use of the word is retrospective and it was not generally current among the esotericists themselves. List actually called his doctrine 'Armanism', while Lanz used the terms 'Theozoology' and 'Ario-Christianity' before the First World War. The ideas of Von List and Lanz von Liebenfels were part of a general occult revival that occurred in Austria and Germany during the late 19th and early 20th centuries; a revival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolf John Gorsleben
Rudolf John Gorsleben (16 March 1883 – 23 August 1930) was a German Ariosophist, Armanist (practitioner of the Armanen runes), journal editor and playwright. Life Gorsleben was born in Metz. During World War I, he fought in a German unit stationed in the Ottoman Empire. He formed the Edda Society ('' Edda-Gesellschaft'') and wrote the book '' Hoch-Zeit der Menschheit'' ('' The Zenith of Humanity''), first published in 1930. It is known as "The Bible of Armanism" and has been translated into English by Karl Hans Welz. Gorsleben died in Bad Homburg of a chronic heart complaint.Goodrick-Clarke, The Occult Roots of Nazism, p. 159 Quotes *"The healing power of medical drugs is the Ur-power of their original essence in conjunction with the power of Ur-vibrations of the human-Divine combination that is composed of body, soul and spirit." - ''Hoch-Zeit der Menschheit'' (English edition) *"With the introduction of Runic knowledge the generation of our days can achieve the control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Maria Wiligut
Karl Maria Wiligut (alias Weisthor, Jarl Widar, Lobesam; 10 December 1866 – 3 January 1946) was an Austrian occultist and SS-Brigadeführer. Early life Wiligut was baptised a Roman Catholic in Vienna. At the age of 14, he joined the ''Kadettenschule'' there. At the age of 17, he was conscripted to the k.u.k. infantry regiment of Milan I King of Serbia. On 17 December 1883 he was appointed to infantry, four days later he became a Gefreiter (private). In 1888, he was promoted to lieutenant. Career In 1889, he joined the quasi-masonic " Schlaraffia-Loge". He published his first book, ''Seyfrieds Runen'', in 1903, under his real name, as "Karl Maria Wiligut (Lobesam)", mentioning his real and additional artist name. 1908 followed the ''Neun Gebote Gôts'', where Wiligut first claimed to be heir to an ancient tradition of Irminism. During World War I, Wiligut served at the southern and eastern fronts and he was decorated for gallantry. On 1 August 1917, he was promoted to colonel. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
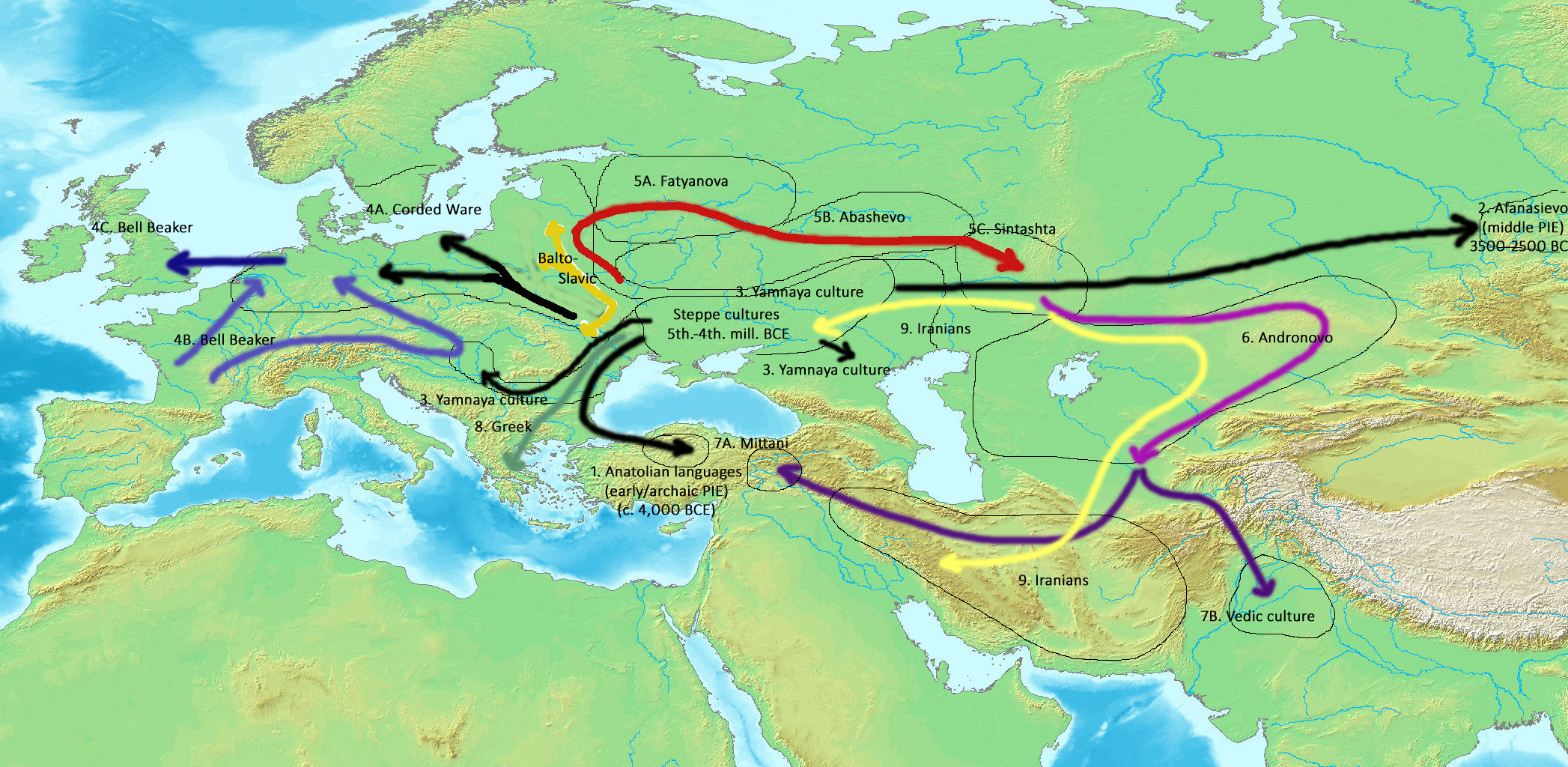
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BC. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eurasia (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia). Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BC) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BC) and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BC, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philipp Stauff
Philipp Stauff (1876–1923) was a prominent German/Austrian journalist and publisher in Berlin. He was an enthusiastic Armanist, a close friend of Guido von List, and a founding member of the Guido-von-List-Society. He was also the obituarist for List in the ''Münchener Beobachter''. Stauff joined the List Society in 1910 and swiftly graduated to the High Armanen Order, the intimate inner circle around List. In 1912 he became a committee member of the List Society and a generous patron. He was the chief German representative of the High Armanen Order at Berlin. His esoteric treatise ''Runenhäuser'' (''Rune Houses''), published in 1912, "extended the Listian thesis of 'armanist' relics with the claim that the ancient runic wisdom had been enshrined in the geometric configuration of beams in half-timbered houses throughout Germany". (See also Runic significance of timber framing.) He was active in both the Reichshammerbund and the Germanenorden (pre-World War I Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religious Aspects Of Nazism
Historians, political scientists and philosophers have studied Nazism with a specific focus on its religious and pseudoreligious, pseudo-religious aspects. It has been debated whether Nazism would constitute a political religion, and there has also been research on the Millenarianism, millenarian, Messianism, messianic, and occult or esoteric aspects of Nazism. Nazism as a political religion Before 1980, the writers who alluded to the religious aspects of Nazism included Aurel Kolnai, Raymond Aron, Albert Camus, Romano Guardini, Denis de Rougemont, Eric Voegelin, George Mosse, Klaus Vondung and Friedrich Heer. Voegelin's work on political religion was first published in German in 1938. Emilio Gentile and Roger Griffin, among others, have drawn on his concept. The French author and philosopher Albert Camus is mentioned here, since he has made some remarks about Nazism as a religion and about Adolf Hitler in particular in ''The Rebel (book), L'Homme révolté''. Nazism and Christi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahnenerbe
The Ahnenerbe (, ''ancestral heritage'') operated as a think tank in Nazi Germany between 1935 and 1945. Heinrich Himmler, the ''Reichsführer-SS'' from 1929 onwards, established it in July 1935 as an SS appendage devoted to the task of promoting the racial doctrines espoused by Adolf Hitler and by his governing Nazi Party. The Ahnenerbe specifically fostered the idea that the modern Germans descended from an ancient Aryan race seen as biologically superior to other racial groups. The group comprised scholars and scientists from a broad range of academic disciplines. Hitler became Chancellor of Germany in 1933, and turned the country into a one-party state under the control of the Nazi Party and governed by his personal dictatorship. He espoused the idea that modern Germans descended from the ancient Aryans, who he claimed—in contrast to established academic understandings of prehistory—had invented most major developments in human history, such as agriculture, art, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Evola
Giulio Cesare Andrea "Julius" Evola (; 19 May 1898 – 11 June 1974) was an Italian philosopher, poet, painter, esotericist, and radical-right ideologue. Evola regarded his values as aristocratic, masculine, traditionalist, heroic, and defiantly reactionary. An eccentric thinker in Fascist Italy, he also had ties to Nazi Germany; in the post-war era, he was known as an ideological mentor of the Italian neo-fascist and militant right. Evola was born in Rome. He served as an artillery officer in the First World War. He became a Dada artist but gave up painting in his twenties. He said he considered suicide until he had a revelation while reading a Buddhist text. In the 1920s he delved into the occult; he wrote on Western esotericism and of Eastern mysticism, developing his doctrine of "magical idealism". His writings blend various ideas of German idealism, Eastern doctrines, traditionalism and the interwar Conservative Revolution, with themes such as Hermeticism, the metaphysic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of the Holocaust. As a member of a reserve battalion during World War I, Himmler did not see active service, and did not fight. He studied agriculture in university, and joined the Nazi Party in 1923 and the SS in 1925. In 1929, he was appointed by Adolf Hitler. Over the next 16 years, he developed the SS from a 290-man battalion into a million-strong paramilitary group, and set up and controlled the Nazi concentration camps. He was known for good organisational skills and for selecting highly competent subordinates, such as Reinhard Heydrich in 1931. From 1943 onwards, he was both Chief of German Police and Minister of the Interior, overseeing all internal and external police and security forces, including the Gestapo (Secret State Police). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzstaffel
The ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS; also stylized as ''ᛋᛋ'' with Armanen runes; ; "Protection Squadron") was a major paramilitary organization under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II. It began with a small guard unit known as the ''Saal-Schutz'' ("Hall Security") made up of party volunteers to provide security for party meetings in Munich. In 1925, Heinrich Himmler joined the unit, which had by then been reformed and given its final name. Under his direction (1929–1945) it grew from a small paramilitary formation during the Weimar Republic to one of the most powerful organizations in Nazi Germany. From the time of the Nazi Party's rise to power until the regime's collapse in 1945, the SS was the foremost agency of security, surveillance, and terror within Germany and German-occupied Europe. The two main constituent groups were the '' Allgemeine SS'' (General SS) and ''Waffen-SS'' (Armed SS). The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadeführer
''Brigadeführer'' (, ) was a paramilitary rank of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) that was used between the years of 1932 to 1945. It was mainly known for its use as an SS rank. As an SA rank, it was used after briefly being known as ''Untergruppenführer'' in late 1929 and 1930. The rank was first created due to an expansion of the SS and assigned to those officers in command of ''SS-Brigaden''. In 1933, the ''SS-Brigaden'' were changed in name to ''SS-Abschnitte''; however, the rank of ''Brigadeführer'' remained the same. Originally, ''Brigadeführer'' was considered the second general officer rank of the SS and ranked between ''Oberführer'' and '' Gruppenführer''. This changed with the rise of the Waffen-SS and the ''Ordnungspolizei''. In both of those organizations, ''Brigadeführer'' was the equivalent to a ''Generalmajor'' and ranked above an ''Oberst'' in the German Army or police. The rank of ''Generalmajor'' was the equivalent of brigadier general, a one-star general in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |