|
Evangelical Reformed Church Of The Canton Of Lucerne
The Evangelical Reformed Church of the Canton of Lucerne or in German the Evangelisch-Reformierte Kirche des Kantons Luzern is a Reformed state church in the Canton of Lucerne, Switzerland. In 2004 it had 43,000 members, 18 parishes and 35 ordained clergy. It has Presbyterian-Synodal church government. Congregations are founded in Aesch, Adligenswil, Alberswil, Altishofen, Altwis, Baldegg, Ballwil, Beromünster, Bramboden, Buchrain, Buchs, Büron, Buttisholtz, Dagmersellen, Dierikon, Doppleschwand, Ebersecken, Ebikon, Egolzwil, Eich, Emmen, Entlebuch, Ermensee, Ecshenbach, Escholzmatt, Ettiswil, Fischbach, Flühli, Geiss, Gelfingen, Gettnau, Geuensee, Gisikon, Greppen, Grossdietwil, Grosswangen, Gunzwil, Hamikon, Hasle, Heiligkreuz, Hergiswil, Herlisberg, Hertenstein, Hildisrieden, Hitzkirch, Hochdorf, Hohenrain, Honau, Horw, Inwil, Kleinwangen, Knutwil, Knottwil, Kriens, Kulmerau, Lieli, Luzern, Littau, Luthern, Malters, Marbach, Mauensee, Meggen, Meierskappen, Menznau, Mosen, Nebik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reformed Tradition
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the Christian theology, theological tradition and forms of Christianity, Christian practice set down by John Calvin and other The Reformation, Reformation-era Protestant Reformers, theologians. It emphasizes the Sovereignty of God in Christianity, sovereignty of God and the Biblical authority, authority of the Bible. Calvinists broke from the Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Church in the 16th century. Calvinists differ from Lutheranism, Lutherans (another major branch of the Reformation) on the Lord's Supper in Reformed theology, spiritual real presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper, regulative principle of worship, theories of worship, the purpose and meaning of baptism, and the Law and Gospel#Lutheran and Reformed differences, use of God's law for believers, among other points. The label ''Calvinism'' can be misle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landeskirche
In Germany and Switzerland, a Landeskirche (plural: Landeskirchen) is the church of a region. The term usually refers to Protestant churches, but—in case of Switzerland—also Roman Catholic dioceses. They originated as the national churches of the independent states, States of Germany (''Länder'') or Cantons of Switzerland (''Kantone'', ''Cantons'', ''Cantoni''), that later unified to form modern Germany (in 1871) or modern Switzerland (in 1848), respectively. Origins in the Holy Roman Empire In the pre-Reformation era, the organization of the church within a ''land'' was understood as a ''landeskirche'', certainly under a higher power (the pope or a patriarch), but also possessing an increased measure of independence, especially as concerning its internal structure and its relations to its king, prince or ruler. Unlike in Scandinavia and England, the bishops in the national churches did not survive the Reformation, making it impossible for a conventional diocesan system to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
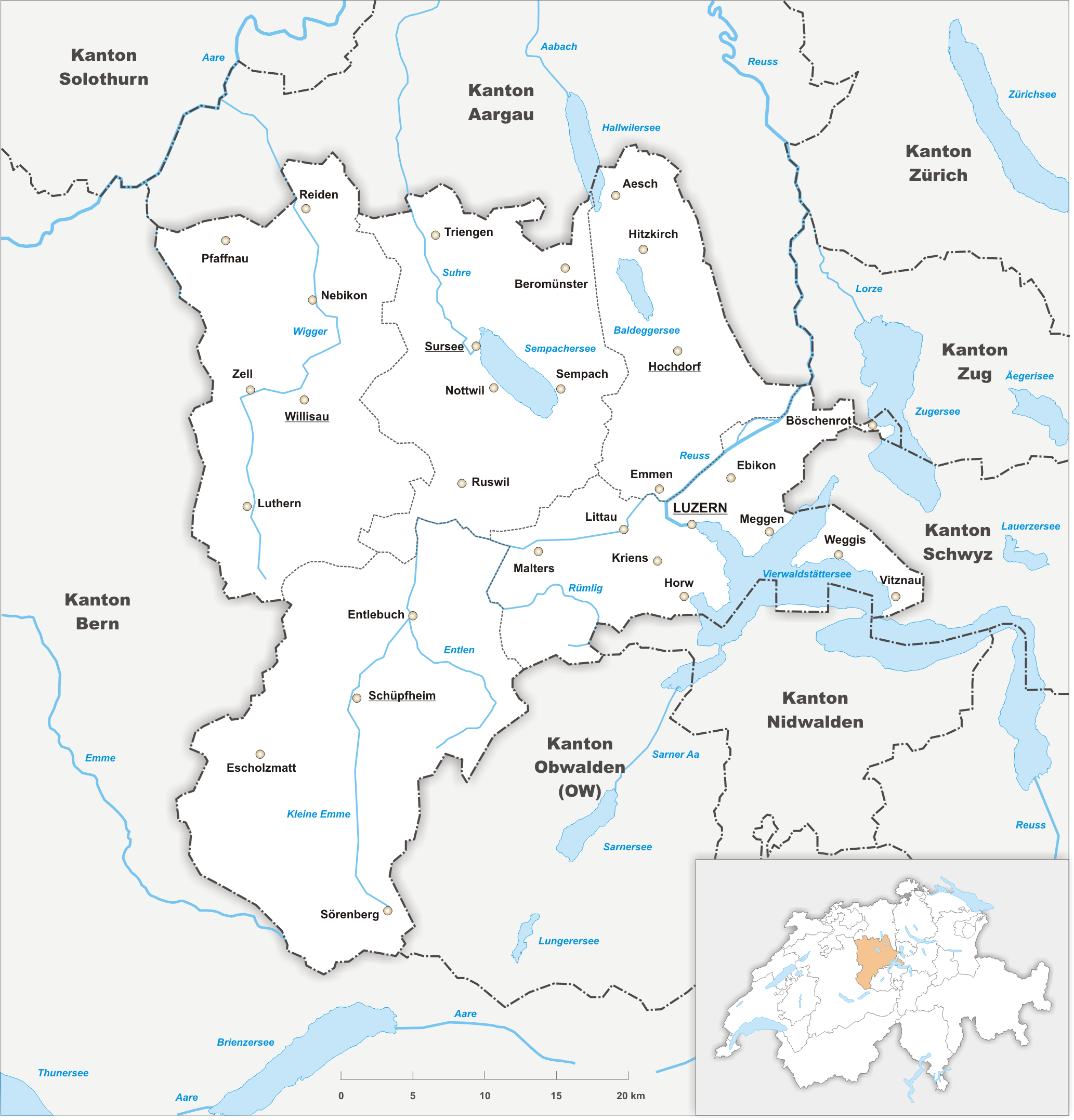
Canton Of Lucerne
The canton of Lucerne (german: Kanton Luzern rm, Chantun Lucerna french: Canton de Lucerne it, Canton Lucerna) is a canton of Switzerland. It is located in the centre of Switzerland. The population of the canton (as of ) is . , the population included 57,268 foreigners, or about 15.8% of the total population. The cantonal capital is Lucerne. History The canton of Lucerne comprises territories acquired by its capital Lucerne, either by treaty, armed occupation or purchase. The first town acquired was Weggis (in 1380), Rothenburg, Kriens, Horw, Sempach and Hochdorf (all in 1394), Wolhusen and Entlebuch (1405), the so-called "Habsburger region" to the northeast of the town of Lucerne (1406), Willisau (1407), Sursee and Beromünster (1415), Malters (1477) and Littau (1481), while in 1803, in exchange for Hitzkirch, Merenschwand (held since 1397) was given up. Prehistory The oldest traces of humans in the Lucerne area are stone artifacts and cave bear bones found in the Ste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federation Of Swiss Protestant Churches
The Protestant Church in Switzerland (PCS), (EKS); french: Église évangélique réformée de Suisse (EERS); it, Chiesa evangelica riformata in Svizzera (CERiS); rm, Baselgia evangelica refurmada da la Svizra (BRRS) formerly named Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches (SEK); french: Fédération des Eglises protestantes de Suisse (FEPS); it, Federazione delle Chiese evangeliche della Svizzera; rm, Federaziun da las baselgias evangelicas da la Svizra until 31 December 2019, is a federation of 25 member churches – 24 cantonal churches and the Evangelical-Methodist Church of Switzerland. The PCS is not a church in a theological understanding, because every member is independent with their own theological and formal organisation. It serves as a legal umbrella before the federal government and represents the church in international relations. Except for the Evangelical-Methodist Church, which covers all of Switzerland, the member churches are restricted to a certain territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordination Of Women In Protestant Denominations
Ordination is the process by which individuals are consecrated, that is, set apart as clergy to perform various religious rites and ceremonies such as celebrating the sacraments. The process and ceremonies of ordination varies by denomination. One who is in preparation for, or who is undergoing the process of ordination is sometimes called an ordinand. The liturgy used at an ordination is sometimes referred to as an ordinal. Ordination of women has been taking place in an increasing number of Protestant churches during the 20th century. While ordination of women has been approved in many denominations over the past half century, it is still a very controversial and divisive topic. Overview of the theological debate Most (although not all) Protestant denominations ordain church leaders who have the task of equipping all believers in their Christian service (). These leaders (variously styled ''elders'', ''pastors'', or ''ministers'') are seen to have a distinct role in teachin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blessing Of Same-sex Unions In Christian Churches
The blessing or wedding of same-sex marriages and same-sex unions is an issue about which Christian churches are in ongoing disagreement. Traditionally, Christianity teaches that homosexual acts are sinful and that holy matrimony can only exist between two persons of the opposite sex. These disagreements are primarily centered on the interpretation of various scripture passages related to homosexuality, sacred Tradition, and in some churches on varying understandings of homosexuality in terms of psychology, genetics and other scientific data. While various Church bodies have widely varying practices and teachings, individual Christians of every major tradition are involved in practical (orthopraxy) discussions about how to respond to the issue. Terminology *Same-sex union *Same-sex marriage Theological views of those who support same-sex unions and/or marriages Those Christians and churches which support blessing of same-sex unions do so from several perspectives: * It is an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestantism In Switzerland
The Reformed branch of Protestantism in Switzerland was started in Zürich by Huldrych Zwingli and spread within a few years to Basel (Johannes Oecolampadius), Bern (Berchtold Haller and Niklaus Manuel), St. Gallen,(Joachim Vadian), to cities in southern Germany and via Alsace (Martin Bucer) to France. Since 1920, the Swiss Reformed Churches have been organized in 26 member churches of the Federation of Swiss Protestant Churches. In the 2000 Swiss census, 33% of Swiss population were reported as registered members of a Reformed cantonal church. History After the early death of Zwingli in 1531, his work was continued by Heinrich Bullinger, the love of the Second Helvetic Confession. The French-speaking cities Neuchâtel, Geneva and Lausanne changed to the Reformation ten years later under William Farel and John Calvin coming from France. The Zwingli and Calvin branches had each their theological distinctions, but in 1549 under the lead of Bullinger and Calvin they came to a commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)