|
Exploration Of Australia
The European exploration of Australia first began in February 1606, when Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon landed in Cape York Peninsula and on October that year when Spanish explorer Luís Vaz de Torres sailed through, and navigated, Torres Strait islands. Twenty-nine other Dutch navigators explored the western and southern coasts in the 17th century, and dubbed the continent New Holland. Other European explorers followed until, in 1770, Lieutenant James Cook charted the east coast of Australia for Great Britain. Later, after Cook's death, Joseph Banks recommended sending convicts to Botany Bay (now in Sydney), New South Wales. A First Fleet of British ships arrived at Botany Bay in January 1788 to establish a penal colony, the first colony on the Australian mainland. In the century that followed, the British established other colonies on the continent, and European explorers ventured into its interior. Massive areas of land were cleared for agriculture and various other purpos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples of the Australian mainland and Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islander peoples from the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the terms First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common; 812,728 people self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal; 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander; while 4.4% identified with both groups. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Thijssen
François Thijssen or Frans Thijsz (died 13 October 1638?) was a Dutch- French explorer who explored the southern coast of Australia. He was the captain of the ship t Gulden Zeepaerdt'' (''The Golden Seahorse'') when sailing from Cape of Good Hope to Batavia. On this voyage, he ended up too far to the south and on 26 January 1627 he came upon the coast of Australia, near Cape Leeuwin, the south-westernmost tip of the continent. Thijssen continued to sail eastwards, mapping more than of Australia's coast. He called the land t Land van Pieter Nuyts'' (''The Land of Pieter Nuyts''), referring to the highest VOC official aboard his ship. Part of Thijssen's map shows the islands St Francis and St Peter, now known collectively with their respective groups as the Nuyts Archipelago. He also mapped the coastline around Fowlers Bay. The ship, which had been built in Middelburg and left Zeeland on 22 May 1626, finally arrived in Batavia on 10 April 1627. Thijssen's observations were inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mercury (Hobart)
''The'' ''Mercury'' is a daily newspaper, published in Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, by Davies Brothers Pty Ltd (DBL), a subsidiary of News Corp Australia, itself a subsidiary of News Corp. The weekend issues of the paper are called ''Mercury on Saturday '' and ''Sunday Tasmanian''. The current editor of ''The'' ''Mercury'' is Craig Warhurst. History The newspaper was started on 5 July 1854 by George Auber Jones and John Davies. Two months subsequently (13 September 1854) John Davies became the sole owner. It was then published twice weekly and known as the ''Hobarton Mercury''. It rapidly expanded, absorbing its rivals, and became a daily newspaper in 1858 under the lengthy title ''The Hobart Town Daily Mercury''. In 1860 the masthead was reduced to ''The Mercury'' and in 2006 it was further shortened to simply ''Mercury''. With the imminent demise of the ( Launceston) ''Daily Telegraph'', ''The Mercury'', from March 1928, used the opportunity to increase their penetration th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Leeuwin
Cape Leeuwin is the most south-westerly (but not most southerly) mainland point of the Australian continent, in the state of Western Australia. Description A few small islands and rocks, the St Alouarn Islands, extend further in Flinders Bay to the east of the cape. The nearest settlement, north of the cape, is Augusta. South-east of Cape Leeuwin, the coast of Western Australia extends much further south. Cape Leeuwin is not the southernmost point of Western Australia, with that distinction belonging to West Cape Howe, which is to the southeast, near Albany. In Australia, the cape is considered where the Indian Ocean meets the Southern Ocean, but most other nations and bodies consider that the Southern Ocean exists only south of 60°S. Located on headland of the cape is the Cape Leeuwin Lighthouse and the buildings that were used by the lighthouse-keepers. Cape Leeuwin is considered one of the three "great capes" of the world. Use of name Cape Leeuwin is often group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirk Hartog
Dirk Hartog (; baptised 30 October 1580 – buried 11 October 1621) was a 17th-century Dutch sailor and explorer. Dirk Hartog's expedition was the second European group to land in Australia and the first to leave behind an artefact to record his visit, the Hartog Plate. His name is sometimes alternatively spelled Dirck Hartog or Dierick Hartochszch. Ernest Giles referred to him as Theodoric Hartog. The Western Australian island Dirk Hartog Island is named after Hartog. Life Born into a seafaring family, he received his first ship's command at the age of 30 and spent several years engaged in successful trading ventures in the Baltic and Mediterranean seas. In 1616 Hartog gained employment with the Dutch East India Company ( nl, Vereenigde Oostindische Compagnie, commonly abbreviated to VOC), and was appointed master of the (meaning "Concord" or "Unity"), in a fleet voyaging from the Netherlands to the Dutch East Indies. Hartog set sail in January 1616 in the company of sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
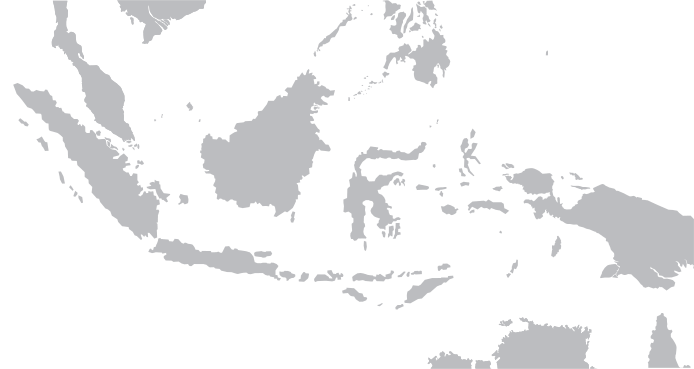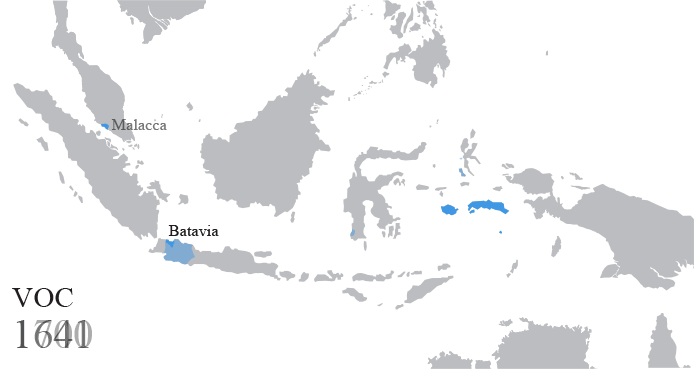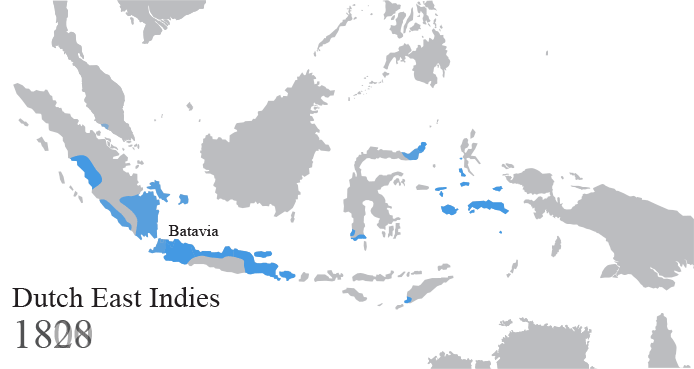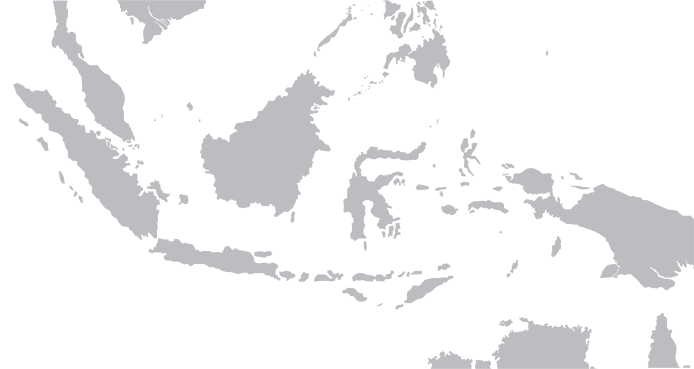
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dampier
William Dampier (baptised 5 September 1651; died March 1715) was an English explorer, pirate, privateer, navigator, and naturalist who became the first Englishman to explore parts of what is today Australia, and the first person to circumnavigate the world three times. He has also been described as Australia's first natural historian, as well as one of the most important British explorers of the period between Francis Drake (16th century) and James Cook (18th century), he "bridged those two eras" with a mix of piratical derring-do of the former and scientific inquiry of the later. His expeditions were among the first to identify and name a number of plants, animals, foods, and cooking techniques for a European audience; being among the first English writers to use words such as avocado, barbecue, and chopsticks. In describing the preparation of avocados, he was the first European to describe the making of guacamole, named the breadfruit plant, and made frequent documenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weipa, Queensland
Weipa () is a coastal mining town in the local government area of Weipa Town in Queensland. It is the largest town on the Cape York Peninsula. It exists because of the enormous bauxite deposits along the coast. The Port of Weipa is mainly involved in exports of bauxite. There are also shipments of live cattle from the port. In the , Weipa had a population of 3,899 people. Geography Weipa is on the western coast of the Cape York Peninsula facing the Gulf of Carpentaria. Weipa is just south of Duyfken Point, which was named by Matthew Flinders on 8 November 1802 after the ship ''Duyfken'' commanded by the Dutch explorer Willem Janszoon. It is claimed that Janszoon was the first European to sight the Australian coast in the Gulf of Carpentaria in 1606, 164 years before Lieutenant James Cook sailed up the east coast of Australia. The town consists of three residential suburbs, Rocky Point, Trunding, and Nanum, in addition to the industrial suburb of Evans Landing; these subur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennefather River
The Pennefather River is a river located on the western Cape York Peninsula in Far North Queensland, Far North Queensland, Australia. Location and features Formed by the confluence of a series of waterways including the Fish Creek in the Port Musgrave Aggregation estuarine wetlands, the Pennefather River flows due west, joined by the Turtle Creek from the north and Dingo Creek from the south, before emptying into the Gulf of Carpentaria south of . The river descends over its watercourse, course. At its widest point, the river is approximately wide. The river has a drainage basin, catchment area of , of which comprises wetlands. Etymology and history Yupangathi language, Yupanguthi (Yuputhimri, Jupangati, Yupangathi, Nggerikudi, Yupungati, Jupangati) is an Australian Aboriginal language spoken on Yupanguthi country. The Yupanguthi language region includes the landscape within the local government boundaries of the landscape within the local government boundaries of the Shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duyfken
''Duyfken'' (; Little Dove), also in the form ''Duifje'' or spelled ''Duifken'' or ''Duijfken'', was a small ship built in the Dutch Republic. She was a fast, lightly armed ship probably intended for shallow water, small valuable cargoes, bringing messages, sending provisions, or privateering. The tonnage of ''Duyfken'' has been given as 25-30 ''lasten'' (50-60 tons). In 1606, during a voyage of discovery from Bantam (Banten), Java, captained by Willem Janszoon, she encountered the Australian mainland. Janszoon is credited with the first authenticated European landing on Australia. In 1608, the ship was damaged beyond repair. A reproduction of ''Duyfken'' was built in Australia and launched in 1999. Voyages In 1596, a ship named ''Duyfken'' sailed in the first expedition to Bantam (city), Bantam, the crew was captured by the islanders on Pulau Enggano. On 23 April 1601, ''Duyfken'' sailed from Texel as ''jacht'', or scout, under skipper Willem Cornelisz Schouten to the Malu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch People
The Dutch (Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aruba, Suriname, Guyana, Curaçao, Argentina, Brazil, Canada,Based on Statistics Canada, Canada 2001 Censusbr>Linkto Canadian statistics. Australia, South Africa, New Zealand and the United States.According tFactfinder.census.gov The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The high degree of urbanization characteristic of Dutch society was attained at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |