|
EF-2
Elongation factors are a set of proteins that function at the ribosome, during protein synthesis, to facilitate translational elongation from the formation of the first to the last peptide bond of a growing polypeptide. Most common elongation factors in prokaryotes are EF-Tu, EF-Ts, EF-G. Bacteria and eukaryotes use elongation factors that are largely homologous to each other, but with distinct structures and different research nomenclatures. Elongation is the most rapid step in translation. In bacteria, it proceeds at a rate of 15 to 20 amino acids added per second (about 45-60 nucleotides per second). In eukaryotes the rate is about two amino acids per second (about 6 nucleotides read per second). Elongation factors play a role in orchestrating the events of this process, and in ensuring the high accuracy translation at these speeds. Nomenclature of homologous EFs In addition to their cytoplasmic machinery, eukaryotic mitochondria and plastids have their own translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually start two to five days after exposure. Symptoms often come on fairly gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever. In severe cases, a grey or white patch develops in the throat. This can block the airway and create a barking cough as in croup. The neck may swell in part due to enlarged lymph nodes. A form of diphtheria which involves the skin, eyes or genitals also exists. Complications may include myocarditis, inflammation of nerves, kidney problems, and bleeding problems due to low levels of platelets. Myocarditis may result in an abnormal heart rate and inflammation of the nerves may result in paralysis. Diphtheria is usually spread between people by direct contact or through th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphtheria Toxin
Diphtheria toxin is an exotoxin secreted by '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae'', the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. The toxin gene is encoded by a prophageA prophage is a virus that has inserted itself into the genome of the host bacterium. called corynephage β. The toxin causes the disease in humans by gaining entry into the cell cytoplasm and inhibiting protein synthesis. Structure Diphtheria toxin is a single polypeptide chain of 535 amino acids consisting of two subunits linked by disulfide bridges, known as an A-B toxin. Binding to the cell surface of the B subunit (the less stable of the two subunits) allows the A subunit (the more stable part of the protein) to penetrate the host cell. The crystal structure of the diphtheria toxin homodimer has been determined to 2.5 Ångstrom resolution. The structure reveals a Y-shaped molecule consisting of three domains. Fragment A contains the catalytic C domain, and fragment B consists of the T and R domains: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EEF-2
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EEF2'' gene. It is the archaeal and eukaryotic counterpart of bacterial EF-G. This gene encodes a member of the GTP-binding translation elongation factor family. This protein is an essential factor for protein synthesis. It promotes the GTP-dependent translocation of the ribosome. This protein is completely inactivated by EF-2 kinase phosphorylation. aEF2/eEF2 found in most archaea and eukaryotes, including humans, contains a post translationally modified histidine diphthamide. It is the target of diphtheria toxin (from ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''), and exotoxin A (from ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerugi ...''). The inactivation of EF-2 by toxins inhibits protei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (genetics)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached at the start codon. # Elongation: The last tRNA validated by the small ribosomal subunit (''accommodation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corynebacterium Diphtheriae
''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'' is the pathogenic bacterium that causes diphtheria. It is also known as the Klebs–Löffler bacillus, because it was discovered in 1884 by German bacteriologists Edwin Klebs (1834–1912) and Friedrich Löffler (1852–1915). The bacteria are usually harmless unless they are infected by a bacteriophage that carries a gene that gives rise to a toxin. This toxin causes the disease. Diphtheria is caused by the adhesion and infiltration of the bacteria into the mucosal layers of the body, primarily affecting the respiratory tract and the subsequent release of an endotoxin. The toxin has a localized effect on skin lesions, as well as a metastatic, proteolytic effects on other organ systems in severe infections. Originally a major cause of childhood mortality, diphtheria has been almost entirely eradicated due to the vigorous administration of the diphtheria vaccination in the 1910s. Diphtheria is no longer transmitted as frequently due to the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
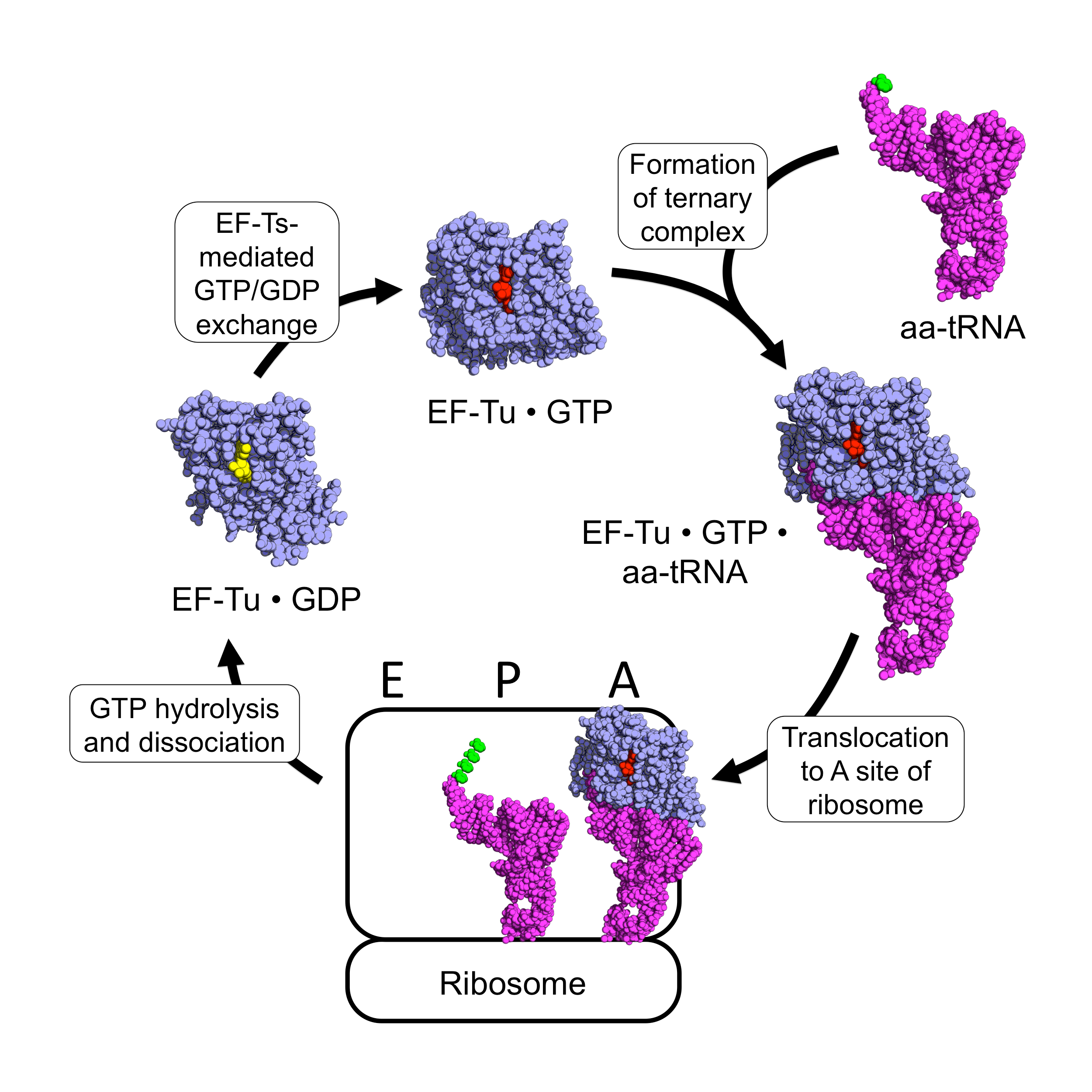
EF-Tu
EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to the A-site of the ribosome. As a reflection of its crucial role in translation, EF-Tu is one of the most abundant and highly conserved proteins in prokaryotes. It is found in eukaryotic mitochondria as TUFM. As a family of elongation factors, EF-Tu also includes its eukaryotic and archaeal homolog, the alpha subunit of eEF-1 (EF-1A). Background Elongation factors are part of the mechanism that synthesizes new proteins through translation in the ribosome. Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) carry the individual amino acids that become integrated into a protein sequence, and have an anticodon for the specific amino acid that they are charged with. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information that encodes the primary structure of a protein, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TSFM
Elongation factor Ts, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TSFM'' gene. It is an EF-Ts EF-Ts (elongation factor thermo stable) is one of the prokaryotic elongation factors. It is found in human mitochrondria as TSFM. It is similar to eukaryotic EF-1B. EF-Ts serves as the guanine nucleotide exchange factor for EF-Tu (elongatio ... homolog. References Further reading * * * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-12-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIF-5A
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EIF5A'' gene. It is the only known protein to contain the unusual amino acid hypusine 'N''ε-(4-amino-2-hydroxybutyl)-lysine which is synthesized on eIF5A at a specific lysine residue from the polyamine spermidine by two catalytic steps. EF-P is the bacterial homolog of eIF5A, which is modified post-translationally in a similar but distinct way. Both proteins are believed to catalyze peptide bond formation and help resolve ribosomal stalls, making them elongation factors despite the "initiation factor Initiation factors are proteins that bind to the small subunit of the ribosome during the initiation of translation, a part of protein biosynthesis. Initiation factors can interact with repressors to slow down or prevent translation. They have t ..." name originally assigned. Clinical relevance Germline deleterious heterozygous ''EIF5A'' variants causFaundes-Banka syndrome This rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EF-4
Elongation factor 4 (EF-4) is an elongation factor that is thought to back- translocate on the ribosome during the translation of RNA to proteins. It is found near-universally in bacteria and in eukaryotic endosymbiotic organelles including the mitochondria and the plastid. Responsible for proofreading during protein synthesis, EF-4 is a recent addition to the nomenclature of bacterial elongation factors. Prior to its recognition as an elongation factor, EF-4 was known as leader peptidase A (LepA), as it is the first cistron on the operon carrying the bacterial leader peptidase. In eukaryotes it is traditionally called GUF1 (GTPase of Unknown Function 1). It has the preliminary EC number 3.6.5.n1. Evolutionary background LepA has a highly conserved sequence. LepA orthologs have been found in bacteria and almost all eukaryotes. The conservation in LepA has been shown to cover the entire protein. More specifically, the amino acid identity of LepA among bacterial ortholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TUFM
Elongation factor Tu, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TUFM'' gene. It is an EF-Tu EF-Tu (elongation factor thermo unstable) is a prokaryotic elongation factor responsible for catalyzing the binding of an aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) to the ribosome. It is a G-protein, and facilitates the selection and binding of an aa-tRNA to th ... homolog. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Release Factor
A release factor is a protein that allows for the termination of translation by recognizing the termination codon or stop codon in an mRNA sequence. They are named so because they release new peptides from the ribosome. Background During translation of mRNA, most codons are recognized by "charged" tRNA molecules, called aminoacyl-tRNAs because they are adhered to specific amino acids corresponding to each tRNA's anticodon. In the standard genetic code, there are three mRNA stop codons: UAG ("amber"), UAA ("ochre"), and UGA ("opal" or "umber"). Although these stop codons are triplets just like ordinary codons, they are not decoded by tRNAs. It was discovered by Mario Capecchi in 1967 that, instead, tRNAs do not ordinarily recognize stop codons at all, and that what he named "release factor" was not a tRNA molecule but a protein. Later, it was demonstrated that different release factors recognize different stop codons. Classification There are two classes of release factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GFM1
Elongation factor G 1, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GFM1'' gene. It is an EF-G homolog. Eukaryotes contain two protein translational systems, one in the cytoplasm and one in the mitochondria. Mitochondrial translation is crucial for maintaining mitochondrial function and mutations in this system lead to a breakdown in the respiratory chain-oxidative phosphorylation system and to impaired maintenance of mitochondrial DNA. This gene encodes one of the mitochondrial translation elongation factors. Its role in the regulation of normal mitochondrial function and in different disease states attributed to mitochondrial dysfunction is not known. Model organisms Model organisms have been used in the study of GFM1 function. A conditional knockout mouse line, called ''Gfm1tm1a(EUCOMM)Wtsi'' was generated as part of the International Knockout Mouse Consortium program — a high-throughput mutagenesis project to generate and distribute animal models of disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |