|
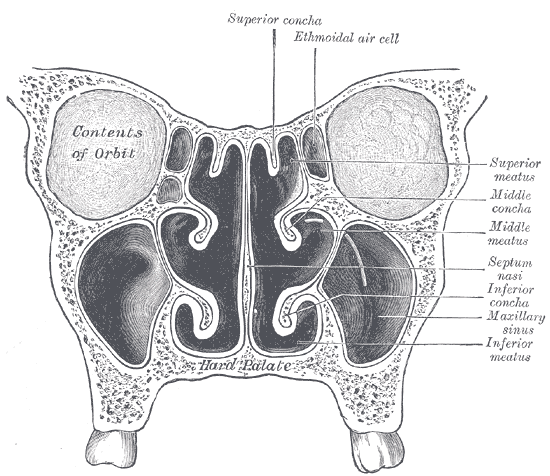
Ethmoidal Labyrinth
The ethmoidal labyrinth or lateral mass of the ethmoid bone consists of a number of thin-walled cellular cavities, the ethmoid air cells, arranged in three groups, anterior, middle, and posterior, and interposed between two vertical plates of bone; the lateral plate forms part of the orbit, the medial plate forms part of the nasal cavity. In the disarticulated bone many of these cells are opened into, but when the bones are articulated, they are closed in at every part, except where they open into the nasal cavity. Surfaces The upper surface of the labyrinth presents a number of half-broken cells, the walls of which are completed, in the articulated skull, by the edges of the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone. Crossing this surface are two grooves, converted into two openings by articulation with the frontal; they are the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina, and open on the inner wall of the orbit. The posterior surface presents large irregular cellular cavities, which a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Bone
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital plate and the nasal conchae are the ethmoidal sinuses or ethmoidal air cells, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina Papyracea
The orbital lamina of ethmoid bone, (or lamina papyracea or orbital lamina) is a smooth, oblong bone plate which forms the lateral surface of the labyrinth of the ethmoid bone in the skull. The plate covers in the middle and posterior ethmoidal cells and forms a large part of the medial wall of the orbit. It articulates above with the orbital plate of the frontal bone, below with the maxilla and the orbital process of palatine bone, in front with the lacrimal, and behind with the sphenoid. Its name lamina papyracea is an appropriate description, as this part of the ethmoid bone is paper-thin and fractures easily. A fracture here could cause entrapment of the medial rectus muscle The medial rectus muscle is a muscle in the orbit near the eye. It is one of the extraocular muscles. It originates from the common tendinous ring, and inserts into the anteromedial surface of the eye. It is supplied by the inferior division o .... Additional Images File:Slide4fen.JPG, Orbital l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Meatus
In anatomy, the term nasal meatus can refer to any of the three meatuses (passages) through the skulls nasal cavity: the superior meatus (''meatus nasi superior''), middle meatus (''meatus nasi medius''), and inferior meatus (''meatus nasi inferior''). The nasal meatuses are located beneath each of the corresponding nasal conchae. In the case where a fourth, supreme nasal concha is present, there is a fourth supreme nasal meatus. Structure The superior meatus is the smallest of the three. It is a narrow cavity located obliquely below the superior concha. This meatus is short, lies above and extends from the middle part of the middle concha below. From behind, the sphenopalatine foramen opens into the cavity of the superior meatus and the meatus communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. Above and at the back of the superior concha is the sphenoethmoidal recess which the sphenoidal sinus opens into. The superior meatus occupies the middle third of the nasal cavity’s l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamella (zoology)
Lamellae on a gecko's foot. In surface anatomy, a lamella is a thin plate-like structure, often one amongst many lamellae very close to one another, with open space between. Aside from respiratory organs, they appear in other biological roles including filter feeding and the traction surfaces of geckos. In fish, gill lamellae are used to increase the surface area in contact with the environment to maximize gas exchange (both to attain oxygen and to expel carbon dioxide) between the water and the blood. In fish gills there are two types of lamellae, primary and secondary. The primary gill lamellae (also called gill filament) extends from the gill arch, and the secondary gill lamellae extends from the primary gill lamellae. Gas exchange primarily occurs at the secondary gill lamellae, where the tissue is notably only one cell layer thick. Furthermore, countercurrent gas exchange at the secondary gill lamellae further maximizes oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide release. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Concha
In anatomy, a nasal concha (), plural conchae (), also called a nasal turbinate or turbinal, is a long, narrow, curled shelf of bone that protrudes into the breathing passage of the nose in humans and various animals. The conchae are shaped like an elongated seashell, which gave them their name (Latin ''concha'' from Greek ''κόγχη''). A concha is any of the scrolled spongy bones of the nasal passages in vertebrates.''Anatomy of the Human Body'' Gray, Henry (1918) The Nasal Cavity. In humans, the conchae divide the nasal airway into four groove-like air passages, and are responsible for forcing inhaled air to flow in a steady, regular pattern around the largest possible of |
Maxillary Sinus
The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus (or antrum of Highmore) is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.Human Anatomy, Jacobs, Elsevier, 2008, page 209-210 Structure It is the largest air sinus in the body. Found in the body of the maxilla, this sinus has three recesses: an alveolar recess pointed inferiorly, bounded by the alveolar process of the maxilla; a zygomatic recess pointed laterally, bounded by the zygomatic bone; and an infraorbital recess pointed superiorly, bounded by the inferior orbital surface of the maxilla. The medial wall is composed primarily of cartilage. The ostia for drainage are located high on the medial wall and open into the semilunar hiatus of the lateral nasal cavity; because of the position of the ostia, gravity cannot drain the maxillary sinus contents when the head is erect (see pathology). The ostium of the maxillary sinus is high up on the medial wall and on average is 2. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncinate Process Of Ethmoid Bone
In the ethmoid bone, a sickle shaped projection, the uncinate process, projects posteroinferiorly from the ethmoid labyrinth. Between the posterior edge of this process and the anterior surface of the ethmoid bulla, there is a two-dimensional space, resembling a crescent shape. This space continues laterally as a three-dimensional slit-like space - the ethmoidal infundibulum. This is bounded by the uncinate process, medially, the orbital lamina of ethmoid bone (lamina papyracea), laterally, and the ethmoidal bulla, posterosuperiorly. This concept is easier to understand if one imagine the infundibulum as a prism so that its medial face is the hiatus semilunaris. The "lateral face" of this infundibulum contains the ostium of the maxillary sinus, which, therefore, opens into the infundibulum. Variations The uncinate process can be attached to either the lateral nasal wall, on the lamina papyracea (50%), the anterior cranial fossa, on the ethmoidal roof (25%), or the middle concha (2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Process Of Palatine Bone
The orbital process of the palatine bone is placed on a higher level than the sphenoidal, and is directed upward and lateralward from the front of the vertical part, to which it is connected by a constricted neck. It presents five surfaces, which enclose an air cell. Of these surfaces, three are articular and two non-articular. The articular surfaces are: # the anterior or maxillary, directed forward, lateralward, and downward, of an oblong form, and rough for articulation with the maxilla # the posterior or sphenoidal, directed backward, upward, and medialward; it presents the opening of the air cell, which usually communicates with the sphenoidal sinus; the margins of the opening are serrated for articulation with the sphenoidal concha # the medial or ethmoidal, directed forward, articulates with the labyrinth of the ethmoid. In some cases the air cell opens on this surface of the bone and then communicates with the posterior ethmoidal cells. More rarely it opens on both surface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoid Bone
The ethmoid bone (; from grc, ἡθμός, hēthmós, sieve) is an unpaired bone in the skull that separates the nasal cavity from the brain. It is located at the roof of the nose, between the two orbits. The cubical bone is lightweight due to a spongy construction. The ethmoid bone is one of the bones that make up the orbit of the eye. Structure The ethmoid bone is an anterior cranial bone located between the eyes. It contributes to the medial wall of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the nasal septum. The ethmoid has three parts: cribriform plate, ethmoidal labyrinth, and perpendicular plate. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and also contributes to formation of the anterior cranial fossa, the ethmoidal labyrinth consists of a large mass on either side of the perpendicular plate, and the perpendicular plate forms the superior two-thirds of the nasal septum. Between the orbital plate and the nasal conchae are the ethmoidal sinuses or ethmoidal air cells, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphenoidal Concha
The sphenoid bone is an unpaired bone of the neurocranium. It is situated in the middle of the skull towards the front, in front of the basilar part of the occipital bone. The sphenoid bone is one of the seven bones that articulate to form the orbit. Its shape somewhat resembles that of a butterfly or bat with its wings extended. Structure It is divided into the following parts: * a median portion, known as the body of sphenoid bone, containing the sella turcica, which houses the pituitary gland as well as the paired paranasal sinuses, the sphenoidal sinuses * two greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two lesser wings from the anterior side. * Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. Two sphenoidal conchae are situated at the anterior and inferior part of the body. Intrinsic ligaments of the sphenoid The more important of these are: * the pterygospinous, stretching between the spina angulari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Ethmoidal Foramen
Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The posterior ethmoidal foramen opens at the back part of this margin under cover of the projecting lamina of the sphenoid, and transmits the posterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system. A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e .... External links * () (#4) Foramina of the skull {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |