|
E11 European Long Distance Path
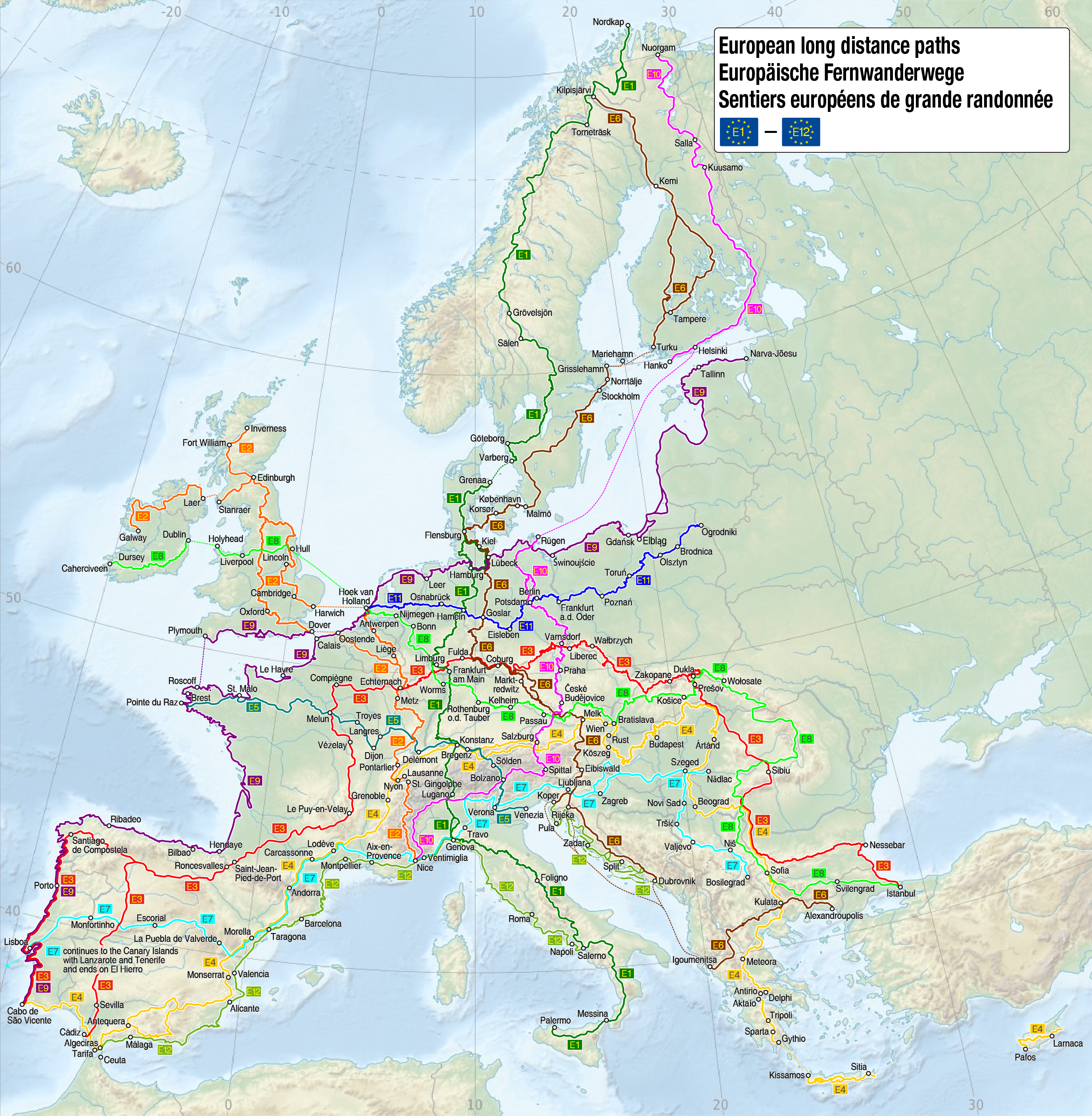
The E11 European long distance path or E11 path is one of the European long-distance paths, running 4700 km (about 2900 miles) west-east from The Hague in the Netherlands through Germany, Poland, Lithuania, Latvia to Tallinn, Estonia. It starts in Scheveningen, a fishing community, commercial harbor and spa in The Hague on the Dutch coast of the North Sea. It ends in Tallinn, a medieval Hanseatic town situated side by side with the 21st century city of modern glass buildings, located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea. The E11 is one of three European long distance paths running East from the Benelux to the Baltic states. In the North, following the German, Polish, Lithuanian, Latvian and Estonian coasts of North Sea and Baltic Sea, the E9 offers a variety of polders, sandy and rocky beaches, dunes, coastal meadows and commercial harbors. In Estonia the route goes along the very seashore for around 100 km, mainly between Haapsalu and Tallinn. But in ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Long-distance Path
The European long-distance paths (alternatively, abbreviated as E-paths) are a network of long-distance footpaths that traverse Europe. While most long-distance footpaths in Europe are located in just one country or region, each of these numbered European long-distance paths passes through many different countries. The first long-distance hiking trail in Europe was the National Blue Trail of Hungary, established in 1938. The formation of the European Union made transnational hiking trails possible. Today the network consists of 12 paths and covers more than , crisscrossing Europe. In general the routes connect and make use of existing national and local trails such as the GR footpaths. The paths are officially designated by the European Ramblers' Association. List See also *Geography of Europe *GR footpath *EuroVelo, the European cycle route network *Long-distance trails in the United States References External links {{commons category, European long-distance pathsOverview o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tick-borne Disease
Tick-borne diseases, which afflict humans and other animals, are caused by infectious agents transmitted by tick bites. They are caused by infection with a variety of pathogens, including rickettsia and other types of bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. The economic impact of tick-borne diseases is considered to be substantial in humans, and tick-borne diseases are estimated to affect ~80 % of cattle worldwide. 18 tick-borne pathogens have been identified in the United States according to the Centers for Disease Control and at least 27 are known globally. New tick-borne diseases have been discovered in the 21st century, due in part to the use of molecular assays and next-generation sequencing. The occurrence of ticks and tick-borne illnesses in humans is increasing. Tick populations are spreading into new areas, in part due to climate change. Tick populations are also affected by changes in the populations of their hosts (e.g. deer, cattle, mice, lizards) and those hosts' p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polders
A polder () is a low-lying tract of land that forms an artificial hydrological entity, enclosed by embankments known as dikes. The three types of polder are: # Land reclaimed from a body of water, such as a lake or the seabed # Flood plains separated from the sea or river by a dike # Marshes separated from the surrounding water by a dike and subsequently drained; these are also known as ''koogs'', especially in Germany The ground level in drained marshes subsides over time. All polders will eventually be below the surrounding water level some or all of the time. Water enters the low-lying polder through infiltration and water pressure of groundwater, or rainfall, or transport of water by rivers and canals. This usually means that the polder has an excess of water, which is pumped out or drained by opening sluices at low tide. Care must be taken not to set the internal water level too low. Polder land made up of peat (former marshland) will sink in relation to its previous l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |