|
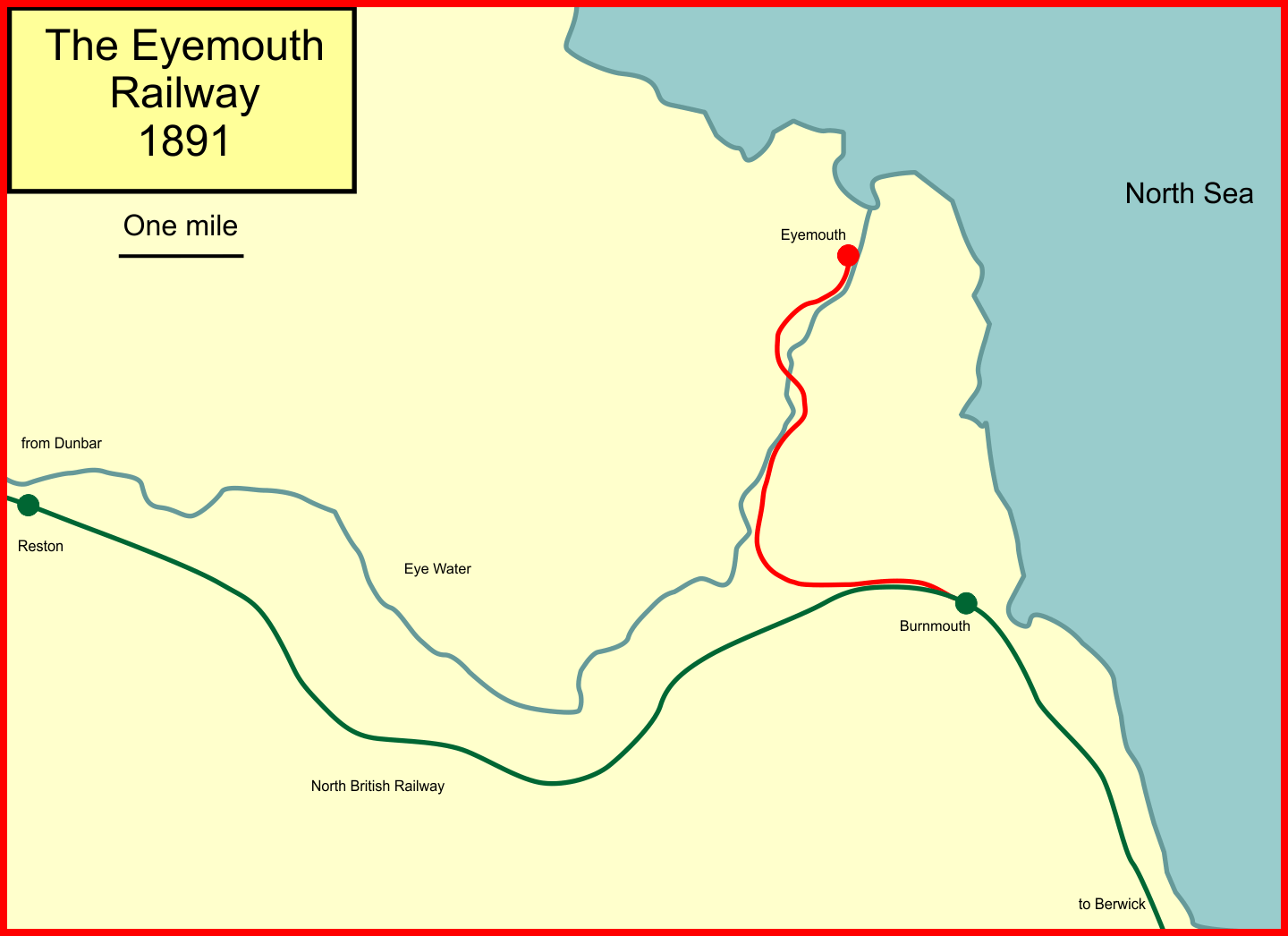
Eyemouth Railway
The Eyemouth Railway was a three-mile single track branch railway, connecting Eyemouth, in the Scottish Borders, Scotland, with Burnmouth on the main line between Dunbar and Berwick-upon-Tweed. It was built by a local company, but they struggled to raise money, and the line was in effect funded by local wealthy businessmen. It opened in 1891. In 1948 there was very heavy rainfall, and the viaduct that carried the line over the Eye Water was partly undermined, and the line was closed for year while repairs were undertaken. The line later succumbed to road competition, and it closed in 1962. Formation As early as 1846, when the North British Railway was in the earliest stages of its railway operation, representatives of the village of Eyemouth requested a branch line connection. At this period the North British was hugely committed financially and was concentrating on securing territory that might be attractive for competing railway companies to enter. Eyemouth did not fall in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
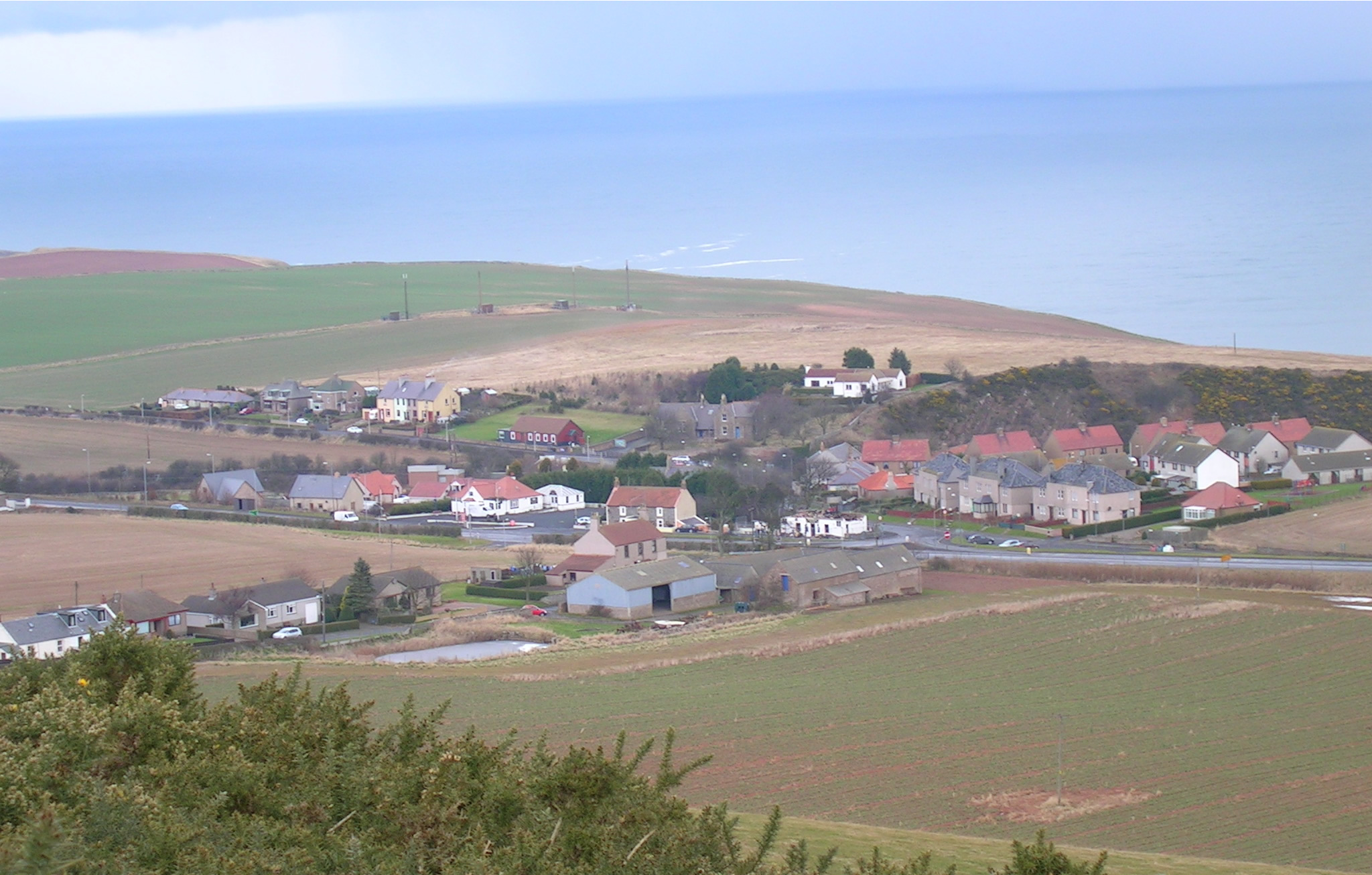
Eyemouth
Eyemouth ( sco, Heymooth) is a small town and civil parish in Berwickshire, in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland. It is east of the main north–south A1 road and north of Berwick-upon-Tweed. The town's name comes from its location at the mouth of the Eye Water river. The Berwickshire coastline consists of high cliffs over deep clear water with sandy coves and picturesque harbours. A fishing port, Eyemouth holds a yearly Herring Queen Festival. Notable buildings in the town include Gunsgreen House and a cemetery watch-house built to stand guard against the Resurrectionists (body snatchers). Many of the features of a traditional fishing village are preserved in the narrow streets and ' vennels'. Eyemouth is not far from the small villages of Ayton, Reston, St Abbs, Coldingham, and Burnmouth, all in Berwickshire. The coast offers opportunities for birdwatching, walking, fishing and diving. Accommodation includes several hotels, B&Bs and a holiday park. History Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hay, 10th Marquess Of Tweeddale
William Montagu Hay, 10th Marquess of Tweeddale, KT, DL (29 January 1826 – 25 November 1911), known before 1878 as Lord William Hay or Lord William Montagu Hay, was a Scottish landowner, peer and politician. He was born at Yester House, near Gifford, East Lothian, and served in British India as a member of the Bengal Civil Service and later as a Liberal Member of Parliament. In 1878 he succeeded his brother as Marquess of Tweeddale and as owner of some 40,000 acres in Scotland. He went on to become Lord High Commissioner to the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland and was appointed a Knight of the Thistle. Early life Hay was born at Yester House on 29 January 1826. He was the third son (of six sons and eight daughters) born to Lady Susan Montagu and George Hay, 8th Marquess of Tweeddale (1787–1876).George Edward Cokayne, ed. Vicary Gibbs, ''The Complete Peerage of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain'', vol. 12, part 2 (1959), p. 84 Among his many prominent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Lines Opened In 1891
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Closed Railway Lines In Scotland
Closed may refer to: Mathematics * Closure (mathematics), a set, along with operations, for which applying those operations on members always results in a member of the set * Closed set, a set which contains all its limit points * Closed interval, an interval which includes its endpoints * Closed line segment, a line segment which includes its endpoints * Closed manifold, a compact manifold which has no boundary Other uses * Closed (poker), a betting round where no player will have the right to raise * ''Closed'' (album), a 2010 album by Bomb Factory * Closed GmbH, a German fashion brand * Closed class, in linguistics, a class of words or other entities which rarely changes See also * * Close (other) * Closed loop (other) * Closing (other) * Closure (other) * Open (other) Open or OPEN may refer to: Music * Open (band), Australian pop/rock band * The Open (band), English indie rock band * ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969 * ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice Girder
A lattice girder is a truss girder where the load is carried by a web of latticed metal. Overview The lattice girder was used prior to the development of larger rolled steel plates. It has been supplanted in modern construction with welded or bolted plate girders, which use more material but have lower fabrication and maintenance costs. The term is also sometimes used to refer to a laced strut or laced tie, structural members commonly made using a combination of structural sections connected with diagonal lacing. This form allows a strut to resist axial compression and a (tie) to resist axial tension. A lattice girder, like any girder, primarily resists bending. The component sections may typically include metal beams, channel and angle sections, with the lacing elements either metal plate strips, or angle sections. The lacing elements are typically attached using either hot rivets or threaded locator bolts. As with lattice girders, laced struts and ties have generally b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burnmouth Station Site Of 1950591 2ba2f43b
Burnmouth is a small fishing village located adjacent to the A1 road on the east coast of Scotland. It is the first village in Scotland on the A1, after crossing the border with England. Burnmouth is located in the Parish of Ayton, in the Scottish Borders area of Scotland and governed by Scottish Borders Council. Burnmouth lies at the point where a burn slices through the high cliffs lining this coast en route to the sea. There may have been a mill here in the Middle Ages, but little else until a fishing harbour was built in the 1830s, later extended in 1879 and 1959. The East Coast Main Line railway passes along the top of the cliff here, and was once served by Burnmouth railway station from 1846 to 1962. The Berwickshire Coastal Path is nearby. Burnmouth itself is split into two areas: Upper Burnmouth and Lower Burnmouth. Upper Burnmouth is sited at the top of the cliff. Lower Burnmouth is hidden away at the foot of cliff and stretches out along the foreshore. Lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir James Percy Miller, 2nd Baronet
Sir James Percy Miller, 2nd Baronet, (22 October 1864 – 22 January 1906) was a British soldier, known as a racehorse owner. Over the 17 years when he had horses in training, Miller won 161 races, worth £114,005. Life Miller was the eldest surviving son of Sir William Miller, 1st Baronet, by Mary Anne, daughter of John Farley Leith, a Queen's Counsel and Member of Parliament for Aberdeen. He was educated at Eton College and Sandhurst. Miller was a Captain in the 14th Hussars from 1885 to 1892, and Adjutant from 1888 to 1892; and served in the Second Boer War from 1900 where in 1901 he was second in command of the sixth battalion, Imperial Yeomanry. He was made an Hon. Major in the army in 1901 and became a full Major in the Lothians and Berwickshire Imperial Yeomanry from March 1902. He was mentioned in dispatches, and was awarded the Distinguished Service Order. Miller was a Deputy Lieutenant and Justice of the Peace for Berwickshire. His father's fortune, made from herr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Borders
The Scottish Borders ( sco, the Mairches, 'the Marches'; gd, Crìochan na h-Alba) is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. It borders the City of Edinburgh, Dumfries and Galloway, East Lothian, Midlothian, South Lanarkshire, West Lothian and, to the south-west, south and east, the English counties of Cumbria and Northumberland. The administrative centre of the area is Newtown St Boswells. The term Scottish Borders, or normally just "the Borders", is also used to designate the areas of southern Scotland and northern England that bound the Anglo-Scottish border. Geography The Scottish Borders are in the eastern part of the Southern Uplands. The region is hilly and largely rural, with the River Tweed flowing west to east through it. The highest hill in the region is Broad Law in the Manor Hills. In the east of the region, the area that borders the River Tweed is flat and is known as 'The Merse'. The Tweed and its tributaries drain the entire region with the river flowi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyemouth Disaster
The Eyemouth disaster was a severe European windstorm that struck the south-eastern coast of Scotland on 14 October 1881. One hundred and eighty-nine fishermen, most of whom were from Eyemouth, were drowned. Many citizens of Eyemouth call the day Black Friday. Disaster Following a period of poor weather, the morning of 14 October was calm. Though the storm was predicted (as the barometric pressure was very low), the fishing fleets put to sea through economic necessity. Many of the fishing boats were either capsized, or wrecked against the coastline. Casualties *Eyemouth - 129 *Burnmouth - 24 * Newhaven - 17 *Cove - 11 *Fisherrow - 7 * Coldingham Shore - 3 Some boats that had not capsized were wrecked on the Hurkar Rocks. Many houses were also destroyed. Two days later, the ''Ariel Gazelle'' turned up in Eyemouth, having braved the storm instead of fleeing. Aftermath A donation-led relief fund was established to provide financial security to families who had lost member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North British Railway
The North British Railway was a British railway company, based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1844, with the intention of linking with English railways at Berwick. The line opened in 1846, and from the outset the company followed a policy of expanding its geographical area, and competing with the Caledonian Railway in particular. In doing so it committed huge sums of money, and incurred shareholder disapproval that resulted in two chairmen leaving the company. Nonetheless the company successfully reached Carlisle, where it later made a partnership with the Midland Railway. It also linked from Edinburgh to Perth and Dundee, but for many years the journey involved a ferry crossing of the Forth and the Tay. Eventually the North British built the Tay Bridge, but the structure collapsed as a train was crossing in high wind. The company survived the setback and opened a second Tay Bridge, followed soon by the Forth Bridge, which together transformed the railway networ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |