|
ESRO 2B
''ESRO-2B'' or ''Iris'' (''International Radiation Investigation Satellite''; sometimes ''Iris 2'') or sometimes ''ESRO II'' (or ''ESRO 2''), was a European astrophysical spin-stabilised research satellite which was launched in 1968. Operated by the European Space Research Organisation, ESRO 2B made astronomical surveys primarily in x-ray and solar particles detectors. Spacecraft ESRO-2B was an cylindrical spacecraft with a length of 85 cm and a diameter of 76 cm. On 10 December 1968 (approx 195 days since mission start) the on-board tape recorder suffered a mechanical failure. This effectively ended the two X-ray experiments as they did not provide any significant data return from then on. Other experiments could still be operated through ground radio links. ESRO-2B was launched on a Scout B rocket into a highly elliptical near-polar orbit on 17 May 1968. Its predecessor satellite, ''ESRO-2A'' (sometimes ''Iris 1'') failed to reach orbit on 29 May 1967, launchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evidenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Per Minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines. Standards ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensionless unit equal to 1, which it refers to as a revolution, but does not define the revolution as a unit. It defines a unit of rotational frequency equal to s−1. The superseded standard ISO 80000-3:2006 did however state with reference to the unit name 'one', symbol '1', that "The special name revolution, symbol r, for this unit is widely used in specifications on rotating machines." The International System of Units (SI) does not recognize rpm as a unit, and defines the unit of frequency, Hz, as equal to s−1. :\begin 1~&\text &&=& 60~&\text \\ \frac~&\text &&=& 1~&\text \end A corresponding but distinct quantity for describing rotation is angular velocity, for which the SI unit is the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spin-stabilized Satellite
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle/satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, etc. Controlling vehicle attitude requires sensors to measure vehicle orientation, actuators to apply the torques needed to orient the vehicle to a desired attitude, and algorithms to command the actuators based on (1) sensor measurements of the current attitude and (2) specification of a desired attitude. The integrated field that studies the combination of sensors, actuators and algorithms is called guidance, navigation and control (GNC). Overview A spacecraft's attitude must typically be stabilized and controlled for a variety of reasons. It is often needed so that the spacecraft high-gain antenna may be accurately pointed to Earth for communications, so that onboard experiments may accomplish precise pointing for accurate collection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandenberg AFB
Vandenberg Space Force Base , previously Vandenberg Air Force Base, is a United States Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County, California. Established in 1941, Vandenberg Space Force Base is a space launch base, launching spacecraft from the Western Range, and also performs missile testing. The United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 30 serves as the host delta for the base. In addition to its military space launch mission, Vandenberg Space Force Base also performs space launches for civil and commercial space entities, such as NASA and SpaceX. History United States Army Camp Cooke (1941–1953) In 1941, the United States Army embarked on an initiative to acquire lands in the United States to be used to train its infantry and armored forces. These areas needed to be of a varied nature to ensure relevant training. In March 1941, the Army acquired approximately of open ranch lands along the Central Coast of California between Lompoc and Santa Maria. Most of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Orbit
A polar orbit is one in which a satellite passes above or nearly above both poles of the body being orbited (usually a planet such as the Earth, but possibly another body such as the Moon or Sun) on each revolution. It has an inclination of about 60 - 90 degrees to the body's equator. Launching satellites into polar orbit requires a larger launch vehicle to launch a given payload to a given altitude than for a near-equatorial orbit at the same altitude, because it cannot take advantage of the Earth's rotational velocity. Depending on the location of the launch site and the inclination of the polar orbit, the launch vehicle may lose up to 460 m/s of Delta-v, approximately 5% of the Delta-v required to attain Low Earth orbit. Usage Polar orbits are used for Earth-mapping, reconnaissance satellites, as well as for some weather satellites.Science Focus 2nd Edition 2, pg. 297 The Iridium satellite constellation uses a polar orbit to provide telecommunications services. Near-polar orb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
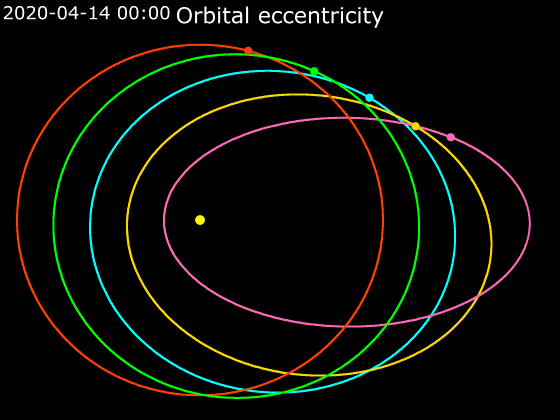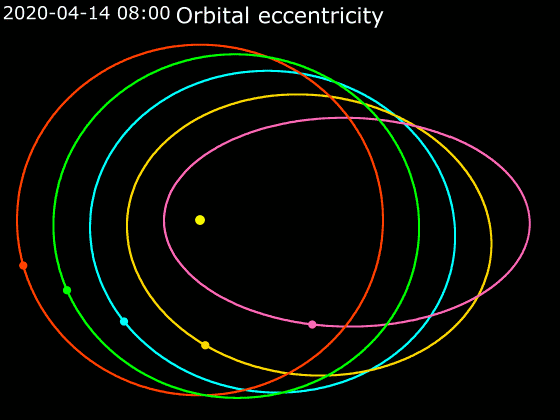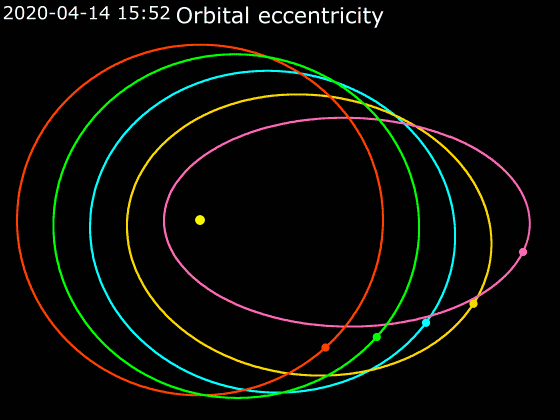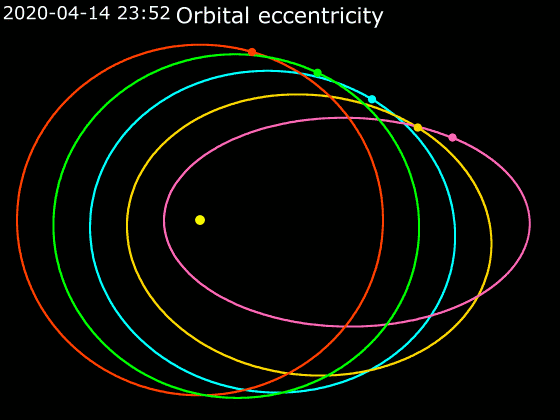
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. In a stricter sense, it is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity greater than 0 and less than 1 (thus excluding the circular orbit). In a wider sense, it is a Kepler's orbit with negative energy. This includes the radial elliptic orbit, with eccentricity equal to 1. In a gravitational two-body problem with negative energy, both bodies follow similar elliptic orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. Also the relative position of one body with respect to the other follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include: Hohmann transfer orbit, Molniya orbit, and tundra orbit. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies m1 and m2, the orbital speed (v\,) of one body trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scout (rocket Family)
The Scout family of rockets were American launch vehicles designed to place small satellites into orbit around the Earth. The Scout multistage rocket was the first orbital launch vehicle to be entirely composed of solid fuel stages. It was also the only vehicle of that type until the successful launch of the Japanese Lambda 4S in 1970. The original Scout (an acronym for Solid Controlled Orbital Utility Test system) was designed in 1957 at the NACA, at Langley center. Scout launch vehicles were used from 1961 until 1994. To enhance reliability the development team opted to use "off the shelf" hardware, originally produced for military programs. According to the NASA fact sheet: "... the first stage motor was a combination of the Jupiter Senior and the Navy Polaris; the second stage came from the Army MGM-29 Sergeant; and the third and fourth stage motors were designed by Langley engineers who adapted a version of the Navy Vanguard." The first successful orbital launch of a Sco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Tape Data Storage
Magnetic-tape data storage is a system for storing digital information on magnetic tape using digital recording. Tape was an important medium for primary data storage in early computers, typically using large open reels of IBM 7 track, 7-track, later 9-track tape, 9-track tape. Modern magnetic tape is most commonly packaged in cartridges and cassettes, such as the widely supported Linear Tape-Open (LTO) and IBM 3592 series. The device that performs the writing or reading of data is called a tape drive. Autoloader (data storage device), Autoloaders and tape library, tape libraries are often used to automate cartridge handling and exchange. Compatibility was important to enable transferring data. Tape data storage is now used more for system backup, data archive and data exchange. The low cost of tape has kept it viable for long-term storage and archive. Open reels Initially, magnetic tape for data storage was wound on reels. This standard for large computer systems persis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Energetic Particles
Solar energetic particles (SEP), formerly known as solar cosmic rays, are high-energy, charged particles originating in the solar atmosphere and solar wind. They consist of protons, electrons and heavy ions with energies ranging from a few tens of keV to many GeV. The exact processes involved in transferring energy to SEPs is a subject of ongoing study. SEPs are relevant to the field of space weather, as they are responsible for SEP events and ground level enhancements. History SEPs were first detected in February and March 1942 by Scott Forbush indirectly as ground level enhancements. Solar particle events SEPs are accelerated during solar particle events. These can originate either from a solar flare site or by shock waves associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs). However, only about 1% of CMEs produce strong SEP events. Two main mechanisms of acceleration are possible: diffusive shock acceleration (DSA, an example of second-order Fermi acceleration) or the shock-drif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |