|
Eblaite Language
Eblaite (, also known as Eblan ISO 639-3), or Palaeo-Syrian, is an extinct East Semitic language used during the 3rd millennium BC by the populations of Northern Syria. It was named after the ancient city of Ebla, in modern western Syria. Variants of the language were also spoken in Mari and Nagar. According to Cyrus H. Gordon, although scribes might have spoken it sometimes, Eblaite was probably not spoken much, being rather a written lingua franca with East and West Semitic features. The language was discovered through cuneiform tablets found in Ebla. Discovery The 1964 discovery at the Tell Mardikh site in Northern Syria of an ancient city from the second half of the third millennium BC completely altered archaeological knowledge of the time, as it indicated the existence of a contemporary urban culture during the Early Dynastic Period of Mesopotamia, within a geographic zone where, at the time, previous excavations had revealed nothing on the same scale. In agreemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
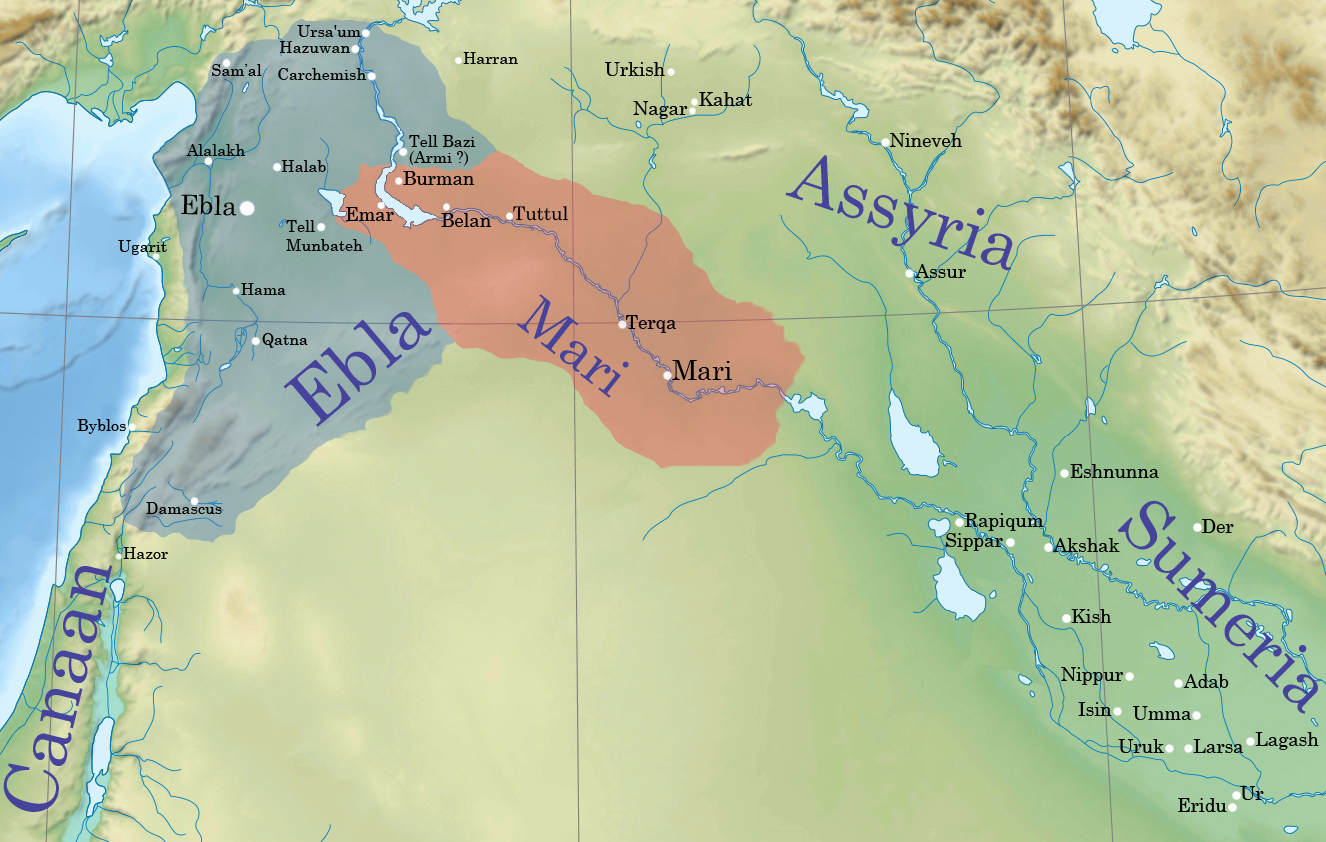
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa and Babylonia) from the third millennium BC until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BC. It is the earliest documented Semitic language. It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BC). The mutual influence between Sumerian and Akkadian had led scholars to describe the languages as a '' Sprachbund''. Akkadian proper names were first attested in Sumerian texts from around the mid 3rd-mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology () is the study of words, how they are formed, and their relationship to other words in the same language. It analyzes the structure of words and parts of words such as stems, root words, prefixes, and suffixes. Morphology also looks at parts of speech, intonation and stress, and the ways context can change a word's pronunciation and meaning. Morphology differs from morphological typology, which is the classification of languages based on their use of words, and lexicology, which is the study of words and how they make up a language's vocabulary. While words, along with clitics, are generally accepted as being the smallest units of syntax, in most languages, if not all, many words can be related to other words by rules that collectively describe the grammar for that language. For example, English speakers recognize that the words ''dog'' and ''dogs'' are closely related, differentiated only by the plurality morpheme "-s", only found bound to noun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicon
A lexicon is the vocabulary of a language or branch of knowledge (such as nautical or medical). In linguistics, a lexicon is a language's inventory of lexemes. The word ''lexicon'' derives from Koine Greek language, Greek word (), neuter of () meaning 'of or for words'. Linguistic theories generally regard human languages as consisting of two parts: a lexicon, essentially a catalogue of a language's words (its wordstock); and a grammar, a system of rules which allow for the combination of those words into meaningful sentences. The lexicon is also thought to include bound morphemes, which cannot stand alone as words (such as most affixes). In some analyses, compound words and certain classes of idiomatic expressions, collocations and other phrases are also considered to be part of the lexicon. Dictionary, Dictionaries are lists of the lexicon, in alphabetical order, of a given language; usually, however, bound morphemes are not included. Size and organization Items in the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Pettinato
Giovanni Pettinato (30 April 1934, in Troina – 19 May 2011, in Rome) was a assyrologist and paleographer of writings from the ancient Near East, specializing in the Eblaite language, His major contributions to the field include the deciphering of the Eblaite script, discovered by Paolo Matthiae in 1974–75. Pettinato graduated from Heidelberg in 1968, where he had studied for ten years. In 1968 he began teaching Assyriology at the University of Rome. Pettinato died on 19 May 2011 at the age of 76. He was an emeritus of several associations, including the Accademia dei Lincei and authored several publications about the Sumerian and Mesopotamia Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...n civilizations. References 1934 births 2011 deaths Italian Assyriologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |