|
Eptatretus Springeri
''Eptatretus springeri'', the Gulf hagfish, is a bathydemersal vertebrate which lives primarily in the northeastern Gulf of Mexico. It has been observed feeding at and around brine pools: areas of high salinity which resemble lakes on the ocean floor that do not mix with the surrounding water due to difference in density. The high salt content, approximately 200 ppt compared to 35 ppt for standard seawater, creates a buoyant surface which renders oceanic submersibles unable to descend into the pool. It is believed that the inside of the pools only supports microbial life, while the majority of macroscopic life, such as methane-utilizing mussels, exists on the edges.S. E. MacAvoy, E. Morgan, R. S. Carney, and S. A. Macko, "Chemoautotrophic Production Incorporated by Heterotrophs in Gulf of Mexico Hydrocarbon Seeps: An Examination of Mobile Benthic Predators and Seep Residents," Journal of Shellfish Research 27(1), 153-161, (1 March 2008). https://doi.org/10.2983/0730-8000(2008)2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bryant Bigelow
Henry Bryant Bigelow (October 3, 1879 – December 11, 1967) was an American oceanographer and marine biologist. He is the grandson of Henry Bryant (naturalist), Henry Bryant who was an American physician and natural history, naturalist. After graduating from Harvard in 1901, he began working with famed ichthyologist Alexander Agassiz. Bigelow accompanied Agassiz on several major marine science expeditions including one aboard the ''USS Albatross (1882), Albatross'' in 1907. He began working at the Museum of Comparative Zoology in 1905 and joined Harvard's faculty in 1906 where he worked for 62 years. In 1911, Bigelow was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences. He helped found the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in 1930 and was its founding director. During his life he published more than one hundred papers and several books. He was a world-renowned expert on coelenterates and elasmobranchs. In 1948 Bigelow was awarded the Daniel Giraud Elliot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersible
A submersible is a small watercraft designed to operate underwater. The term "submersible" is often used to differentiate from other underwater vessels known as submarines, in that a submarine is a fully self-sufficient craft, capable of independent cruising with its own power supply and air renewal system, whereas a submersible is usually supported by a nearby ship, surface vessel, very large floating structure, platform, shore team or sometimes a larger submarine. In common usage by the general public, however, the word "submarine" may be used to describe a craft that is by the technical definition actually a submersible. There are many types of submersibles, including both crewed and uncrewed craft, otherwise known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses worldwide, such as oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, adventure, equipment maintenance and recovery, and underwater videography. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1952
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. Most fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the property of a material which allows it to change or assume different properties in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. It can be defined as a difference, when measured along different axes, in a material's physical or mechanical properties (absorbance, refractive index, conductivity, tensile strength, etc.). An example of anisotropy is light coming through a polarizer. Another is wood, which is easier to split along its grain than across it. Fields of interest Computer graphics In the field of computer graphics, an anisotropic surface changes in appearance as it rotates about its geometric normal, as is the case with velvet. Anisotropic filtering (AF) is a method of enhancing the image quality of textures on surfaces that are far away and steeply angled with respect to the point of view. Older techniques, such as bilinear and trilinear filtering, do not take into account the angle a surface is viewed from, which can result in aliasing or bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
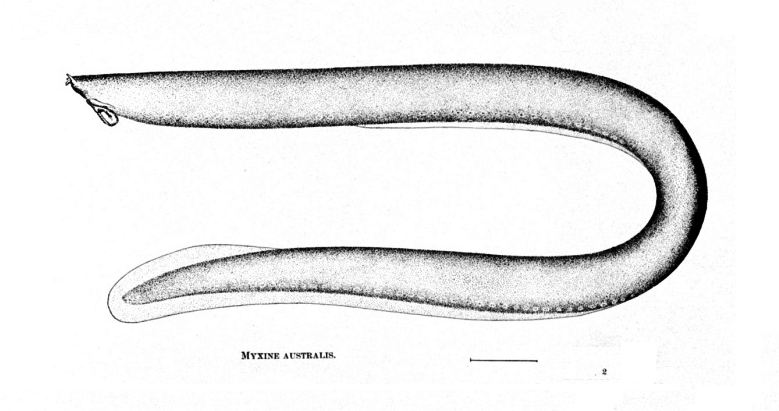
Myxine
''Myxine'' is a genus of hagfish, from the Greek μυξῖνος (''myxinos'', "slimy"). In 2021, three new species of ''Myxine'' were described from the Galápagos including '' M. phantasma'', the only species of ''Myxine'' to not have melanin-based pigments. Species * ''Myxine affinis'' Günther, 1870 (Patagonian hagfish) * '' Myxine australis'' Jenyns, 1842 (southern hagfish) * ''Myxine capensis'' Regan, 1913 (Cape hagfish) * ''Myxine circifrons'' Garman, 1899 (whiteface hagfish) * ''Myxine debueni'' Wisner & C. B. McMillan, 1995 (Magellan hagfish) * ''Myxine fernholmi'' Wisner & C. B. McMillan, 1995 (Falkland Islands hagfish) * ''Myxine formosana'' H. K. Mok & C. H. Kuo, 2001 (Formosa hagfish) * ''Myxine garmani'' D. S. Jordan & Snyder, 1901 (Garman's hagfish) * ''Myxine glutinosa'' Linnaeus, 1758 (Atlantic hagfish) *''Myxine greggi'' * ''Myxine hubbsi'' Wisner & C. B. McMillan, 1995 (Hubbs' hagfish) * ''Myxine hubbsoides'' Wisner & C. B. McMillan, 1995 * '' Myx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Hagfish
The Pacific hagfish (''Eptatretus stoutii'') is a species of hagfish. It lives in the mesopelagic to abyssal zone, abyssal Pacific ocean, near the ocean floor. It is a Agnatha, jawless fish and has a body plan that resembles early Paleozoic Era, paleozoic fish. They are able to excrete prodigious amounts of slime in self-defense. Description The Pacific hagfish has a long, eel-like body, but is not closely related to eels. Maximum body lengths of have been reported; typical length at maturity is around . It is dark brown, gray or brownish red, often tinted with blue or purple. The belly is lighter and sometimes has larger white patches. It has no true fins, but there is a Anatomical terms of location#Dorsal and ventral, dorsal fin-fold. The head, as in all agnathans, does not have jaws, and the sucker-like mouth is always open. The Pacific hagfish confused the scientists at first because Linnaeus mistakenly classified the organism as an "intestinal worm". Hagfish have loosely fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eptatretus
''Eptatretus'' is a large genus of hagfish. Species There are currently 49 recognized species in this genus: * ''Eptatretus aceroi'' Polanco Fernández & Fernholm, 2014 (Acero's hagfish)Polanco Fernandez, A. & Fernholm, B. (2014): A New Species of Hagfish (Myxinidae: ''Eptatretus'') from the Colombian Caribbean. ''Copeia, 2014 (3): 530–533.'' * ''Eptatretus alastairi'' Mincarone & Fernholm, 2010 (Alastair's hagfish) * ''Eptatretus ancon'' H. K. Mok, Saavedra-Diaz & Acero P, 2001 * ''Eptatretus astrolabium'' Fernholm & Mincarone, 2010 (Astrolabe hagfish) * ''Eptatretus atami'' Dean, 1904 (Brown hagfish) * '' Eptatretus bischoffii'' A. F. Schneider, 1880 (Bischoff's hagfish) * ''Eptatretus bobwisneri'' Fernholm, Norén, S. O. Kullander, Quattrini, Zintzen, C. D. Roberts, H. K. Mok & C. H. Kuo, 2013 (Bob Wisner's hagfish)Fernholm, B., Norén, M., Kullander, S.O., Quattrini, A.M., Zintzen, V., Roberts, C.D., Mok, H.-K. & Kuo, C.-H. (2013): Hagfish phylogeny and tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
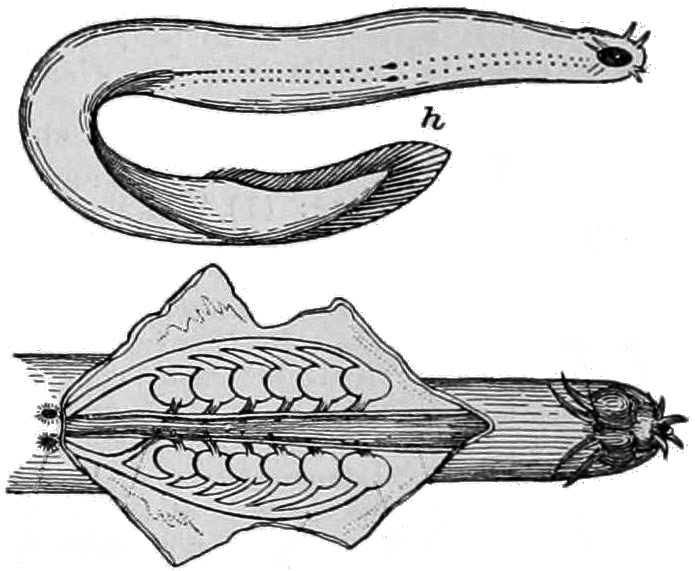
Hagfish
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, although hagfish do have rudimentary vertebrae. Along with lampreys, hagfish are jawless; the two form the sister group to jawed vertebrates, and living hagfish remain similar to hagfish from around 300 million years ago. The classification of hagfish had been controversial. The issue was whether the hagfish was a degenerate type of vertebrate-fish that through evolution had lost its vertebrae (the original scheme) and was most closely related to lampreys, or whether hagfish represent a stage that precedes the evolution of the vertebral column (the alternative scheme) as is the case with lancelets. Recent DNA evidence has supported the original scheme. The original scheme groups hagfish and lampreys together as cyclostomes (or historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate and inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotroph
A Chemotroph is an organism that obtains energy by the oxidation of electron donors in their environments. These molecules can be organic ( chemoorganotrophs) or inorganic (chemolithotrophs). The chemotroph designation is in contrast to phototrophs, which use photons. Chemotrophs can be either autotrophic or heterotrophic. Chemotrophs can be found in areas where electron donors are present in high concentration, for instance around hydrothermal vents. Chemoautotroph Chemoautotrophs, in addition to deriving energy from chemical reactions, synthesize all necessary organic compounds from carbon dioxide. Chemoautotrophs can use inorganic energy sources such as hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, ferrous iron, molecular hydrogen, and ammonia or organic sources to produce energy. Most chemoautotrophs are extremophiles, bacteria or archaea that live in hostile environments (such as deep sea vents) and are the primary producers in such ecosystems. Chemoautotrophs generally fall into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathymodiolus Childressi
''Bathymodiolus childressi'' is a species of deepwater mussel, a marine bivalve mollusk species in the family Mytilidae, the mussels. Although this species has been known since 1985,Childress J.J., Fisher C.R., Brooks J.M., Kennicutt M.C., II, Bidigare R. & Anderson A. (1986) A methanotrophic marine molluscan symbiosis: mussels fueled by gas. Science, 233, 1306-1308. it was formally described as a species in 1998. Habitat This species lives in cold seeps in the Gulf of Mexico. ''Bathymodiolus childressi'' is stenothermal species living in temperatures ranging from 6.5 to 7.2 °C.Berger M. S. & Young C. M. (2006). "Physiological response of the cold-seep mussel ''Bathymodiolus childressi'' to acutely elevated temperature". ''Marine Biology'' 149(6): 1397-1402. However it was able to survive the temperature of 20 °C in the laboratory. Symbiosis This mussel harbors intracellular methanotrophic bacteria in its gills. The bacteria provide carbon to the mussel. Inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in older texts. The informal synonym ''microbe'' () comes from μικρός, mikrós, "small" and βίος, bíos, "life". is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from ancient times, such as in Jain scriptures from sixth century BC India. The scientific study of microorganisms began with their observation under the microscope in the 1670s by Anton van Leeuwenhoek. In the 1850s, Louis Pasteur found that microorganisms caused food spoilage, debunking the theory of spontaneous generation. In the 1880s, Robert Koch discovered that microorganisms caused the diseases tuberculosis, cholera, diphtheria, and anthrax. Because mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_with_its_prey.jpg)

