|
Executive Pay In The United States
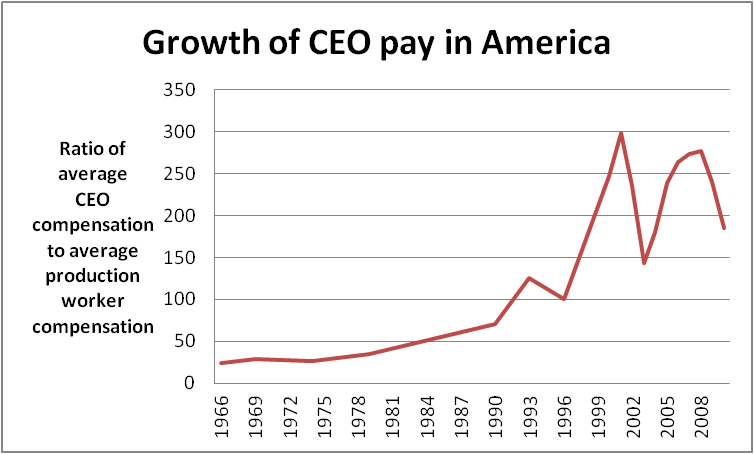
In the United States, the compensation of company executives is distinguished by the forms it takes and its dramatic rise over the past three decades. Within the last 30 years, executive compensation or pay has risen dramatically beyond what can be explained by changes in firm size, performance, and industry classification. This has received a wide range of criticism leveled against it. The top CEO's compensation increased by 940.3% from 1978 to 2018 in the US. In 2018, the average CEO's compensation from the top 350 US firms was $17.2 million. The typical worker's annual compensation grew just 11.9% within the same period. It is the highest in the world in both absolute terms and relative to the median salary in the US. It has been criticized not only as excessive but also for "rewarding failure" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CEO Pay V
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of Corporate Executive, corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especially an independent Legal person, legal entity such as a company or Nonprofit organization, nonprofit institution. CEOs find roles in a range of organizations, including public and private corporations, non-profit organizations and even some government organizations (notably state-owned enterprises). The CEO of a corporation or company typically reports to the board of directors and is charged with maximizing the value of the business, which may include maximizing the share price, market share, revenues or another element. In the non-profit and government sector, CEOs typically aim at achieving outcomes related to the organization's mission, usually provided by legislation. CEOs are also frequently assigned the role of main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business. Management includes the activities of setting the strategy of an organization and coordinating the efforts of its employees (or of volunteers) to accomplish its objectives through the application of available resources, such as financial, natural, technological, and human resources. "Run the business" and "Change the business" are two concepts that are used in management to differentiate between the continued delivery of goods or services and adapting of goods or services to meet the changing needs of customers - see trend. The term "management" may also refer to those people who manage an organization—managers. Some people study management at colleges or universities; major degrees in management includes the Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com.), Bachelor of Business Administra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larry Ellison
Lawrence Joseph Ellison (born August 17, 1944) is an American business magnate and investor who is the co-founder, executive chairman, chief technology officer (CTO) and former chief executive officer (CEO) of the American computer technology company Oracle Corporation. As of November 2022, he was listed by ''Bloomberg Billionaires Index'' as the seventh-wealthiest person in the world, with an estimated fortune of $91 billion. Ellison is also known for his 98% ownership stake in Lanai, the sixth-largest island in the Hawaiian Archipelago. Early life and education Larry Ellison was born in New York City, to an unwed Jewish mother. His biological father was an Italian-American United States Army Air Corps pilot. After Ellison contracted pneumonia at the age of nine months, his mother gave him to her aunt and uncle for adoption. He did not meet his biological mother again until he was 48. Ellison moved to Chicago's South Shore, then a middle-class neighborhood. He remembers hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comparing CEO Pay
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and to what degree. Where characteristics are different, the differences may then be evaluated to determine which thing is best suited for a particular purpose. The description of similarities and differences found between the two things is also called a comparison. Comparison can take many distinct forms, varying by field: To compare things, they must have characteristics that are similar enough in relevant ways to merit comparison. If two things are too different to compare in a useful way, an attempt to compare them is colloquially referred to in English as "comparing apples and oranges." Comparison is widely used in society, in science and in the arts. General usage Comparison is a natural activity, which even animals engage in when dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bogle
John Clifton "Jack" Bogle (May 8, 1929 – January 16, 2019) was an American investor, business magnate, and philanthropist. He was the founder and chief executive of The Vanguard Group, and is credited with creating the index fund. An avid investor and money manager himself, he preached investment over speculation, long-term patience over short-term action, and reducing broker fees as much as possible. The ideal investment vehicle for Bogle was a low-cost index fund held over a lifetime with dividends reinvested and purchased with dollar cost averaging. His 1999 book '' Common Sense on Mutual Funds: New Imperatives for the Intelligent Investor'' became a bestseller and is considered a classic within the investment community. Early life and education John Bogle was born on May 8, 1929, in Montclair, New Jersey, to William Yates Bogle, Jr. and Josephine Lorraine Hipkins. His family was harmed by the Great Depression. They lost their money and had to sell their home, with his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privately Held Companies
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in the respective listed markets, but rather the company's stock is offered, owned, traded, exchanged privately, or over-the-counter. In the case of a closed corporation, there are a relatively small number of shareholders or company members. Related terms are closely-held corporation, unquoted company, and unlisted company. Though less visible than their publicly traded counterparts, private companies have major importance in the world's economy. In 2008, the 441 largest private companies in the United States accounted for ($1.8 trillion) in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In 2005, using a substantially smaller pool size (22.7%) for comparison, the 339 companies on ''Forbes'' survey of closely held U.S. businesses sold a trillion dollars' worth of goods and services (4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Directors
A board of directors (commonly referred simply as the board) is an executive committee that jointly supervises the activities of an organization, which can be either a for-profit or a nonprofit organization such as a business, nonprofit organization, or a government agency. The powers, duties, and responsibilities of a board of directors are determined by government regulations (including the jurisdiction's corporate law) and the organization's own constitution and by-laws. These authorities may specify the number of members of the board, how they are to be chosen, and how often they are to meet. In an organization with voting members, the board is accountable to, and may be subordinate to, the organization's full membership, which usually elect the members of the board. In a stock corporation, non-executive directors are elected by the shareholders, and the board has ultimate responsibility for the management of the corporation. In nations with codetermination (such as Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arm's Length Principle
The arm's length principle (ALP) is the condition or the fact that the parties of a transaction are independent and on an equal footing. Such a transaction is known as an "arm's-length transaction". It is used specifically in contract law to arrange an agreement that will stand up to legal scrutiny, even though the parties may have shared interests (e.g., employer-employee) or are too closely related to be seen as completely independent (e.g., the parties have familial ties). An arm's length relationship is distinguished from a fiduciary relationship, where the parties are not on an equal footing, but rather, power and information asymmetries exist. It is also one of the key elements in international taxation as it allows an adequate allocation of profit taxation rights among countries that conclude double tax conventions, through transfer pricing, among each other. Transfer pricing and the arm's length principle was one of the focal points of the Base Erosion and Profit Shif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University Press
Harvard University Press (HUP) is a publishing house established on January 13, 1913, as a division of Harvard University, and focused on academic publishing. It is a member of the Association of American University Presses. After the retirement of William P. Sisler in 2017, the university appointed as Director George Andreou. The press maintains offices in Cambridge, Massachusetts near Harvard Square, and in London, England. The press co-founded the distributor TriLiteral LLC with MIT Press and Yale University Press. TriLiteral was sold to LSC Communications in 2018. Notable authors published by HUP include Eudora Welty, Walter Benjamin, E. O. Wilson, John Rawls, Emily Dickinson, Stephen Jay Gould, Helen Vendler, Carol Gilligan, Amartya Sen, David Blight, Martha Nussbaum, and Thomas Piketty. The Display Room in Harvard Square, dedicated to selling HUP publications, closed on June 17, 2009. Related publishers, imprints, and series HUP owns the Belknap Press imprint, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucian Bebchuk
Lucian Arye Bebchuk (born 1955) is a professor at Harvard Law School focusing on economics and finance. Bebchuck has a B.A. in mathematics and economics from the University of Haifa (1977), an LL.B. from the University of Tel Aviv (1979), an LL.M. and S.J.D. from Harvard Law School (1980 and 1984) and an M.A. and Ph.D. in economics, also from Harvard (1992 and 1993). He was a junior fellow of the Harvard Society of Fellows from 1983 to 1985. He joined the Harvard Law faculty in 1986. Bebchuck is the co-author, with Jesse Fried, of '' Pay without Performance: The Unfulfilled Promise of Executive Compensation''. Distinctions Prof. Bebchuk was named one of the top 100 most influential players in corporate governance in the US by '' Directorship'' magazine. He was elected a fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 2000. In 2004, he was awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship Guggenheim Fellowships are grants that have been awarded annually since by the John Simon Guggenhe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal–agent Problem
The principal–agent problem refers to the conflict in interests and priorities that arises when one person or entity (the "agent") takes actions on behalf of another person or entity (the " principal"). The problem worsens when there is a greater discrepancy of interests and information between the principal and agent, as well as when the principal lacks the means to punish the agent. The deviation from the principal's interest by the agent is called " agency costs".''Pay Without Performance'', Lucian Bebchuk and Jesse Fried, Harvard University Press 2004preface and introduction Common examples of this relationship include corporate management (agent) and shareholders (principal), elected officials (agent) and citizens (principal), or brokers (agent) and markets (buyers and sellers, principals). In all these cases, the principal has to be concerned with whether the agent is acting in the best interest of the principal. The concepts of moral hazard and conflict of interest re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shareholder
A shareholder (in the United States often referred to as stockholder) of a corporation is an individual or legal entity (such as another corporation, a body politic, a trust or partnership) that is registered by the corporation as the legal owner of shares of the share capital of a public or private corporation. Shareholders may be referred to as members of a corporation. A person or legal entity becomes a shareholder in a corporation when their name and other details are entered in the corporation's register of shareholders or members, and unless required by law the corporation is not required or permitted to enquire as to the beneficial ownership of the shares. A corporation generally cannot own shares of itself. The influence of a shareholder on the business is determined by the shareholding percentage owned. Shareholders of a corporation are legally separate from the corporation itself. They are generally not liable for the corporation's debts, and the shareholders' liabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |