|
Evolution Of Nervous Systems
The evolution of nervous systems dates back to the first development of nervous systems in animals (or metazoans). Neurons developed as specialized electrical signaling cells in multicellular animals, adapting the mechanism of action potentials present in motile single-celled and colonial eukaryotes. Primitive systems, like those found in protists, use chemical signalling for movement and sensitivity; data suggests these were precursors to modern neural cell types and their synapses. When some animals started living a mobile lifestyle and eating larger food particles externally, they developed ciliated epithelia, contractile muscles and coordinating & sensitive neurons for it in their outer layer. Simple nerve nets seen in acoels (basal bilaterians) and cnidarians are thought to be the ancestral condition for the Planulozoa (bilaterians plus cnidarians and, perhaps, placozoans). A more complex nerve net with simple nerve cords is present in ancient animals called ctenopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nervous Systems
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes that impact the body, then works in tandem with the endocrine system to respond to such events. Nervous tissue first arose in wormlike organisms about 550 to 600 million years ago. In vertebrates, it consists of two main parts, the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord. The PNS consists mainly of nerves, which are enclosed bundles of the long fibers, or axons, that connect the CNS to every other part of the body. Nerves that transmit signals from the brain are called motor nerves (efferent), while those nerves that transmit information from the body to the CNS are called sensory nerves (afferent). The PNS is divided into two separate subsystems, the somatic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planulozoa
Planulozoa is a clade which includes the Placozoa, Cnidaria (corals and jellyfish) and the Bilateria (all the more complex animals including worms, insects and vertebrates). The designation Planulozoa may be considered a synonym to ParaHoxozoa. Within Planulozoa, the Placozoa may be a sister of Cnidaria to the exclusion of Bilateria. The clade excludes basal animals such as the Ctenophora (comb jellies), and Porifera (sponges). Although this clade was sometimes used to specify a clade of Cnidaria and Bilateria to the exclusion of Placozoa (against the original intention of its proposal), this is no longer favoured due to recent data (several 2018 studies) indicating a sister group relationship between Cnidaria and Placozoa. However, a 2023 study supports Placozoa as sister to Cnidaria+Bilateria in several analyses. The phylogenetic tree A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
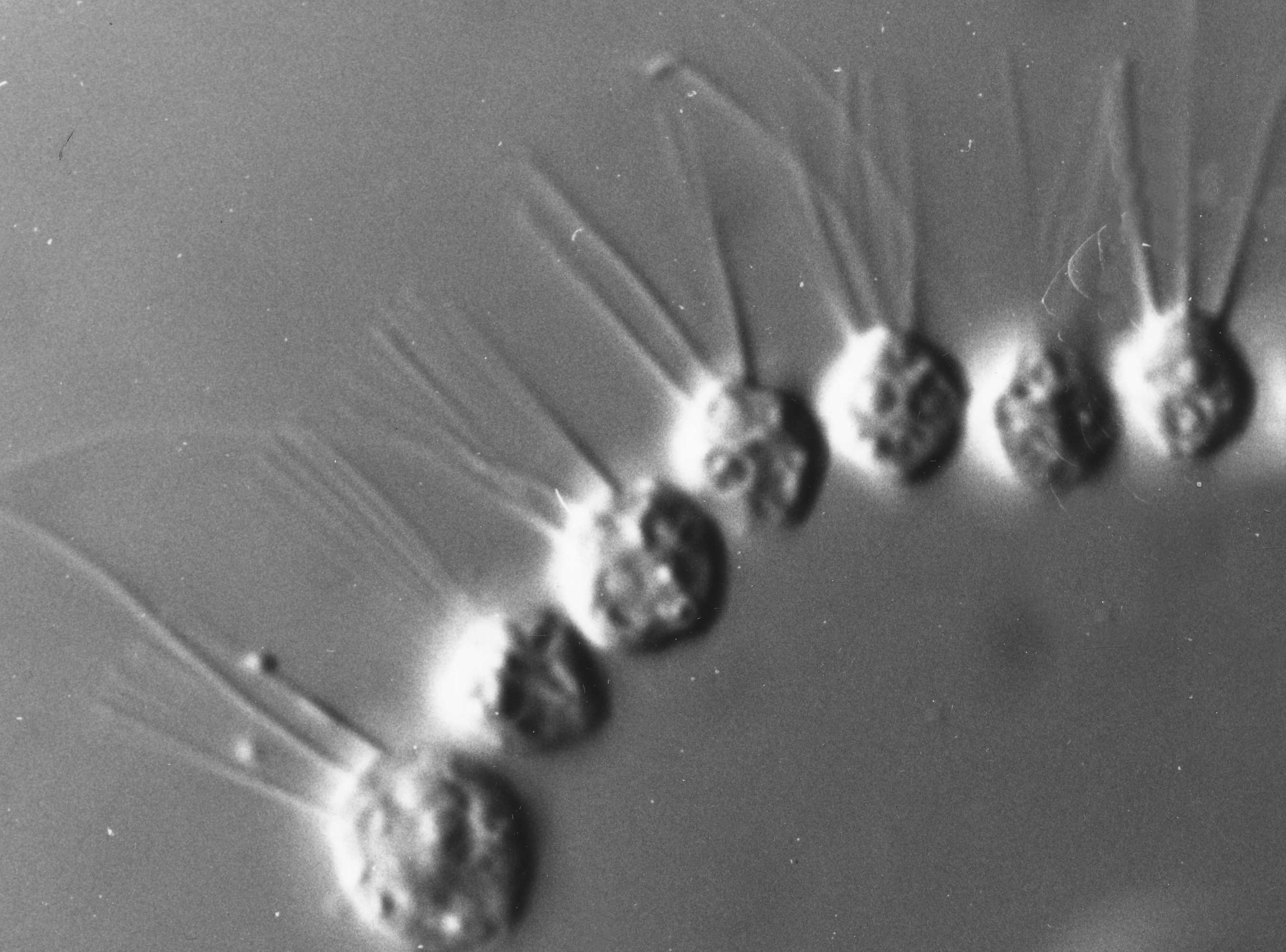
Obelia
''Obelia'' is a genus of hydrozoans, a class of mainly marine and some freshwater animal species that have both polyp and medusa stages in their life cycle. Hydrozoa belongs to the phylum Cnidaria, which are aquatic (mainly marine) organisms that are relatively simple in structure with a diameter around 1mm. There are currently 120 known species, with more to be discovered. These species are grouped into three broad categories: ''O. bidentata'', ''O. dichotoma'', and ''O. geniculata''. ''O. longissima'' was later accepted as a legitimate species, but taxonomy regarding the entire genus is debated over. ''Obelia'' is also called sea fur. ''Obelia'' has a worldwide distribution except the high-Arctic and Antarctic seas. and a stage of ''Obelia'' species are common in coastal and offshore plankton around the world.Cornelius, P.F.S., 1995b. North-West European thecate hydroids and their Medusae. Part 2. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series), No 50. ''Obelia'' are usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social Amoeba, amoebae such as the genus ''Dictyostelium''. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells. Colonial organisms are the result of many identical individuals joining together to form a colony (biology), colony. However, it can often be hard to separate colonial protists from true multicellular organisms, because the two concepts are not distinct; colonial protists have been dubbed "pluricellular" rather than "multicellular". There are also macroscopic organisms that are multinucleate though technically unicellular, such as the Xenophyophorea that can reach 20 cm. Evolutionary history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action Potentials
An action potential (also known as a nerve impulse or "spike" when in a neuron) is a series of quick changes in voltage across a cell membrane. An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of excitable cells, which include animal cells like neurons and muscle cells, as well as some plant cells. Certain endocrine cells such as pancreatic beta cells, and certain cells of the anterior pituitary gland are also excitable cells. In neurons, action potentials play a central role in cell–cell communication by providing for—or with regard to saltatory conduction, assisting—the propagation of signals along the neuron's axon toward synaptic boutons situated at the ends of an axon; these signals can then connect with other neurons at synapses, or to motor cells or glands. In other types of cells, their mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Nerve Cord
The dorsal nerve cord is an anatomical feature found in chordate animals, mainly in the subphyla Vertebrata and Cephalochordata, as well as in some hemichordates. It is one of the five embryonic features unique to all chordates, the other four being a notochord, a post-anal tail, an endostyle, and pharyngeal slits. All chordates (vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates) have dorsal hollow nerve cords. The dorsal nerve cord is located ''dorsal'' to the notochord and thus also to the gut tube (hence the name). It is formed from clustered neuronal differentiation at the axial region of the ectoderm, known as the neural plate. During embryonic development, the neural plate first invaginates longitudinally to form the neural groove, whose edges ( neural folds) fuse over to form a hollow neural tube. This is an important feature as it distinguishes chordates from other invertebrate phyla such as annelids and arthropods, who have solid nerve cords that are located '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Nerve Cord
The ventral nerve cord is a major structure of the invertebrate central nervous system. It is the functional equivalent of the vertebrate spinal cord. The ventral nerve cord coordinates neural signaling from the brain to the body and vice versa, integrating sensory input and locomotor output. Because arthropods have an open circulatory system, decapitated insects can still walk, groom, and mate — illustrating that the circuitry of the ventral nerve cord is sufficient to perform complex motor programs without brain input. Structure The ventral nerve cord runs down the ventral ("belly", as opposed to back) plane of the organism. It is made of nervous tissue and is connected to the brain. Ventral nerve cord neurons are physically organized into neuromeres that process signals for each body segment. Anterior neuromeres control the anterior body segments, such as the forelegs, and more posterior neuromeres control the posterior body segments, such as the hind legs. Neurom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalization
Cephalization is an evolutionary trend in animals that, over a sufficient number of generations, concentrates the special sense organ (biology), organs and nerve ganglia towards the front of the body where the mouth is located, often producing an enlarged head. This is associated with the animal's animal locomotion, movement direction and bilateral symmetry (biology), bilateral symmetry. Cephalization of the nervous system has led to the formation of a brain with varying degrees of functional centralization in three phylum, phyla of bilaterian animals, namely the arthropods, cephalopod molluscs, and vertebrates. Hox genes organise aspects of cephalization in the bilaterians. Bilateria Cephalization is both a characteristic feature of any animal that habitually moves in one direction, thereby gaining a front end, and an evolutionary trend which created the head of these animals. In practice, this primarily means the bilaterians, a large group containing the majority of anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
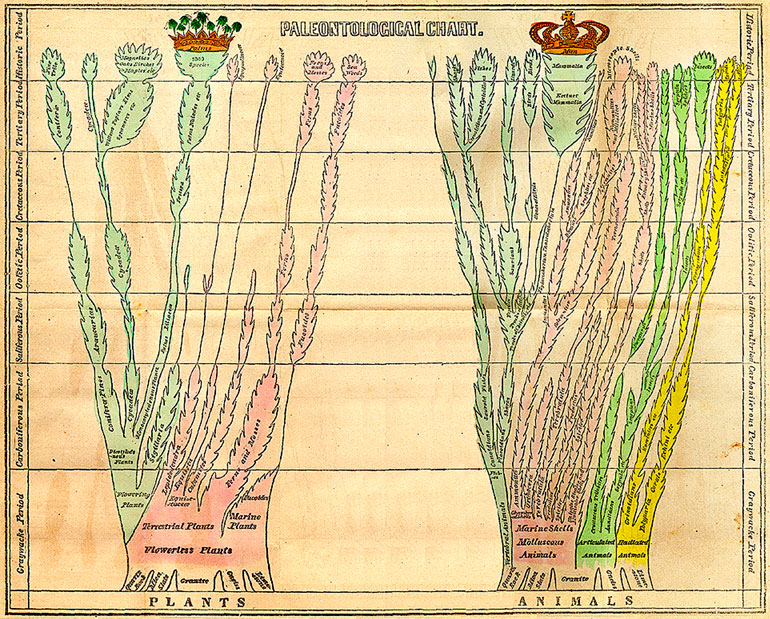
Tree Of Life (biology)
The tree of life or universal tree of life is a metaphor, conceptual model, and research tool used to explore the evolution of life and describe the relationships between organisms, both living and extinct, as described in a famous passage in Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Tree diagrams originated in the Middle Ages, medieval era to represent family tree, genealogical relationships. Phylogenetic tree diagrams in the evolutionary sense date back to the mid-nineteenth century. The term phylogeny for the evolutionary relationships of species through time was coined by Ernst Haeckel, who went further than Charles Darwin, Darwin in proposing Phylogenetics, phylogenic histories of life. In contemporary usage, ''tree of life'' refers to the compilation of comprehensive phylogenetic databases rooted at the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth. Two public databases for the tree of life are ''TimeTree'', for phylogeny and divergence times, and the ''Ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data and observed heritable traits of DNA sequences, protein amino acid sequences, and morphology. The results are a phylogenetic tree—a diagram depicting the hypothetical relationships among the organisms, reflecting their inferred evolutionary history. The tips of a phylogenetic tree represent the observed entities, which can be living taxa or fossils. A phylogenetic diagram can be rooted or unrooted. A rooted tree diagram indicates the hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa represented on the tree. An unrooted tree diagram (a network) makes no assumption about directionality of character state transformation, and does not show the origin or "root" of the taxa in question. In addition to their use for inferring phylogenetic pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongilla
''Spongilla'' is a genus of freshwater sponges containing over 200 different species. Spongilla was first publicly recognized in 1696 by Leonard Plukenet and can be found in lakes, ponds and slow streams.''Spongilla'' have a leuconoid body form with a skeleton composed of siliceous spicules. They are sessile organisms, attaching themselves to hard substrate like rocks, logs. and sometimes to ground. Using their ostia and osculum these sponges filter the water for various small aquatic organisms such as protozoans, bacteria, and other free-floating pond life. Sponges of the genus ''Spongilla'' partake in symbiotic relationships with the green algae, zoochlorellae, which gives the sponges a green appearance, and without which they would appear white. ''Spongilla'' was used by John Hogg in the 19th century to attempt to justify a fourth kingdom of life. Reproduction Sponges are hermaphrodites, producing both egg and sperm. Sperm is released from one sponge and brought in throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choanocyte
Choanocytes (also known as "collar cells") are cells that line the interior of asconoid, syconoid and leuconoid body types of sponges that contain a central flagellum, or ''cilium,'' surrounded by a collar of microvilli which are connected by a thin membrane. They make up the choanoderm, a type of cell layer found in sponges Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and ar .... The cell has the closest resemblance to the choanoflagellates which are the closest related single celled protists to the animal kingdom (metazoans). The flagellae beat regularly, creating a water flow across the microvilli which can then filter nutrients from the water taken from the collar of the sponge. Food particles are then phagocytosed by the cell.Anderson, D. (2001) ''Invertebrate Zoology'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |