|
Ecological Interface Design
Ecological interface design (EID) is an approach to user interface, interface design that was introduced specifically for complex sociotechnical, real-time, and dynamic systems. It has been applied in a variety of domains including process control (e.g. nuclear power plants, petrochemical plants), aviation, and medicine. EID differs from some interface design methodologies like user-centered design (UCD) in that the focus of the analysis is on the work domain or environment, rather than on the end user or a specific task. The goal of EID is to make constraints and complex relationships in the work environment perceptually evident (e.g. visible, audible) to the user. This allows more of users' cognitive resources to be devoted to higher cognitive processes such as problem solving and decision making. EID is based on two key concepts from cognitive engineering and cognitive systems engineering research: the Abstraction Hierarchy (AH) and the Skills, Rules, Knowledge (SRK) framewor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology. Generally, the goal of user interface design is to produce a user interface that makes it easy, efficient, and enjoyable (user-friendly) to operate a machine in the way which produces the desired result (i.e. maximum usability). This generally means that the operator needs to provide minimal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Task Analysis
Task analysis is the analysis of how a task is accomplished, including a detailed description of both manual and mental activities, task and element durations, task frequency, task allocation, task complexity, environmental conditions, necessary clothing and equipment, and any other unique factors involved in or required for one or more people to perform a given task. Information from a task analysis can then be used for many purposes, such as personnel selection and training, tool or equipment design, procedure design (e.g., design of checklists, or decision support systems) and automation. Though distinct, task analysis is related to user analysis. Safety Critical Task Analysis Safety Critical Task Analysis (SCTA) focuses on how tasks that are critical to major accident risk are performed. SCTA is a crucial assessment designed to predict and understand the role that human error plays in major accidents. This is a type or workshop conducted to support Major Accident Hazard (M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Psychology
Ecological psychology is the scientific study of perception-action from a direct realist approach. Ecological psychology is a school of psychology that follows much of the writings of Roger Barker and James J. Gibson. Those in the field of Ecological Psychology reject the mainstream explanations of perception laid out by cognitive psychology. The ecological psychology can be broken into a few sub categories: perception, action, and dynamical systems. As a clarification, many in this field would reject the separation of perception and action, stating that perception and action are inseparable. These perceptions are shaped by an individual's ability to engage with their emotional experiences in relation to the environment and reflect on and process these. This capacity for emotional engagement leads to action, collective processing, social capital, and pro environmental behaviour. Barker Roger Barker's work was based on his empirical work at the Midwest Field Station. He wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, intelligence, the formation of knowledge, memory and working memory, judgment and evaluation, reasoning and computation, problem solving and decision making, comprehension and production of language. Imagination is also a cognitive process, it is considered as such because it involves thinking about possibilities. Cognitive processes use existing knowledge and discover new knowledge. Cognitive processes are analyzed from different perspectives within different contexts, notably in the fields of linguistics, musicology, anesthesia, neuroscience, psychiatry, psychology, education, philosophy, anthropology, biology, systemics, logic, and computer science. These and other approaches to the analysis of cognition (such as embodied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automaticity
Automaticity is the ability to do things without occupying the mind with the low-level details required, allowing it to become an automatic response pattern or habit. It is usually the result of learning, repetition, and practice. Examples of tasks carried out by 'muscle memory' often involve some degree of automaticity. Examples of automaticity are common activities such as walking, speaking, bicycle-riding, assembly-line work, and driving a car (the last of these sometimes being termed "highway hypnosis"). After an activity is sufficiently practiced, it is possible to focus the mind on other activities or thoughts while undertaking an automatized activity (for example, holding a conversation or planning a speech while driving a car). Characteristics John Bargh (1994), based on over a decade of research, suggested that four characteristics usually accompany automatic behavior: ;Awareness :A person may be unaware of the mental process that is occurring. ;Intentionality :A perso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piaget's Theory Of Cognitive Development
Piaget's theory of cognitive development is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. It was originated by the Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget (1896–1980). The theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come to acquire, construct, and use it. Piaget's theory is mainly known as a developmental stage theory. In 1919, while working at the Alfred Binet Laboratory School in Paris, Piaget "was intrigued by the fact that children of different ages made different kinds of mistakes while solving problems". His experience and observations at the Alfred Binet Laboratory were the beginnings of his theory of cognitive development. He believed that children of different ages made different mistakes because of the “quality rather than quantity” of their intelligence. Piaget proposed four stages to describe the development process of children: sensorimotor stage, pre-operational stage, concrete operational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Compressor
A compressor is a mechanical device that increases the pressure of a gas by reducing its volume. An air compressor is a specific type of gas compressor. Compressors are similar to pumps: both increase the pressure on a fluid and both can transport the fluid through a pipe. The main distinction is that the focus of a compressor is to change the density or volume of the fluid, which is mostly only achievable on gases. Gases are compressible, while liquids are relatively incompressible, so compressors are rarely used for liquids. The main action of a pump is to pressurize and transport liquids. Many compressors can be staged, that is, the fluid is compressed several times in steps or stages, to increase discharge pressure. Often, the second stage is physically smaller than the primary stage, to accommodate the already compressed gas without reducing its pressure. Each stage further compresses the gas and increases its pressure and also temperature (if inter cooling between stages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refrigeration Cycle
Thermodynamic heat pump cycles or refrigeration cycles are the conceptual and mathematical models for heat pump, air conditioning and refrigeration systems. A heat pump is a mechanical system that allows for the transmission of heat from one location (the "source") at a lower temperature to another location (the "sink" or "heat sink") at a higher temperature. Thus a heat pump may be thought of as a "heater" if the objective is to warm the heat sink (as when warming the inside of a home on a cold day), or a "refrigerator" or “cooler” if the objective is to cool the heat source (as in the normal operation of a freezer). In either case, the operating principles are similar. Heat is moved from a cold place to a warm place. Thermodynamic cycles According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat cannot spontaneously flow from a colder location to a hotter area; work is required to achieve this. An air conditioner requires work to cool a living space, moving heat from the interio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
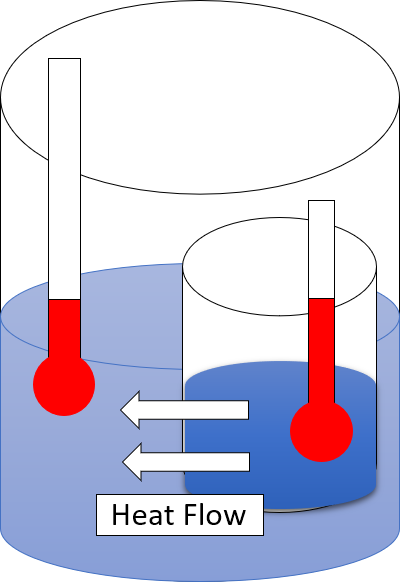
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unless energy in some form is supplied to reverse the direction of heat flow. Another definition is: "Not all heat energy can be converted into work in a cyclic process."Young, H. D; Freedman, R. A. (2004). ''University Physics'', 11th edition. Pearson. p. 764. The second law of thermodynamics in other versions establishes the concept of entropy as a physical property of a thermodynamic system. It can be used to predict whether processes are forbidden despite obeying the requirement of conservation of energy as expressed in the first law of thermodynamics and provides necessary criteria for spontaneous processes. The second law may be formulated by the observation that the entropy of isolated systems left to spontaneous evolution cannot decr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pump
A heat pump is a device that can heat a building (or part of a building) by transferring thermal energy from the outside using a refrigeration cycle. Many heat pumps can also operate in the opposite direction, cooling the building by removing heat from the enclosed space and rejecting it outside. Units that only provide cooling are called air conditioners. When in heating mode, a refrigerant at outside temperature is being compressed. As a result, the refrigerant becomes hot. This thermal energy can be transferred to an indoor unit. After being moved outdoors again, the refrigerant is decompressed — evaporated. It has lost some of its thermal energy and returns colder than the environment. It can now take up the surrounding energy from the air or from the ground before the process repeats. Compressors, fans, and pumps run with electric energy. Common types are air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps and exhaust air heat pumps. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between rational a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |