|
Eastern Galindians
Galindians were two distinct, and now extinct, tribes of the Balts. Most commonly, Galindians refers to the Western Galindians who lived in the southeast part of Prussia. Less commonly, it is used for a tribe that lived in the area of what is today Moscow. The name "Galinda" is thought to derive from the Baltic word *''galas'' ("the end"), alluding to the fact that they settled for some time further west and further east than any other Baltic tribe. Western Galindians The Western Galindians (Old Prussian: *''Galindis'',An asterisk placed before the word means that it is reconstructed and is therefore not attested. Latin: ''Galindae'') – at first a West Baltic tribe, and later an Old Prussian clan – lived in Galindia, roughly the area of present-day Masuria but including territory further south in what would become the Duchy of Masovia. The region lay adjacent to the territory of the Yotvingians, which is today in Podlaskie Voivodeship.The name ''Galind''- is probably der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Tribes C 1200
Baltic may refer to: Peoples and languages *Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian *Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originating from the Baltic countries *Baltic Germans, historical ethnic German minority in Latvia and Estonia *Baltic Finnic peoples, the Finnic peoples historically inhabiting the area on the northeastern side of the Baltic sea Places Northern Europe * Baltic Sea, in Europe * Baltic region, an ambiguous term referring to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea * Baltic states (also Baltic countries, Baltic nations, Baltics), a geopolitical term, currently referring to Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania * Baltic Provinces or governorates, former parts of the Swedish Empire and then Russian Empire (in modern Latvia, Estonia) * Baltic Shield, the exposed Precambrian northwest segment of the East European Craton * Baltic Plate, an ancient tectonic pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koine Greek
Koine Greek (; Koine el, ἡ κοινὴ διάλεκτος, hē koinè diálektos, the common dialect; ), also known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek or New Testament Greek, was the common supra-regional form of Greek spoken and written during the Hellenistic period, the Roman Empire and the early Byzantine Empire. It evolved from the spread of Greek following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the fourth century BC, and served as the lingua franca of much of the Mediterranean region and the Middle East during the following centuries. It was based mainly on Attic and related Ionic speech forms, with various admixtures brought about through dialect levelling with other varieties. Koine Greek included styles ranging from conservative literary forms to the spoken vernaculars of the time. As the dominant language of the Byzantine Empire, it developed further into Medieval Greek, which then turned into Modern Greek. Literary Koine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurentian Codex
Laurentian Codex or Laurentian Letopis (russian: Лаврентьевский список, Лаврентьевская летопись) is a collection of chronicles that includes the oldest extant version of the ''Primary Chronicle'' and its continuations, mostly relating the events in Northern Russia (Vladimir-Suzdal). The scribe and his source The codex was not just copied by the Nizhegorod monk Laurentius commissioned by Dionysius of Suzdal in 1377. The original text on events from 1284 to 1305 was a lost codex compiled for the Grand Duke Mikhail of Tver in 1305, but Laurentius re-edited the presentation of Yuri Vsevolodovich, the founder of Nizhny Novgorod, from positive into a negative, partly rehabilitating the role of Tatars. Vasily Komarovich studied traces of changes within the manuscript and established a hypothesis about differences between Laurentius' version and the lost one of the Tver chronicle. Content The Laurentian Codex compiled several codices of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early East Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the Slavic nations through the Slavic states of the High Middle Ages. The Slavs' original homeland is still a matter of debate due to a lack of historical records; however, scholars believe that it was in Eastern Europe, with Polesia being the most commonly accepted location. The first written use of the name "Slavs" dates to the 6th century, when the Slavic tribes inhabited a large portion of Central and Eastern Europe. By then, the nomadic Iranian-speaking ethnic groups living on the Eurasian Steppe (the Scythians, Sarmatians, Alans etc.) had been absorbed by the region's Slavic-speaking population. Over the next two centuries, the Slavs expanded west to the Elbe river and south towards the Alps and the Balkans, absorbing the Celtic, Germanic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaluga Oblast
Kaluga Oblast (russian: Калу́жская о́бласть, translit=Kaluzhskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Kaluga. The 2021 Russian Census found a population of 1,069,904. Geography Kaluga Oblast lies in the central part of the East European Plain. The oblast's territory is located between the Central Russian Upland (with and average elevation of above and a maximum elevation of in the southeast), the Smolensk–Moscow Upland and the Dnieper– Desna watershed. Most of the oblast is occupied by plains, fields and forests with diverse flora and fauna. The administrative center is located on the Baryatino-Sukhinichy plain. The western part of the oblast — located within the drift plain — is dominated by the Spas-Demensk ridge. To the south is an outwash plain that is part of the Bryansk-Zhizdra woodlands, with average elevation up to 200 m. From north to south, Kaluga Oblast extends for more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moshchiny Culture
The Moshchiny culture (russian: Мощинская культура) was an archaeological culture of the Iron Age from the 4th to the 7th century in present-day western Russia. It is the easternmost known Baltic culture. Distribution area The settlement area was located in the forest areas at the upper Dnepr and the upper Oka in today's Russian Oblast Kaluga, Tula, Oryol and Smolensk. It is named after a settlement near the village '' Moshchiny '' (russian: Мощины) in the Mosalsky District in the Kaluga Oblast. (russian: Мощины) Kaluga Oblast. Russia. Genesis The Moshchiny culture emerged in the 4th century from the ''[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borovsk
Borovsk (russian: Бо́ровск) is a town and the administrative center of Borovsky District of Kaluga Oblast, Russia, located on the Protva River just south from the oblast's border with Moscow Oblast. Population: 12,000 (1969). History It is known to have existed since 1356 as a part of the Principality of Ryazan. In the 14th century, it was owned by Vladimir the Bold, but passed to the Grand Duchy of Moscow when his granddaughter Maria of Borovsk married Vasily II. In 1444, the St. Paphnutius Monastery was founded near Borovsk. Its strong walls, towers, and a massive cathedral survive from the reign of Boris Godunov. Two famous Old Believers—archpriest Avvakum Petrovich and boyarynya Feodosiya Morozova—were incarcerated at this monastery in the second half of the 17th century. The town was liberated by the Red Army on January 4, 1942. Administrative and municipal status Within the framework of administrative divisions, Borovsk serves as the administrativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vereya
{{Set index article, populated places in Russia ...
Vereya (russian: Верея) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia. ;Urban localities *Vereya, Naro-Fominsky District, Moscow Oblast, a town in Naro-Fominsky District of Moscow Oblast ;Rural localities * Vereya, Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District, Moscow Oblast, a settlement in Vereyskoye Rural Settlement of Orekhovo-Zuyevsky District in Moscow Oblast * Vereya, Ramensky District, Moscow Oblast, a village in Vereyskoye Rural Settlement of Ramensky District in Moscow Oblast * Vereya, Ryazan Oblast, a village in Oskinsky Rural Okrug of Klepikovsky District in Ryazan Oblast * Vereya, Zabaykalsky Krai, a settlement in Priargunsky District of Zabaykalsky Krai Zabaykalsky Krai ( rus, Забайкальский край, r=Zabaikal'skii krai, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲskʲɪj kraj, lit. "Transbaikal krai"; bua, Yбэр Байгалай хизаар, Uber Baigalai Xizaar) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozhaysk
MozhayskAlternative transliterations include ''Mozhaisk'', ''Mozhajsk'', ''Mozhaĭsk'', and ''Možajsk''. ( rus, Можа́йск, p=mɐˈʐajsk) is a town and the administrative center of Mozhaysky District in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located to the west of Moscow, on the historic road leading to Smolensk and then to Poland. Population: History First mentioned in 1231 as an appanage of Chernigov; A theory says Mozhaysk took its name from the Mozhay (Mozhaya) River, whose name could be of Baltic origin (compare Lithuanian ''mažoji'' "small" - in contrast to the larger Moskva River nearby). Later Mozhaysk became an important stronghold of the Smolensk dynasty, in the 13th century ruled by Duke (later Saint) Theodore the Black. Muscovites seized Mozhaysk in 1303, but in the course of the following century had serious troubles defending it against Algirdas (Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1345 to 1377). A younger brother of the ruling Grand Duke of Moscow usually held the Principality o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and shares Borders of Russia, land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than List of countries and territories by land borders, any other country but China. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's ninth-most populous country and List of European countries by population, Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city is Moscow, the List of European cities by population within city limits, largest city entirely within E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protva
The Protva () is a river in Moscow and Kaluga Oblasts in Russia, left tributary of the Oka. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .«Река ПРОТВА» Russian State Water Registry The area of its basin is . The Protva freezes up in early December and stays icebound until early April. Its main tributary is the Luzha. The towns of , , |
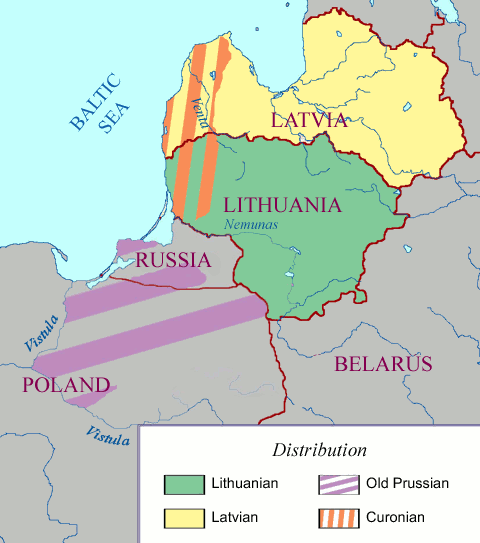
East Baltic Languages
The Baltic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 4.5 million people mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. Together with the Slavic languages, they form the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European family. Scholars usually regard them as a single subgroup divided into two branches: Western Baltic (containing only extinct languages) and Eastern Baltic (containing at least two living languages, Lithuanian, Latvian, and by some counts including Latgalian and Samogitian as separate languages rather than dialects of the two aforementioned languages). The range of the Eastern Baltic linguistic influence once possibly reached as far as the Ural Mountains, but this hypothesis has been questioned. Old Prussian, a Western Baltic language that became extinct in the 18th century, has possibly retained the greatest number of properties from Proto-Baltic. Although related, Lit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |