|
Equatorial Electrojet
The equatorial electrojet (EEJ) is a narrow ribbon of current flowing eastward in the day time equatorial region of the Earth's ionosphere. The abnormally large amplitude of variations in the horizontal components measured at equatorial geomagnetic observatories, as a result of EEJ, was noticed as early as 1920 from Huancayo Huancayo (; in qu, label=Wanka Quechua, Wankayuq , '(place) with a (sacred) rock') is the capital of Junín Region, in the central highlands of Peru. Location Huancayo is located in Huancayo Province, of which it is also the capital. Sit ... geomagnetic observatory. Observations by radar, rockets, satellites, and geomagnetic observatories are used to study EEJ. Causes The explanation for the existence of the equatorial electrojet lies with the anisotropic nature of ionospheric electrical conductivity and a process of self-reinforcement. Global-scale ionospheric circulation establishes a Sq (solar quiet) current system in the E region of the Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geomagnetic
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huancayo
Huancayo (; in qu, label=Wanka Quechua, Wankayuq , '(place) with a (sacred) rock') is the capital of Junín Region, in the central highlands of Peru. Location Huancayo is located in Huancayo Province, of which it is also the capital. Situated in the Mantaro Valley at an altitude of 3,271 meters, it belongs to the Quechua region. Depending on delimitation, the agglomeration has a population between 340,000 and 380,000 and is the fifth most populous city of the country. Huancayo is the cultural and commercial center of the whole central Peruvian Andes area. Huancayo Metropolitano is made up of seven districts that form the urban center of the Junín region. This region is considered central Peru's economic and social hub. Historical overview Pre-Columbian era The area was originally inhabited by the Huancas. At around 500 BC, they were incorporated into the Wari Empire. Despite efforts to defend its independence, the Huancas were eventually subdued by the Inca leader ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
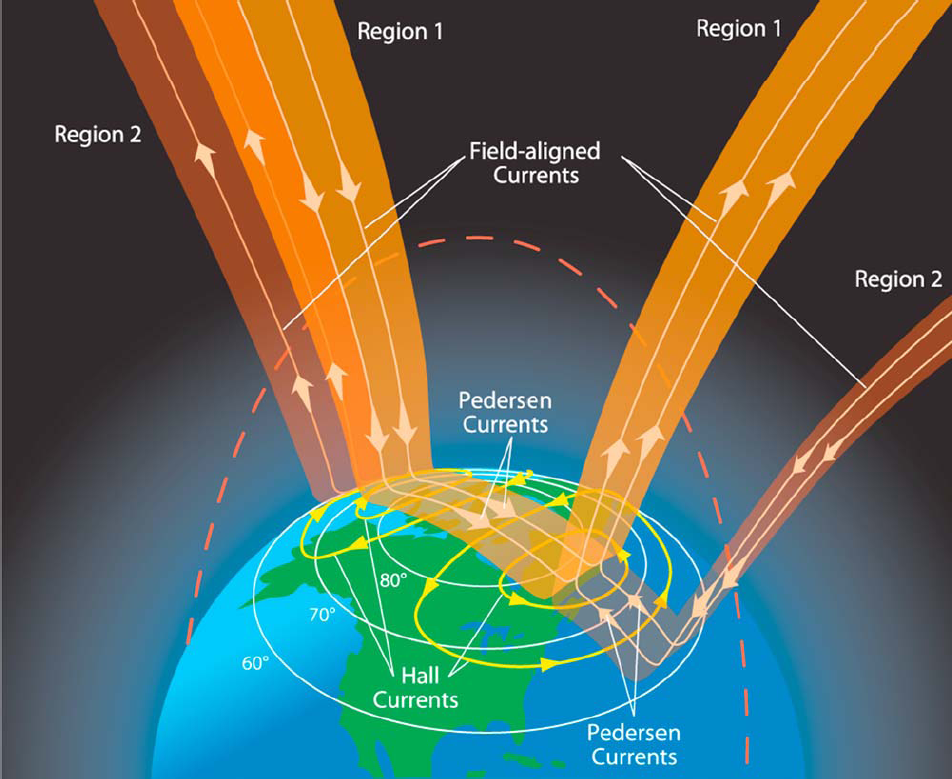
Pedersen Current
A Pedersen current is an electric current formed in the direction of the applied electric field when a conductive material with charge carriers is acted upon by an external electric field and an external magnetic field. Pedersen currents emerge in a material where the charge carriers collide with particles in the conductive material at approximately the same frequency as the gyratory frequency induced by the magnetic field. Pedersen currents are associated with a Pedersen conductivity related to the applied magnetic field and the properties of the material. History The first expression for the Pedersen conductivity was formulated by Peder Oluf Pedersen from Denmark in his 1927 work "The Propagation of Radio Waves along the Surface of the Earth and in the Atmosphere", where he pointed out that the geomagnetic field means that the conductivity of the ionosphere is anisotropic. Physical explanation When a moving charge carrier in a conductor is under the influence of a magnetic fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guiding Center
In physics, the motion of an electrically charged particle such as an electron or ion in a plasma in a magnetic field can be treated as the superposition of a relatively fast circular motion around a point called the guiding center and a relatively slow drift of this point. The drift speeds may differ for various species depending on their charge states, masses, or temperatures, possibly resulting in electric currents or chemical separation. Gyration If the magnetic field is uniform and all other forces are absent, then the Lorentz force will cause a particle to undergo a constant acceleration perpendicular to both the particle velocity and the magnetic field. This does not affect particle motion parallel to the magnetic field, but results in circular motion at constant speed in the plane perpendicular to the magnetic field. This circular motion is known as the gyromotion. For a particle with mass m and charge q moving in a magnetic field with strength B, it has a frequency, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Current
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879. A Hall effect can also occur across a void or hole in a semiconductor or metal plate, when current is injected via contacts that lie on the boundary or edge of the void or hole, and the charge flows outside the void or hole, in the metal or semiconductor. This Hall effect becomes observable in a perpendicular applied magnetic field across voltage contacts that lie on the boundary of the void on either side of a line connecting the current contacts. It exhibits apparent sign reversal in comparison to the standard "ordinary Hall effect" in the simply connected specimen, and depends only on the current injected from within the void. Superposition may also be realized in the Hall effect: first imagine the standard H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ørsted (satellite)
Ørsted is Denmark's first satellite, named after Hans Christian Ørsted (1777–1851), a Danish physicist and professor at the University of Copenhagen, who discovered electromagnetism in 1820. Objectives The spacecraft primary science objectives were to perform highly accurate and sensitive measurements of the geomagnetic field and to perform global monitoring of the high energy charged particle environment. Instruments The instrumentation consisted of two magnetometers ( proton precession and fluxgate), a star imager for attitude determination, a solid-state charged particle detector package, and a GPS receiver. The Science Instrument Team is responsible for the design of the instruments, while the Science Team is responsible for the science mission planning and international science participation. The science data obtained during the planned one-year mission will be used to derive an updated model of the geomagnetic field and its secular variation and to study the magneto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |