|
Eclectic Chronicle
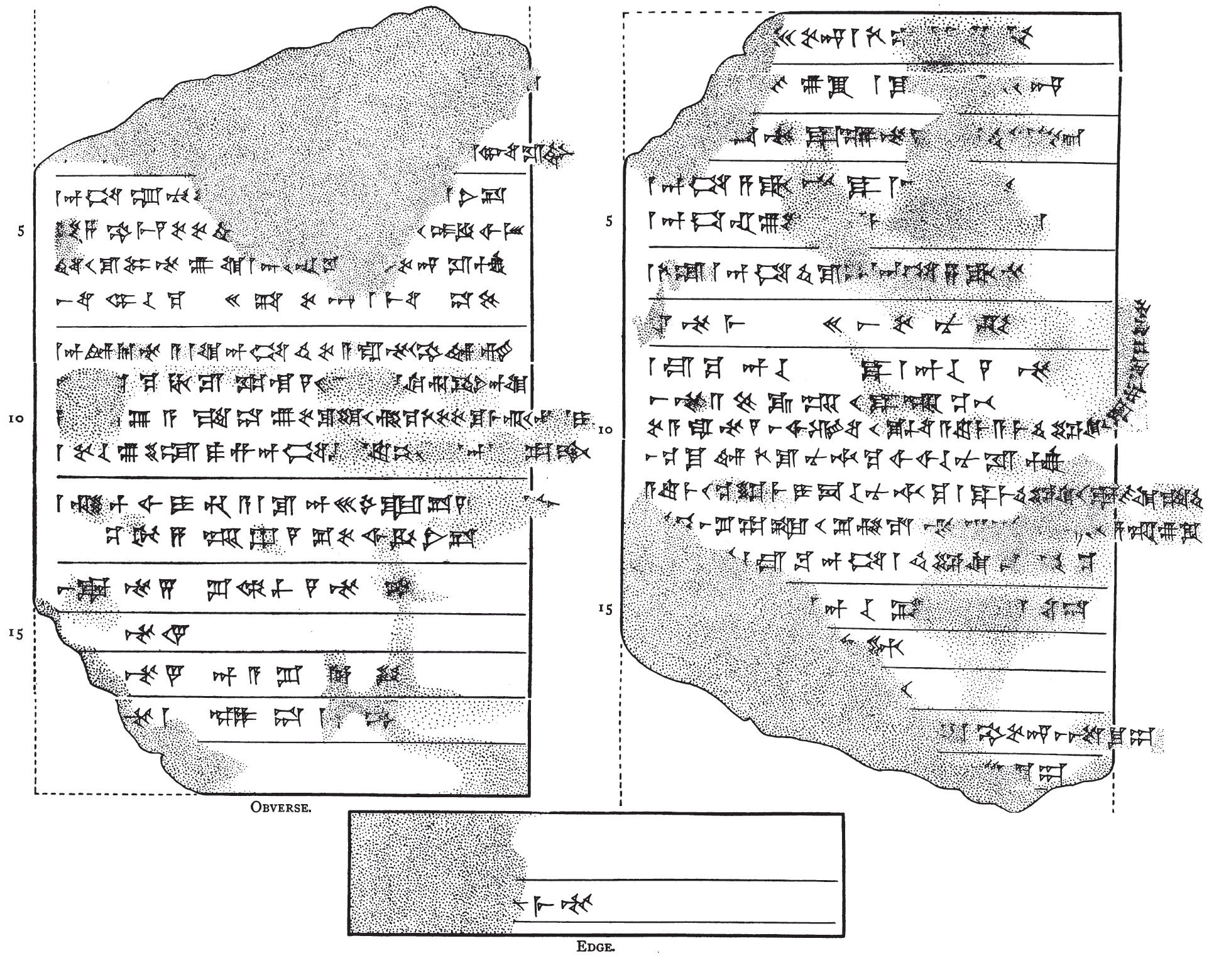
The Eclectic Chronicle, referred to in earlier literature as the ''New Babylonian Chronicle'', is an ancient Mesopotamian account of the highlights of Babylonian history during the post-Kassite era prior to the 689 BC fall of the city of Babylon. It is an important source of historiography from the period of the early iron-age dark-age with few extant sources to support its telling of events. The text Although its provenance is unknown, it is thought to originate from Babylon itself as it is written in standard Babylonian in the late cuneiform script of the region. It was acquired by the British Museum in 1898 and given the accession number 98,0711.124, subsequently the Museum reference BM 27859. Approximately two-thirds of the text has survived with the top part of the tablet broken off, losing the beginning and end of the narrative. The work is written in a single column on a small tablet in the format of an administrative or economic text, suggesting it was for private use, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclectic Chronicle
The Eclectic Chronicle, referred to in earlier literature as the ''New Babylonian Chronicle'', is an ancient Mesopotamian account of the highlights of Babylonian history during the post-Kassite era prior to the 689 BC fall of the city of Babylon. It is an important source of historiography from the period of the early iron-age dark-age with few extant sources to support its telling of events. The text Although its provenance is unknown, it is thought to originate from Babylon itself as it is written in standard Babylonian in the late cuneiform script of the region. It was acquired by the British Museum in 1898 and given the accession number 98,0711.124, subsequently the Museum reference BM 27859. Approximately two-thirds of the text has survived with the top part of the tablet broken off, losing the beginning and end of the narrative. The work is written in a single column on a small tablet in the format of an administrative or economic text, suggesting it was for private use, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eulmash-shakin-shumi
Eulmaš-šākin-šumi, inscribed in cuneiform as ''É-ul-maš-''GAR-MU,In contemporary arrowheads, such as IMJ 74.049.0124 in the Israel Museum, Jerusalem, aCDLI/ref> or prefixed with the masculine determinative m,''Babylonian King List A'', BM 33332, iii '10. “Eulmaš''Eulmaš'' was the name of the Ištar temple in the city of Agade. (is) the establisher of offspring”, 1000–984 BC, was the founder of the 6th Dynasty of Babylon, known as the ''Bῑt-Bazi'' Dynasty, after the Kassite tribal group from which its leaders were drawn. The '' Dynastic Chronicle''''Dynastic Chronicle'' v 9. tells us that he ruled for fourteen years, the King List A, seventeen years. Biography A small settlement near the Tigris in the 23rd century had been adopted by a minor Kassite clan by the 14th century, the name being co-opted as the ancestor figure for the tribe. In the midst of the turmoil inflicted by the Aramean migrations and the famines that drove them, Eulmaš-šākin-šumi seems t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marduk-zakir-shumi I
Marduk-zâkir-šumi, inscribed mdAMAR.UTU''-za-kir-''MU in a reconstruction of two kinglists,''Synchronistic Kinglist'' KAV 10 (VAT 11261) ii 9.''Synchronistic Kinglist'' KAV 182 (Ass. 13956dh) iii 12. “Marduk pronounced the name,” was a king of Babylon from 855 to 819 BC during the mixed dynastic period referred to in antiquity as the dynasty of ''E''. He was a contemporary of the Assyrian kings, Salmānu-ašarēdu III) (commonly known as Shalmaneser III)''Synchronistic Kinglist'', KAV 216 (Ass. 14616c), iii 20. (859–824 BC) and Šamši-Adad V (824–811 BC) with whom he was allied.''Eclectic Chronicle'' (ABC 24) BM 27859 reverse (r 5-7). Biography There are few contemporary inscriptions bearing witness to his reign. A kudurru granting Ibni-Ištar, a ''kalû-''priest of the temple of Eanna in Uruk, land by Marduk-zâkir-šumi, is dated to his second year. Nazi-Enlil was governor or ''šandabakku'' (inscribed LÚGÚ.EN.NA) of Nippur, the first appearance of this office sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
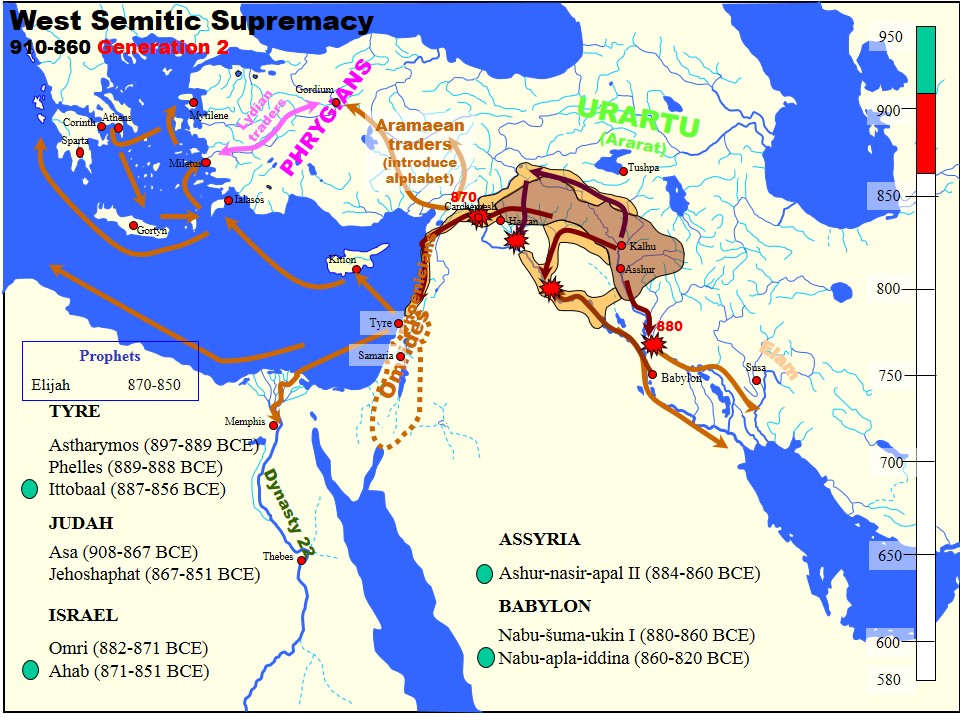
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II (transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning " Ashur is guardian of the heir") was king of Assyria from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II, in 883 BC. During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. His harshness prompted a revolt that he crushed decisively in a pitched, two-day battle. According to his monument inscription, while recalling this massacre he says: Following this victory, he advanced without opposition as far as the Mediterranean and exacted tribute from Phoenicia. On his return home, he moved his capital to the city of Kalhu (Nimrud). Family Ashurnasirpal II's father was Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III. His queen was Mullissu-muk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabu-apla-iddina
Nabû-apla-iddina, inscribed md''Nábû-ápla-iddina''na''Synchronistic History'', tablet K4401a (ABC 21), iii 22–26. or md''Nábû-apla-íddina'';''Synchronistic Kinglist'' fragments VAT 11261 (KAV 10), ii 8, and Ass. 13956dh (KAV 182), iii 11. reigned about 886–853 BC, was the sixth king of the dynasty of ''E'' of Babylon and he reigned for at least thirty-two years.Kudurru AO 21422 in the Louvre. During much of Nabû-apla-iddina's reign Babylon faced a significant rival in Assyria under the rule of Ashurnasirpal II. Nabû-apla-iddina was able to avoid both outright war and significant loss of territory. There was some low level conflict, including a case where he sent a party of troops led by his brother to aid rebels in Suhu (Suhi, Sukhu, Suru). Later in his reign Nabu-apla-iddina agreed to a treaty with Ashurnasirpal II’s successor Shalmaneser III. Internally Nabu-apla-iddina worked on the reconstruction of temples and something of a literary revival took place during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukulti-Ninurta II
Tukulti-Ninurta II was King of Assyria from 890 BC to 884 BC. He was the second king of the Neo Assyrian Empire. History His father was Adad-nirari II, the first king of the Neo-Assyrian period. Tukulti-Ninurta consolidated the gains made by his father over the Neo-Hittites, Babylonians and Arameans, and successfully campaigned in the Zagros Mountains of Iran, subjugating the newly arrived Iranian peoples of the area, the Persians and Medes, during his brief reign. Tukulti-Ninurta II was victorious over Ammi-Ba'al, the king of Bit-Zamani, and then entered into a treaty with him (which included prohibitions against selling horses to Assyria's foes), as a result of which Bit-Zamani became an ally, and in fact a vassal of Assyria. Ammi-Ba'al remained in power, but from that moment on, he had to support Tukulti-Ninurta II during his military expeditions to the Upper Tigris against the Hurrians and Urartians in Nairi. Tukulti-Ninurta II developed both Nineveh and Assur, in which he im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabu-shuma-ukin I
Nabû-šuma-ukin I, inscribed md''Nābû-šuma-ú-kin'',''Synchronistic King List'' iii 16 and variant fragments KAV 10 ii 7, KAV 182 iii 10. meaning “Nabû has established legitimate progeny,” was the 5th king listed in the sequence of the so-called dynasty of ''E'', possibly a mixed series of dynasties, that ruled over Babylon during the early Iron Age. The exact duration of his reign is unknown but was probably at the beginning of the 9th century BC. His rule marks a temporary resurgence in the fortunes of Babylonia, which was to last on through his son and successor, Nabû-apla-iddina’s reign and the two kings who followed in this four-generation dynasty. Biography The circumstances of his ascendancy and his relationship with his predecessor are not known. The beginning of his reign was marked by war with Assyria when Adad-Nārāri II swept down on his second campaign and supposedly defeated him according to the Assyrian version, apparently sacking several cities and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adad-nirari II
Adad-nirari II (reigned from 911 to 891 BC) was the first King of Assyria in the Neo-Assyrian period. Biography Adad-nirari II's father was Ashur-dan II, whom he succeeded after a minor dynastic struggle. It is probable that the accession encouraged revolts amongst Assyria's nominal vassals. He firmly subjugated the areas previously under only nominal Assyrian vassalage, conquering and deporting troublesome Arameans following a battle at the junction of the Khabur and Euphrates in 910 BC. After subduing Neo-Hittite and Hurrian populations in the north, Adad-nirari II then twice attacked and defeated Shamash-mudammiq of Babylonia, annexing a large area of land north of the Diyala River and the towns of Hīt and Zanqu in mid Mesopotamia in the same year. He made further gains over Babylonia under Nabu-shuma-ukin I later in his reign. He also campaigned to the west, subjugating the Aramean cities of Kadmuh and Nisibin. Along with vast amounts of treasure collected, he also secu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamash-mudammiq
Šamaš-mudammiq, inscribed md''Šamaš-''mu''mudammiq'' (mdUTU-''mu''-SIG5),''Synchronistic King List'' fragment, KAV 182, Ass 13956dh, iii 9. meaning “Šamaš shows favor,” was the 4th king of Babylon in a sequence designated as the Dynasty of ''E'' and ruled during the latter part of the 10th century BC. He was contemporary with the Assyrian king Adad-Nārāri IIChronicle 24, BM 27859, the ''Eclectic Chronicle'', r 2. with whom he sparred.''Synchronistic History'' (ABC 21), tablet K 4401a + Rm 854, iii 1–8. Biography Of unknown ancestry, the duration of his reign is equally uncertain. That he followed Mār-bῑti-áḫḫē-idinna is indicated by the sequence on the Assyrian ''Synchronistic King List'',''Synchronistic King List'' , KAV 216, Ass 14616c, iii 13. but Assyrian contact was scanty and this may merely record those rulers who had interacted, omitting those who did not. His rule marks the resumption of contacts characterized as “battles, alliances, shifting of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mar-biti-ahhe-iddina
Mār-bῑti-aḫḫē-idinna, md''Mār-bῑti-áḫḫē-idinna'' (mdDUMU-E-PAP-AŠ),''Synchronistic King List'' Fragments (KAV 10) ii 5 and (KAV 182) iii 8. meaning ''Mār-bīti'' (a Babylonian god with a sanctuary at Borsippa) ''has given me brothers'', became king of Babylonia 939 BC, succeeding his brother, Ninurta-kudurrῑ-uṣur II, and was the 3rd king of the Dynasty of ''E'' to sit on the throne. He is known only from king lists, a brief mention in a chronicle and as a witness on a kudurru from his father, Nabû-mukin-apli's reign. Biography He was first recorded as a witness to a title deed inscribed on a kudurruKudurru BM 90835, BBSt 9. after his (presumably) older brothers, Ninurta-kudurrῑ-uṣur, who was to become his immediate predecessor on the throne, and Rīmūt-ilī, the temple administrator. The ''Eclectic Chronicle''''Eclectic Chronicle'' (ABC 24), BM 27859: r 1. refers laconically to “the Nth year of Mār-bῑti-aḫḫē-idinna” but the context is lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ninurta-kudurri-usur II
Ninurta-kudurrῑ-uṣur II, a name meaning “O Ninurta, protect my offspring”, inscribed in cuneiform as mdMAŠ-NÍG.DU-PAP,''Synchronistic King List'' fragments VAT 11261 (KAV 10) ii 4’ and VAT 11261 (KAV 182) iii 7’. or mdNIN.IB-NÍG.DU-PAP,Kudurru BM 90835, BBSt 9, in the British Museum, iv A 30 939 BC, was the 2nd king of the Dynasty of ''E'', a sequence of mixed dynasties, of Babylon; he reigned for 8 months 12 days, according to the ''King List A''.''King List A'', BM 33332, iii 16: ITI 8 12 D No contemporary documents survive for his reign or that of his successor, his younger brother, Mār-bῑti-aḫḫē-idinna. Biography He succeeded his long-reigning father, Nabû-mukin-apli, during whose time he appeared as a witness on a kudurru recording a title deed, dated to either his father's 23rd or 25th year, more than a decade before he ascended the throne, suggesting he was fairly elderly when he became king. The dynastic affiliation of the family is unknown and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabû-mukin-apli
Nabû-mukin-apli, typically inscribed dAG-DU-A, “Nabû (is) establisher of a legitimate heir,” ruled 974–939 BC, founded Babylon’s 8th dynasty, the so-called ''Dynasty of E'', and ruled for thirty-six years.''Babylonian King List A'', tablet BM 33332 iii 15 in the British Museum. The ''Synchronistic Kinglist'' records him as a contemporary of the Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser II.The ''Synchronistic Kinglist'' A.117, KAV 216 (Ass. 14616c), iii 9 ( İstanbul Arkeoloji Műzeleri) and also fragments KAV 10 (VAT 11261, in the Vorderasiatisches Museum Berlin) ii 3 KAV 182 (Ass. 13956dh) iii 6. His reign was plagued by Aramean invasions, resulting in Babylon being cut off from its agricultural hinterland for several years and consequently being unable to celebrate the new year festival. Biography His reign falls in the midst of the Babylonian dark age and consequently his ancient sources are meager. He is mentioned in the ''Eclectic Chronicle''''Chronicle 24'', tablet BM 27859, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |