|
Early Childhood Trauma
Early childhood trauma refers to various types of adversity and traumatic events experienced during the early years of a person's life. This is deemed the most critical developmental period in human life by psychologists.Colombo, J. (1982). The critical period concept: Research, methodology, and theoretical issues. Psychological Bulletin, 91(2), 260. A critical period refers to a sensitive time during the early years of childhood in which children may be more vulnerable to be affected by environmental stimulation. These traumatic events can include serious sickness, natural disasters, family violence, sudden separation from a family member, being the victim of abuse, or suffering the loss of a loved one.Copeland, W. E., Keeler, G., Angold, A., & Costello, E. J. (2007). Traumatic events and posttraumatic stress in childhood. ''Archives of General Psychiatry'', ''64''(5), 577-584. Traumatic experiences in early childhood can result in severe consequences throughout adulthood, for inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Childhood Experiences
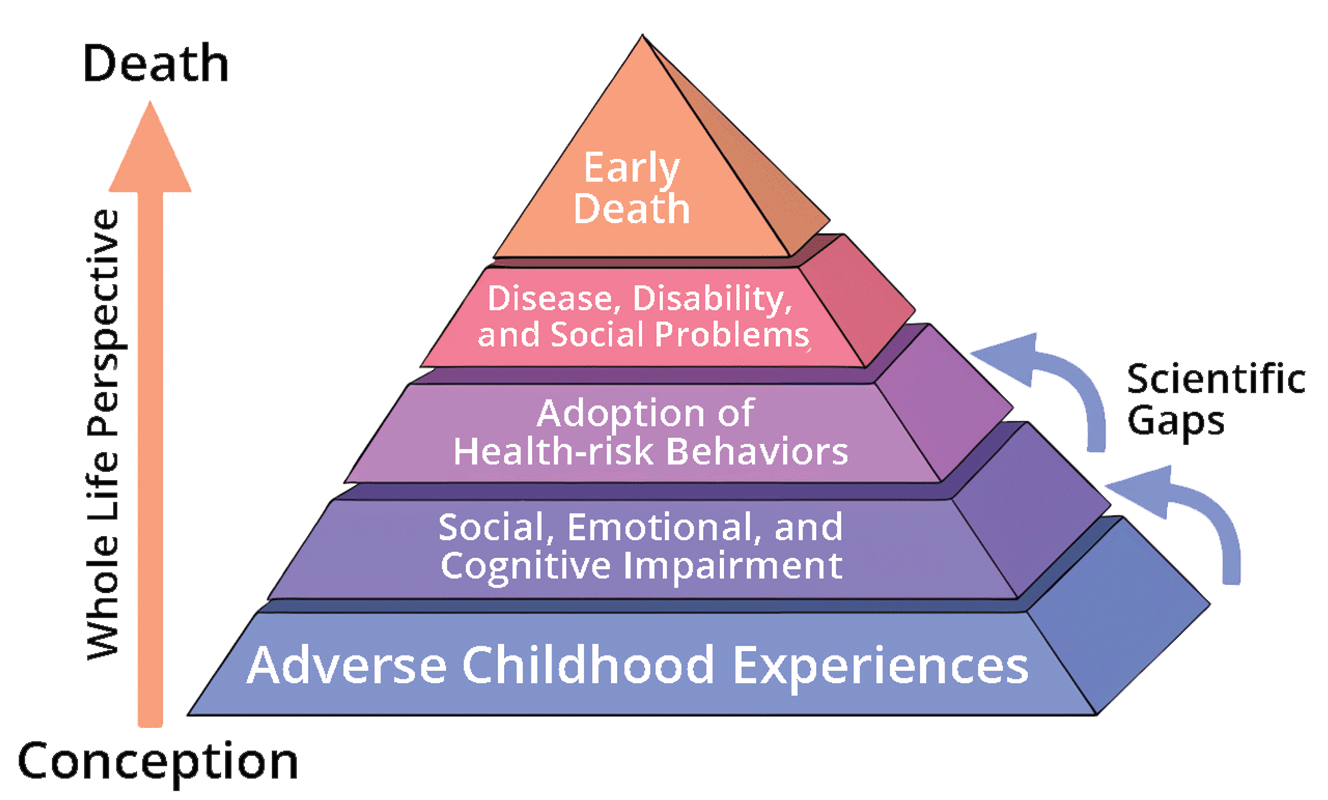
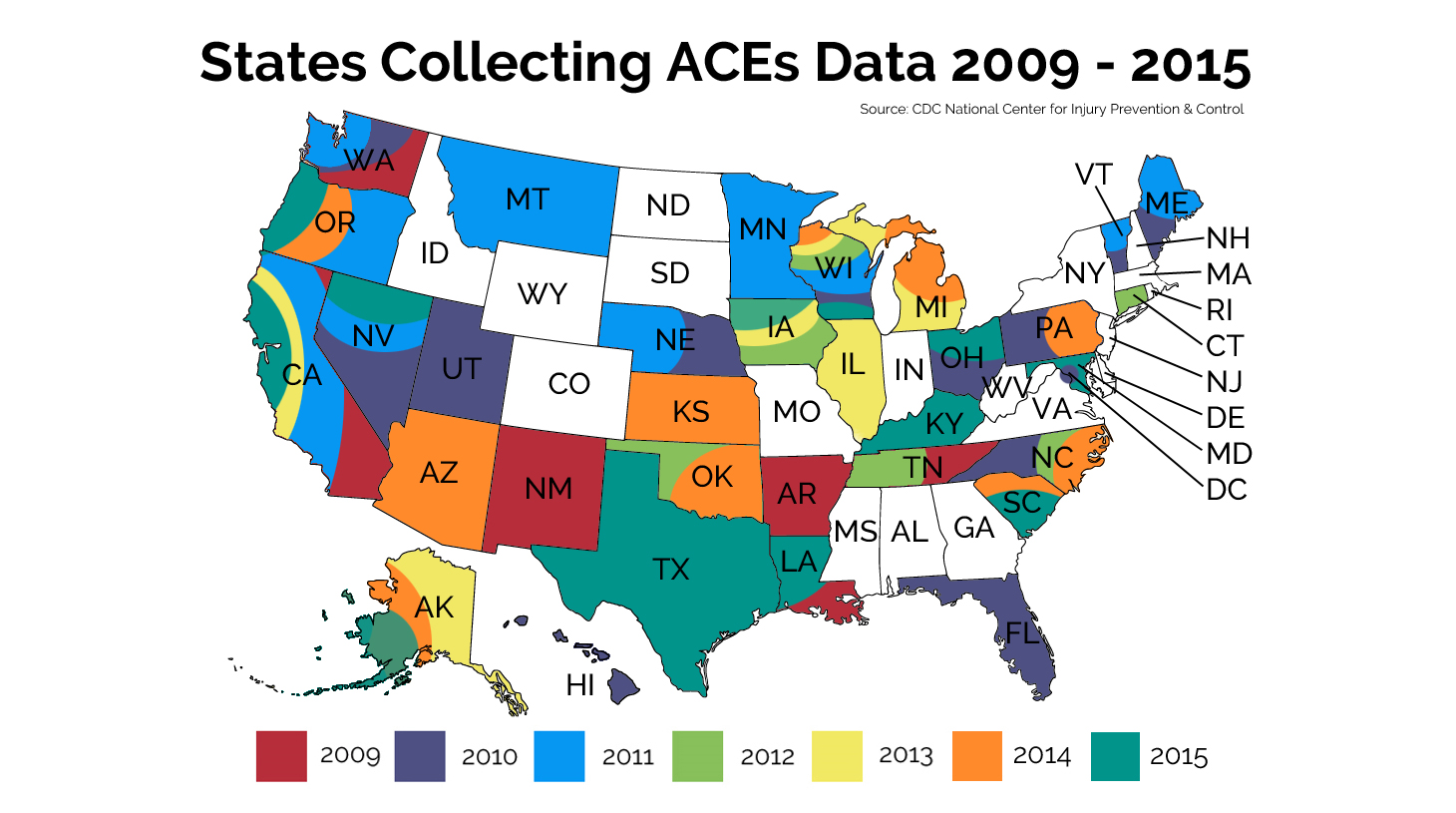
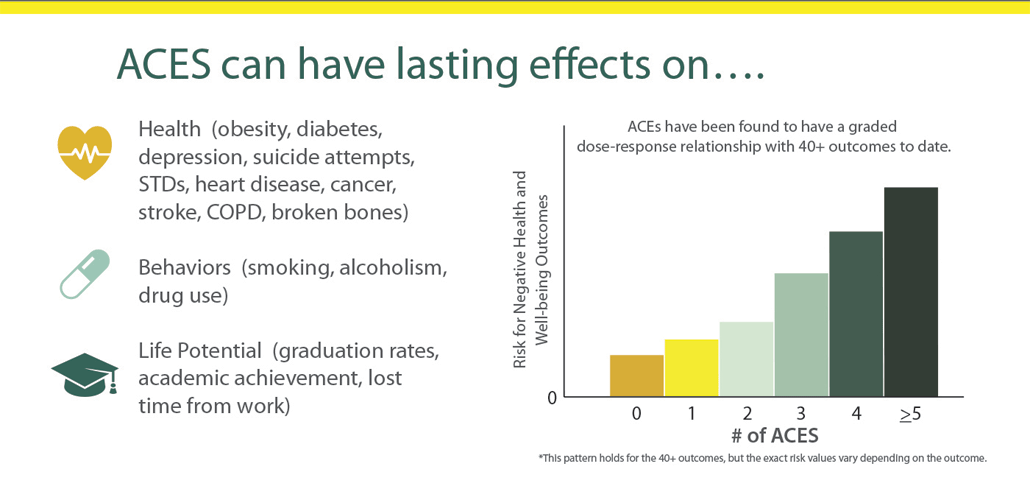
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) encompass various forms of physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction experienced in childhood. The harms of ACEs can be long-lasting, affecting people even in their adulthood. ACEs have been linked to premature death as well as to various health conditions, including those of mental disorders. Toxic stress linked to child abuse is related to a number of neurological changes in the structure of the brain and its function. Definition and types The concept of adverse childhood experiences refers to various traumatic events or circumstances affecting children before the age of 18 and causing mental or physical harm. There are 10 types of ACEs: * physical abuse * sexual abuse * psychological abuse * physical neglect * psychological neglect * witnessing domestic abuse * having a close family member who misused drugs or alcohol * having a close family member with mental health problems * having a close family member wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Period
In developmental psychology and developmental biology, a critical period is a maturational stage in the lifespan of an organism during which the nervous system is especially sensitive to certain environmental stimuli. If, for some reason, the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period" to learn a given skill or trait, it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, to develop certain associated functions later in life. Functions that are indispensable to an organism's survival, such as vision, are particularly likely to develop during critical periods. "Critical period" also relates to the ability to acquire one's first language. Researchers found that people who passed the "critical period" would not acquire their first language fluently. Some researchers differentiate between 'strong critical periods' and 'weak critical periods' (a.k.a. 'sensitive' periods) — defining 'weak critical periods' / 'sensitive periods' as mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverse Childhood Experiences Study
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) encompass various forms of physical and emotional abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction experienced in childhood. The harms of ACEs can be long-lasting, affecting people even in their adulthood. ACEs have been linked to premature death as well as to various health conditions, including those of mental disorders. Toxic stress linked to child abuse is related to a number of neurological changes in the structure of the brain and its function. Definition and types The concept of adverse childhood experiences refers to various traumatic events or circumstances affecting children before the age of 18 and causing mental or physical harm. There are 10 types of ACEs: * physical abuse * sexual abuse * psychological abuse * physical neglect * psychological neglect * witnessing domestic abuse * having a close family member who misused drugs or alcohol * having a close family member with mental health problems * having a close family member who serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Perception
Facial perception is an individual's understanding and interpretation of the face. Here, perception implies the presence of consciousness and hence excludes automated facial recognition systems. Although facial recognition is found in other species, this article focuses on facial perception in humans. The perception of facial features is an important part of social cognition. Information gathered from the face helps people understand each other's identity, what they are thinking and feeling, anticipate their actions, recognize their emotions, build connections, and communicate through body language. Developing facial recognition is a necessary building block for complex societal constructs. Being able to perceive identity, mood, age, sex, and race lets people mold the way we interact with one another, and understand our immediate surroundings. Though facial perception is mainly considered to stem from visual intake, studies have shown that even people born blind can learn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotional Regulation
Emotional self-regulation or emotion regulation is the ability to respond to the ongoing demands of experience with the range of emotions in a manner that is socially tolerable and sufficiently flexible to permit spontaneous reactions as well as the ability to delay spontaneous reactions as needed. It can also be defined as extrinsic and intrinsic processes responsible for monitoring, evaluating, and modifying emotional reactions. Emotional self-regulation belongs to the broader set of emotion regulation processes, which includes both the regulation of one's own feelings and the regulation of other people's feelings. Emotion regulation is a complex process that involves initiating, inhibiting, or modulating one's state or behavior in a given situationfor example, the subjective experience (feelings), cognitive responses (thoughts), emotion-related physiological responses (for example heart rate or hormonal activity), and emotion-related behavior (bodily actions or expressions). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periaqueductal Gray
The periaqueductal gray (PAG, also known as the central gray) is a brain region that plays a critical role in autonomic function, motivated behavior and behavioural responses to threatening stimuli. PAG is also the primary control center for descending pain modulation. It has enkephalin-producing cells that suppress pain. The periaqueductal gray is the gray matter located around the cerebral aqueduct within the tegmentum of the midbrain. It projects to the nucleus raphe magnus, and also contains descending autonomic tracts. The ascending pain and temperature fibers of the spinothalamic tract send information to the PAG via the spinomesencephalic tract (so-named because the fibers originate in the spine and terminate in the PAG, in the mesencephalon or midbrain). This region has been used as the target for brain-stimulating implants in patients with chronic pain. Role in analgesia Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray matter of the midbrain activates enkephalin-releasing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine System
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine systems often act together in a process called neuroendocrine integration, to regulate the physiological processes of the human body. Neuroendocrinology arose from the recognition that the brain, especially the hypothalamus, controls secretion of pituitary gland hormones, and has subsequently expanded to investigate numerous interconnections of the endocrine and nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands throughout the body that produce and secrete hormones of diverse chemical structure, including peptides, steroids, and neuroamines. Collectively, hormones regulate many physiological processes. The neuroendocrine system is the mechanism by which the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, regulating reproduction, metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPA Axis
HPA may refer to: Organizations * Harry Potter Alliance, a charity * Halifax Port Authority, Canada * Hamburg Port Authority, Germany * Hawaii Preparatory Academy, a school in Hawaii, US * Health Protection Agency, UK * Heerespersonalamt, the German Army Personnel Agency 1920-1944 * Hollywood Post Alliance, an American trade organization * Houston Peace Academy of the Islamic Education Institute of Texas, US * Hurlingham Polo Association, UK polo governing body * HPA Toucan human-powered aircraft built by Hertfordshire Pedal Aeronauts People * Hans Peter Anvin (born 1972), Swedish computer programmer * Howlin' Pelle Almqvist (Born 1978), Swedish lead singer of garage rock band The Hives Science * Hectopascal (hPa), a unit of pressure * Human platelet antigen * Human Protein Atlas * Hydrogen pinch analysis * Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in physiology Technology *High-performance addressing, in LCD displays * Host protected area of computer data storage *H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental and behavioral disorder, the experience of depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, motivation, feelings, and sense of well-being. The core symptom of depression is said to be anhedonia, which refers to loss of interest or a loss of feeling of pleasure in certain activities that usually bring joy to people. Depressed mood is a symptom of some mood disorders such as major depressive disorder and dysthymia; it is a normal temporary reaction to life events, such as the loss of a loved one; and it is also a symptom of some physical diseases and a side effect of some drugs and medical treatments. It may feature sadness, difficulty in thinking and concentration and a significant increase or decrease in appetite and time spent sleeping. People experiencing depression may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childhood Trauma
Childhood trauma is often described as serious adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Children may go through a range of experiences that classify as psychological trauma; these might include neglect, abandonment, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, and physical abuse, witnessing abuse of a sibling or parent, or having a mentally ill parent. These events have profound psychological, physiological, and sociological impacts and can have negative, lasting effects on health and well-being such as unsocial behaviors, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and sleep disturbances. Similarly, children with mothers who have experienced traumatic or stressful events during pregnancy can increase the child's risk of mental health disorders and other neurodevelopmental disorders. Kaiser Permanente and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's 1998 study on adverse childhood experiences determined that traumatic experiences during childhood are a root cause of many social, emotion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Abuse
Sexual abuse or sex abuse, also referred to as molestation, is abusive sexual behavior by one person upon another. It is often perpetrated using force or by taking advantage of another. Molestation often refers to an instance of sexual assault against a small child, whereas sexual abuse is a term used for a persistent pattern of sexual assaults. The offender is referred to as a sexual abuser or (often pejoratively) molester. The term also covers behavior by an adult or older adolescent towards a child to stimulate any of the involved sexually. The use of a child, or other individuals younger than the age of consent, for sexual stimulation is referred to as child sexual abuse or statutory rape. Live streaming sexual abuse involves trafficking and coerced sexual acts and or rape in real time on webcam. Victims Spouses Spousal sexual abuse is a form of domestic violence. When the abuse involves threats of unwanted sexual contact or forced sex by a woman's husband or e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that can develop because of exposure to a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event. Young children are less likely to show distress but instead may express their memories through play. A person with PTSD is at a higher risk of suicide and intentional self-harm. Most people who experience traumatic events do not develop PTSD. People who experience interpersonal violence such as rape, other sexual assaults, being kidnapped, stalking, physical abuse by an intimate partner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)