|
Extensible Messaging And Presence Protocol
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP, originally named Jabber) is an Open standard, open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML (Extensible Markup Language), it enables the near-real-time exchange of structured data between two or more network entities. Designed to be Extensibility, extensible, the protocol offers a multitude of applications beyond traditional IM in the broader realm of message-oriented middleware, including signalling for Voice over IP, VoIP, video, file transfer, Game, gaming and other uses. Unlike most commercial instant messaging protocols, XMPP is defined in an open standard in the application layer. The architecture of the XMPP network is similar to email; anyone can run their own XMPP server and there is no central master server. This Federation (information technology), federated open system (computing), open system approach allows users to interoperate with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XAMPP
XAMPP ( or ) is a free and open-source cross-platform web server solution stack package developed by Apache Friends, consisting mainly of the Apache HTTP Server, MariaDB database, and interpreters for scripts written in the PHP and Perl programming languages. Since most actual web server deployments use the same components as XAMPP, it makes transitioning from a local test server to a live server possible. XAMPP's ease of deployment means a WAMP or LAMP stack can be installed quickly and simply on an operating system by a developer, with the advantage that common add-in applications such as WordPress and Joomla! can also be installed with similar ease using Bitnami. Etymology The term XAMPP is an apparent acronym. However, there is no official acronym expansion specified on the Apache Friends website. Their homepage header reads "XAMPP Apache + MariaDB + PHP + Perl", indicating that this abbreviation is a recursive acronym. The term can be unofficially broken down as follows: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Email
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
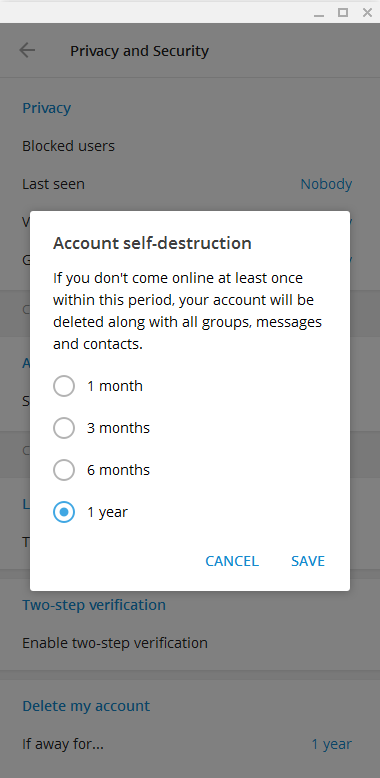
Telegram (software)
Telegram Messenger is a globally accessible freemium, cross-platform, encrypted, cloud-based and centralized instant messaging (IM) service. The application also provides optional end-to-end encrypted chats, popularly known as secret chat and video calling, VoIP, file sharing and several other features. It was launched for iOS on 14 August 2013 and Android on 20 October 2013. The servers of Telegram are distributed worldwide with five data centers in different parts of the world, while the operational center is based in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. Various client apps are available for desktop and mobile platforms including official apps for Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, and Linux (although registration requires an iOS or Android device and a working phone number). There are also two official Telegram web twin apps, WebK and WebZ, and numerous unofficial clients that make use of Telegram's protocol. Telegram's official components are open source, with the exception of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WhatsApp
WhatsApp (also called WhatsApp Messenger) is an internationally available freeware, cross-platform, centralized instant messaging (IM) and voice-over-IP (VoIP) service owned by American company Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook). It allows users to send text and voice messages, make voice and video calls, and share images, documents, user locations, and other content. WhatsApp's client application runs on mobile device A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physica ...s, and can be accessed from computers. The service requires a cellular network, cellular telephone number, mobile telephone number to sign up. In January 2018, WhatsApp released a standalone business app called WhatsApp Business which can communicate with the standard WhatsApp client. The client application was cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows Live Messenger
MSN Messenger (also known colloquially simply as "Messenger"), later rebranded as Windows Live Messenger, was a cross-platform instant messaging client, instant-messaging client developed by Microsoft. It connected to the Microsoft Messenger service and, in later versions, was compatible with Yahoo! Messenger and Facebook Messenger. Versions were developed for Windows, Xbox 360, Mac OS X (later under the name Microsoft Messenger for Mac), BlackBerry OS, iOS, Java ME, S60 (software platform), S60 on Symbian OS 9.x, MSN TV, Zune HD, Windows Phone, Windows Mobile and Windows CE. The client was first released as MSN Messenger Service on July 22, 1999, and was marketed under the MSN brand until 2005, when it was rebranded under the Windows Live name. It has since been officially known by the latter name, although its first name remained in common use. In June 2009, Microsoft reported the service attracted over 330 million active users each month, placing it among the most widely used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIM (software)
AIM (AOL Instant Messenger) was an instant messaging and presence information, presence computer program created by AOL, which used the proprietary software, proprietary OSCAR protocol, OSCAR instant messaging protocol and the TOC protocol to allow registered users to communicate in real time. AIM was popular by the late 1990s, in United States and other countries, and was the leading instant messaging application in that region into the following decade. Teens and college students were known to use the messenger's away message feature to keep in touch with friends, often frequently changing their away message throughout a day or leaving a message up with one's computer left on to inform buddies of their ongoings, location, parties, thoughts, or jokes. AIM's popularity declined as AOL subscribers started decreasing and steeply towards the 2010s, as Gmail's Google Talk, SMS, and Internet social networks, like Facebook gained popularity. Its fall has often been compared with other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Client–server Model
The client–server model is a distributed application structure that partitions tasks or workloads between the providers of a resource or service, called servers, and service requesters, called clients. Often clients and servers communicate over a computer network on separate hardware, but both client and server may reside in the same system. A server host runs one or more server programs, which share their resources with clients. A client usually does not share any of its resources, but it requests content or service from a server. Clients, therefore, initiate communication sessions with servers, which await incoming requests. Examples of computer applications that use the client–server model are email, network printing, and the World Wide Web. Client and server role The "client–server" characteristic describes the relationship of cooperating programs in an application. The server component provides a function or service to one or many clients, which initiate requests for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is an Internet standard communication protocol for electronic mail transmission. Mail servers and other message transfer agents use SMTP to send and receive mail messages. User-level email clients typically use SMTP only for sending messages to a mail server for relaying, and typically submit outgoing email to the mail server on port 587 or 465 per . For retrieving messages, IMAP (which replaced the older POP3) is standard, but proprietary servers also often implement proprietary protocols, e.g., Exchange ActiveSync. SMTP's origins began in 1980, building on concepts implemented on the ARPANET since 1971. It has been updated, modified and extended multiple times. The protocol version in common use today has extensible structure with various extensions for authentication, encryption, binary data transfer, and internationalized email addresses. SMTP servers commonly use the Transmission Control Protocol on port number 25 (for plaintext) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XMPP Standards Foundation
XMPP Standards Foundation (XSF) is the foundation in charge of the standardization of the protocol extensions of XMPP, the open standard of instant messaging and presence of the IETF. History The XSF was originally called the Jabber Software Foundation (JSF). The Jabber Software Foundation was originally established to provide an independent, non-profit, legal entity to support the development community around Jabber technologies (and later XMPP). Originally its main focus was on developing JOSL, the Jabber Open Source License (since deprecated), and an open standards process for documenting the protocols used in the Jabber/XMPP developer community. Its founders included Michael Bauer and Peter Saint-Andre. Process Members of the XSF vote on acceptance of new members, a technical Council, and a Board of Directors. However, membership is not required to publish, view, or comment on the standards that it promulgates. The unit of work at the XSF is the XMPP Extension Protoco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Software
Commercial software, or seldom payware, is a computer software that is produced for sale or that serves commercial purposes. Commercial software can be proprietary software or free and open-source software. Background and challenge While software creation by programming is a time and labor-intensive process, comparable to the creation of physical goods, the reproduction, duplication and sharing of software as digital goods is in comparison disproportionately easy. No special machines or expensive additional resources are required, unlike almost all physical goods and products. Once a software is created it can be copied in infinite numbers, for almost zero cost, by anyone. This made commercialization of software for the mass market in the beginning of the computing era impossible. Unlike hardware, it was not seen as trade-able and commercialize-able good. Software was plainly shared for free (hacker culture) or distributed bundled with sold hardware, as part of the service t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freeware
Freeware is software, most often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines ''freeware'' unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models. History The term ''freeware'' was coined in 1982 by Andrew Fluegelman, who wanted to sell PC-Talk, the communications application he had created, outside of commercial distribution channels. Fluegelman distributed the program via a process now termed '' shareware''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |