|
East New Britain Province
East New Britain is a province of Papua New Guinea, consisting of the north-eastern part of the island of New Britain and the Duke of York Islands. The capital of the province is Kokopo, not far from the old capital of Rabaul, which was largely destroyed in a volcanic eruption in 1994. East New Britain covers a total land area of , and the province's population was reported as 220,133 in the 2000 census, rising to 328,369 in the 2011 count. Provincial coastal waters extend over an area of . The province's only land border is with West New Britain Province to the west, and it also shares a maritime border with New Ireland Province to the east. East New Britain has a dual economy: a cash economy operates side by side with the subsistence-farming sector. The main crops produced for export are cocoa and copra. Tourism continues to be an increasingly important sector of the provincial economy. Languages There are sixteen Austronesian languages spoken in the province, of which Kuanua, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niugini; ho, Independen Stet bilong Papua Niu Gini), is a country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and its offshore islands in Melanesia (a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean north of Australia). Its capital, located along its southeastern coast, is Port Moresby. The country is the world's third largest island country, with an area of . At the national level, after being ruled by three external powers since 1884, including nearly 60 years of Australian administration starting during World War I, Papua New Guinea established its sovereignty in 1975. It became an independent Commonwealth realm in 1975 with Elizabeth II as its queen. It also became a member of the Commonwealth of Nations in its own right. There are 839 known languages of Papua New Guinea, one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
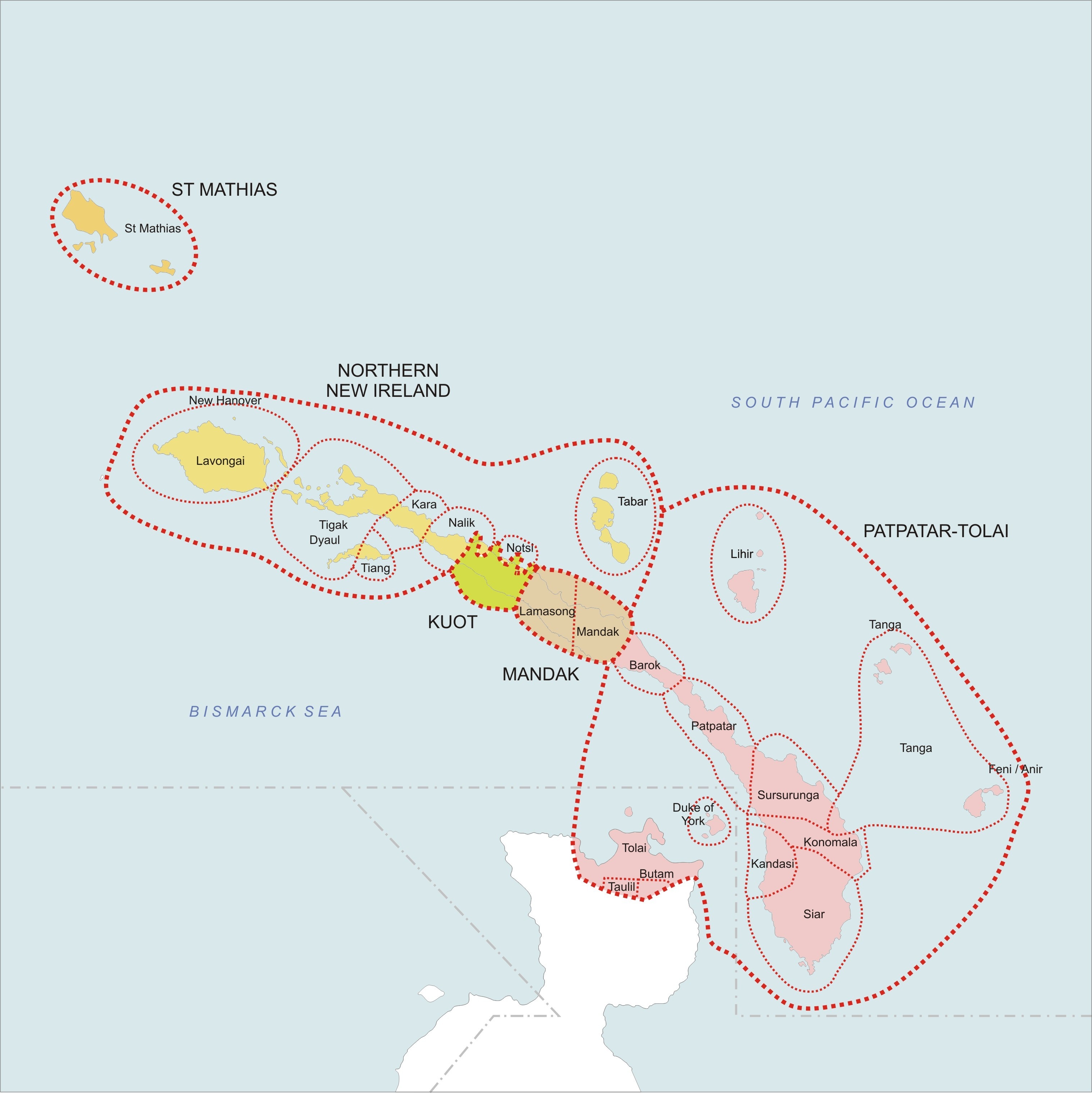
New Ireland Province
New Ireland Province, formerly New Mecklenburg (german: Neu-Mecklenburg), and Nova Hibernia, is the northeasternmost province of Papua New Guinea. Physical geography The largest island of the province is New Ireland. Also part of the province are numerous smaller islands, including Saint Matthias Group (Mussau, Emirau), New Hanover, Djaul, Tabar Group ( Tabar, Tatau, Simberi), Lihir, Tanga Group (Malendok, Boang), Feni Islands (Ambitle, Babase) and Anir. The land area of the province is around 9 560 km². The sea area within the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) of New Ireland Province is around 230,000 km². Ecology In the early days of the French Revolution while searching for a lost scientific expedition the vessel La Recherche passed by New Ireland. On board was the prominent botanist Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière who noted in his journal fine stands of teak (tectona grandis) trees growing at the southern end of the island. This marks the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makolkol Language
Makolkol is a possible Papuan language formerly spoken on the Gazelle Peninsula of East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Stebbins (2010) reports it is unattested. Palmer (2018) treats it as unclassified. It is not known if it was related to the neighboring Baining languages. Rosensteel (1988) contains a 174-word list of Makolkol. Sociolinguistic situation Makolkol was spoken only in the village of Gunapeo. Speakers were shifting to Tok Pisin Tok Pisin (,Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student’s Handbook'', Edinburgh ; Tok Pisin ), often referred to by English speakers as "New Guinea Pidgin" or simply Pidgin, is a creole language spoken throughout Papua New Guinea. It is an ... and Meramera. ''Languages of Papua New Guinea''. SIL International. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kol Language (Papua New Guinea)
The Kol language is a language spoken in eastern New Britain island, Papua New Guinea. There are about 4000 speakers in Pomio District of East New Britain Province, mostly on the southern side of New Britain island. Kol appears to be a language isolate, though it may be distantly related to the poorly attested Sulka language or form part of the proposed East Papuan languages. Phonology Phonology of the Kol language: /b, r/ can be realized as [β, d] as intervocalic allophones. /r/ is pronounced as [d] when following a nasal consonant. Kol displays vowel length contrast. Vocabulary The following basic vocabulary words are from SIL field notes (1962, 1981), as cited in the Trans-New Guinea database: : See also * East Papuan languages References External linksKol language word list at TransNewGuinea.org {{Languages of Papua New Guinea East Papuan languages Language isolates of New Guinea Languages of East New Britain Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ata Language
The Ata language, also known as Pele-Ata after its two dialects, or Wasi, is a Papuan language spoken on New Britain island, Papua New Guinea. It appears to be related to neighboring Anêm, and possibly also to Yélî Dnye in a proposed Yele-West New Britain family. There are about 2000 speakers. Ata is spoken in West Pomio-Mamusi Rural LLG, East New Britain Province, and in Talasea District, West New Britain Province. Dialects According to Yanagida (2004), there are two dialects of Ata, a ''Lower'' dialect spoken in the lowlands and an ''Upper'' dialect spoken in the mountains.Yanagida, Tatsuya. 2004. Socio-historic overview of the Ata language, an endangered Papuan language in New Britain, Papua New Guinea. In Shibata Norio and Shionoya, Toru (eds.), ''Kan minami Taiheiyoo no gengo 3'' anguages of the South Pacific Rim 3 61-94. Suita: Faculty of Informatics, Osaka Gakuin University. The Lower dialect is spoken in Bialla Rural LLG, West New Britain Province, while the Upp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taulil Language
Taulil is a Papuan language spoken in East New Britain Province on the island of New Britain, Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in Kadaulung village of () of Inland Baining Rural LLG, and in Taulil 1 () and Taulil 2 () villages of Vunadidir/Toma Rural LLG Vunadidir/Toma Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of East New Britain Province, Papua New Guinea. Wards *02. Rabagi No.1 *03. Rabagi No.2 *05. Rapitok No.1 *06. Rapitok No.2 *07. Rapitok No.3 *08. Rapitok No.4 *09. Ratavul *10. Vunakabi .... Butam (now extinct) is related. Like the Butam, the Taulil people trace their ancestry to New Ireland. Phonology Taulil consonants: : References * Languages of East New Britain Province Taulil–Butam languages Vulnerable languages {{papuan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baining Languages
The Baining languages are a small language family spoken by the Baining people on the Gazelle Peninsula of New Britain in Papua New Guinea. They appear to be related to the neighboring Taulil–Butam languages, which immigrated from New Ireland. Languages The languages are: *Mali Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ... (2,200 speakers) * Qaqet (6,400 speakers) * Kairak (900 speakers) * Simbali (450 speakers) * Ura (1,900 speakers) Extinct Makolkol neighbored the (other) Baining languages to their southwest but is unattested. Vocabulary comparison The following basic vocabulary words are from SIL field notes (1970, 1971, 1975), as cited in the Trans-New Guinea database: : References {{Papuan languages East New Britain languages Languages of East New Britain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papuan Languages
The Papuan languages are the non- Austronesian and non-Australian languages spoken on the western Pacific island of New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, as well as neighbouring islands, by around 4 million people. It is a strictly geographical grouping, and does not imply a genetic relationship. The concept of Papuan (non-Austronesian) speaking Melanesians as distinct from Austronesian-speaking Melanesians was first suggested and named by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1892. New Guinea is the most linguistically diverse region in the world. Besides the Austronesian languages, there are some (arguably) 800 languages divided into perhaps sixty small language families, with unclear relationships to each other or to any other languages, plus many language isolates. The majority of the Papuan languages are spoken on the island of New Guinea, with a number spoken in the Bismarck Archipelago, Bougainville Island and the Solomon Islands to the east, and in Halmahera, Timor and the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gazelle Peninsula
The Gazelle Peninsula is a large peninsula in northeastern East New Britain, Papua New Guinea located on the island of New Britain within the Bismarck Archipelago, situated in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The Rabaul caldera is located on the northern tip of the peninsula. Upon the Gazelle Peninsula are the Baining Mountains, of which the highest point is Mount Sinewit at . The Gazelle Peninsula houses Vulcan Crater and Mount Tavurvur, both of which conducted volcanic activity in the 20th and 21st centuries and have provided extremely fertile soils. The body of the Gazelle Peninsula is about . The southern isthmus upon which the Gazelle Peninsula is connected to the main body of East New Britain is reduced to about . The Editors of Encyclopædia Britannica, (2015). Gazelle peninsula. Retrieved April 23, 2019 from https://www.britannica.com/place/Gazelle-Peninsula History The peninsula was named by Georg Gustav Freiherr von Schleinitz after his ship, . 1884-1909 1884: Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolai People
The Tolai are the indigenous people of the Gazelle Peninsula and the Duke of York Islands of East New Britain in the New Guinea Islands region of Papua New Guinea. They are ethnically close kin to the peoples of adjacent New Ireland and tribes like the Tanga people and are thought to have migrated to the Gazelle Peninsula in relatively recent times, displacing the Baining people who were driven westwards. The majority of Tolais speak Kuanua as their first language (~100,000). Two other languages are spoken as first languages: Lungalunga and Bilur, each with approximately 2,000 speakers. The Tolais almost universally define themselves as Christian and are predominantly Roman Catholic and United Church. Christianity was introduced to the island when Methodist ministers and teachers from Fiji arrived in the New Guinea islands region in 1875. However, in 1878 when some of the tribespeople ate four of the missionaries, the Englishman who led the missionaries, George Brown, direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuanua
The Tolai language, or Kuanua, is spoken by the Tolai people of Papua New Guinea, who live on the Gazelle Peninsula in East New Britain Province. Nomenclature This language is often referred to in the literature as ''Tolai''. However, Tolai is actually the name of the cultural group. The Tolais themselves refer to their language as ''a tinata tuna'', which translates as "the real language". ''Kuanua'' is apparently a word in Ramoaaina meaning "the place over there". Characteristics Unlike many languages in Papua New Guinea, Tolai is a healthy language and not in danger of dying out to Tok Pisin, although even Tolai suffers from a surfeit of loanwords from Tok Pisin, e.g. the original ''kubar'' has been completely usurped by the Tok Pisin ''braun'' for brown, and the Tok Pisin for bicycle has replaced the former ''aingau''. It is considered a prestigious language and is the primary language of communication in the two major centers of East New Britain: Kokopo and Rabaul. Tol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |