|
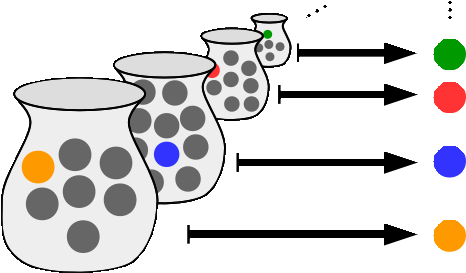
Equinumerous
In mathematics, two sets or classes ''A'' and ''B'' are equinumerous if there exists a one-to-one correspondence (or bijection) between them, that is, if there exists a function from ''A'' to ''B'' such that for every element ''y'' of ''B'', there is exactly one element ''x'' of ''A'' with ''f''(''x'') = ''y''. Equinumerous sets are said to have the same cardinality (number of elements). The study of cardinality is often called equinumerosity (''equalness-of-number''). The terms equipollence (''equalness-of-strength'') and equipotence (''equalness-of-power'') are sometimes used instead. Equinumerosity has the characteristic properties of an equivalence relation. The statement that two sets ''A'' and ''B'' are equinumerous is usually denoted :A \approx B \, or A \sim B, or , A, =, B, . The definition of equinumerosity using bijections can be applied to both finite and infinite sets, and allows one to state whether two sets have the same size even if they are infinite. Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Cantor
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor ( ; ; – 6 January 1918) was a mathematician who played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a foundations of mathematics, fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between the members of two sets, defined infinite set, infinite and well-order, well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. Cantor's method of proof of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal number, cardinal and ordinal number, ordinal numbers and their arithmetic. Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he was well aware of. Originally, Cantor's theory of transfinite numbers was regarded as counter-intuitive – even shocking. This caused it to encounter resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré and later from Hermann Wey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinal Number
In mathematics, a cardinal number, or cardinal for short, is what is commonly called the number of elements of a set. In the case of a finite set, its cardinal number, or cardinality is therefore a natural number. For dealing with the case of infinite sets, the infinite cardinal numbers have been introduced, which are often denoted with the Hebrew letter \aleph (aleph) marked with subscript indicating their rank among the infinite cardinals. Cardinality is defined in terms of bijective functions. Two sets have the same cardinality if, and only if, there is a one-to-one correspondence (bijection) between the elements of the two sets. In the case of finite sets, this agrees with the intuitive notion of number of elements. In the case of infinite sets, the behavior is more complex. A fundamental theorem due to Georg Cantor shows that it is possible for two infinite sets to have different cardinalities, and in particular the cardinality of the set of real numbers is gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantor's Theorem
In mathematical set theory, Cantor's theorem is a fundamental result which states that, for any Set (mathematics), set A, the set of all subsets of A, known as the power set of A, has a strictly greater cardinality than A itself. For finite sets, Cantor's theorem can be seen to be true by simple enumeration of the number of subsets. Counting the empty set as a subset, a set with n elements has a total of 2^n subsets, and the theorem holds because 2^n > n for all non-negative integers. Much more significant is Cantor's discovery of an argument that is applicable to any set, and shows that the theorem holds for infinite set, infinite sets also. As a consequence, the cardinality of the real numbers, which is the same as that of the power set of the integers, is strictly larger than the cardinality of the integers; see Cardinality of the continuum for details. The theorem is named for Georg Cantor, who first stated and proved it at the end of the 19th century. Cantor's theorem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiom Of Choice
In mathematics, the axiom of choice, abbreviated AC or AoC, is an axiom of set theory. Informally put, the axiom of choice says that given any collection of non-empty sets, it is possible to construct a new set by choosing one element from each set, even if the collection is infinite. Formally, it states that for every indexed family (S_i)_ of nonempty sets (S_i as a nonempty set indexed with i), there exists an indexed set (x_i)_ such that x_i \in S_i for every i \in I. The axiom of choice was formulated in 1904 by Ernst Zermelo in order to formalize his proof of the well-ordering theorem. The axiom of choice is equivalent to the statement that every partition has a transversal. In many cases, a set created by choosing elements can be made without invoking the axiom of choice, particularly if the number of sets from which to choose the elements is finite, or if a canonical rule on how to choose the elements is available — some distinguishing property that happens to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initial Ordinal
The von Neumann cardinal assignment is a cardinal assignment that uses ordinal numbers. For a well-orderable set ''U'', we define its cardinal number to be the smallest ordinal number equinumerous to ''U'', using the von Neumann definition of an ordinal number. More precisely: :, U, = \mathrm(U) = \inf \, where ON is the class of ordinals. This ordinal is also called the initial ordinal of the cardinal. That such an ordinal exists and is unique is guaranteed by the fact that ''U'' is well-orderable and that the class of ordinals is well-ordered, using the axiom of replacement. With the full axiom of choice, every set is well-orderable, so every set has a cardinal; we order the cardinals using the inherited ordering from the ordinal numbers. This is readily found to coincide with the ordering via ≤''c''. This is a well-ordering of cardinal numbers. Initial ordinal of a cardinal Each ordinal has an associated cardinal, its cardinality, obtained by simply forgetting the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinite Set
In set theory, an infinite set is a set that is not a finite set. Infinite sets may be countable or uncountable. Properties The set of natural numbers (whose existence is postulated by the axiom of infinity) is infinite. It is the only set that is directly required by the axioms to be infinite. The existence of any other infinite set can be proved in Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (ZFC), but only by showing that it follows from the existence of the natural numbers. A set is infinite if and only if for every natural number, the set has a subset whose cardinality is that natural number. If the axiom of choice holds, then a set is infinite if and only if it includes a countable infinite subset. If a set of sets is infinite or contains an infinite element, then its union is infinite. The power set of an infinite set is infinite. Any superset of an infinite set is infinite. If an infinite set is partitioned into finitely many subsets, then at least one of them must be infinite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinality
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the index finger. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is ''pollex'' (compare ''hallux'' for big toe), and the corresponding adjective for thumb is ''pollical''. Definition Thumb and fingers The English word ''finger'' has two senses, even in the context of appendages of a single typical human hand: 1) Any of the five terminal members of the hand. 2) Any of the four terminal members of the hand, other than the thumb. Linguistically, it appears that the original sense was the first of these two: (also rendered as ) was, in the inferred Proto-Indo-European language, a suffixed form of (or ), which has given rise to many Indo-European-family words (tens of them defined in English dictionaries) that involve, or stem from, concepts of fiveness. The thumb shares the following with each of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Theory
Set theory is the branch of mathematical logic that studies Set (mathematics), sets, which can be informally described as collections of objects. Although objects of any kind can be collected into a set, set theory – as a branch of mathematics – is mostly concerned with those that are relevant to mathematics as a whole. The modern study of set theory was initiated by the German mathematicians Richard Dedekind and Georg Cantor in the 1870s. In particular, Georg Cantor is commonly considered the founder of set theory. The non-formalized systems investigated during this early stage go under the name of ''naive set theory''. After the discovery of Paradoxes of set theory, paradoxes within naive set theory (such as Russell's paradox, Cantor's paradox and the Burali-Forti paradox), various axiomatic systems were proposed in the early twentieth century, of which Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory (with or without the axiom of choice) is still the best-known and most studied. Set the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Set
In mathematics, the power set (or powerset) of a set is the set of all subsets of , including the empty set and itself. In axiomatic set theory (as developed, for example, in the ZFC axioms), the existence of the power set of any set is postulated by the axiom of power set. The powerset of is variously denoted as , , , \mathbb(S), or . Any subset of is called a ''family of sets'' over . Example If is the set , then all the subsets of are * (also denoted \varnothing or \empty, the empty set or the null set) * * * * * * * and hence the power set of is . Properties If is a finite set with the cardinality (i.e., the number of all elements in the set is ), then the number of all the subsets of is . This fact as well as the reason of the notation denoting the power set are demonstrated in the below. : An indicator function or a characteristic function of a subset of a set with the cardinality is a function from to the two-element set , denoted as , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinal Number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets. A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least natural number that has not been previously used. To extend this process to various infinite sets, ordinal numbers are defined more generally using linearly ordered greek letter variables that include the natural numbers and have the property that every set of ordinals has a least or "smallest" element (this is needed for giving a meaning to "the least unused element"). This more general definition allows us to define an ordinal number \omega (omega) to be the least element that is greater than every natural number, along with ordinal numbers , , etc., which are even greater than . A linear order such that every non-empty subset has a least element is called a well-order. The axiom of choice implies that every set can be well-orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Product
In mathematics, specifically set theory, the Cartesian product of two sets and , denoted , is the set of all ordered pairs where is an element of and is an element of . In terms of set-builder notation, that is A\times B = \. A table can be created by taking the Cartesian product of a set of rows and a set of columns. If the Cartesian product is taken, the cells of the table contain ordered pairs of the form . One can similarly define the Cartesian product of sets, also known as an -fold Cartesian product, which can be represented by an -dimensional array, where each element is an -tuple. An ordered pair is a 2-tuple or couple. More generally still, one can define the Cartesian product of an indexed family of sets. The Cartesian product is named after René Descartes, whose formulation of analytic geometry gave rise to the concept, which is further generalized in terms of direct product. Set-theoretic definition A rigorous definition of the Cartesian product re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |