|
Environmental Chemistry
Environmental chemistry is the scientific study of the chemical and biochemical phenomena that occur in natural places. It should not be confused with green chemistry, which seeks to reduce potential pollution at its source. It can be defined as the study of the sources, reactions, transport, effects, and fates of chemical species in the air, soil, and water environments; and the effect of human activity and biological activity on these. Environmental chemistry is an interdisciplinary science that includes atmospheric, aquatic and soil chemistry, as well as heavily relying on analytical chemistry and being related to environmental and other areas of science. Environmental chemistry involves first understanding how the uncontaminated environment works, which chemicals in what concentrations are present naturally, and with what effects. Without this it would be impossible to accurately study the effects humans have on the environment through the release of chemicals. Envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemist
A chemist (from Greek ''chēm(ía)'' alchemy; replacing ''chymist'' from Medieval Latin ''alchemist'') is a graduated scientist trained in the study of chemistry, or an officially enrolled student in the field. Chemists study the composition of matter and its properties. Chemists carefully describe the properties they study in terms of quantities, with detail on the level of molecules and their component atoms. Chemists carefully measure substance proportions, chemical reaction rates, and other chemical properties. In Commonwealth English, pharmacists are often called chemists. Chemists use their knowledge to learn the composition and properties of unfamiliar substances, as well as to reproduce and synthesize large quantities of useful naturally occurring substances and create new artificial substances and useful processes. Chemists may specialize in any number of Chemistry#Subdisciplines, subdisciplines of chemistry. Materials science, Materials scientists and metallurgists sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is Dissolution (chemistry), dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium at the given temperature. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%). Oxygen saturation can be measured regionally and noninvasively. Artery, Arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is commonly measured using pulse oximetry. Tissue saturation at peripheral scale can be measured using near-infrared spectroscopy, NIRS. This technique can be applied on both muscle and brain. In medicine In medicine, oxygen saturation refers to ''oxygenation'', or when oxygen molecules () enter the Tissue (biology), tissues of the body. In this case blood is oxygenated in the lungs, where oxygen molecules travel from the air into the blood. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
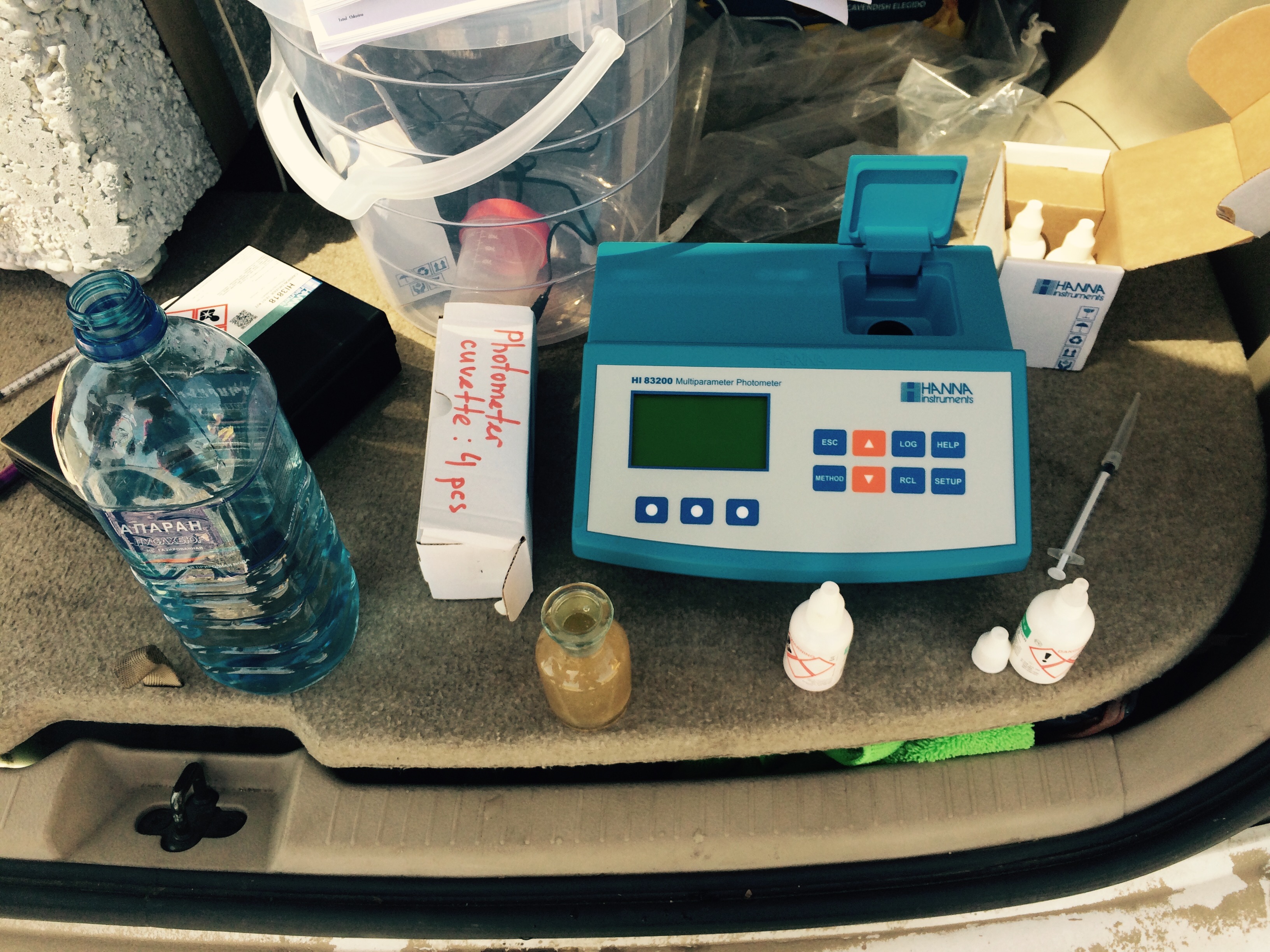
Water Quality
Water quality refers to the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water based on the standards of its usage. It is most frequently used by reference to a set of standards against which compliance, generally achieved through treatment of the water, can be assessed. The most common standards used to monitor and assess water quality convey the health of ecosystems, safety of human contact, extent of water pollution and condition of drinking water. Water quality has a significant impact on water supply and often determines supply options. Impacts on public health Over time, there has been increasing recognition of the importance of drinking water quality and its impact on public health. This has led to increasing protection and management of water quality. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a creativecommons:by/4.0/, Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License The understanding of the links between water quality and healt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Sink
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial carbon sequestration process that "removes a greenhouse gas, an aerosol or a precursor of a greenhouse gas from the atmosphere". These sinks form an important part of the natural carbon cycle. An overarching term is carbon pool, which is all the places where carbon on Earth can be, i.e. the atmosphere, oceans, soil, florae, fossil fuel reservoirs and so forth. A carbon sink is a type of carbon pool that has the capability to take up more carbon from the atmosphere than it releases. Globally, the two most important carbon sinks are vegetation and the ocean. Soil is an important carbon storage medium. Much of the organic carbon retained in the soil of agricultural areas has been depleted due to intensive farming. '' Blue carbon'' designates carbon that is fixed via certain marine ecosystems. ''Coastal blue carbon'' includes mangroves, salt marshes and seagrasses. These make up a majority of ocean plant life and store large quantities of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollutant
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effect, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming (i.e. minerals or extracted compounds like oil) or anthropogenic in origin (i.e. manufactured materials or byproducts). Pollutants result in environmental pollution or become of public health concern when they reach a concentration high enough to have significant negative impacts. A pollutant may cause long- or short-term damage by changing the growth rate of plant or animal species, or by interfering with resources used by humans, human health or wellbeing, or property values. Some pollutants are biodegradable and therefore will not persist in the environment in a long term. However, the degradation products of some pollutants are themselves pollutants such as DDE and DDD produced from the degradation of DDT. Pollution has widespread negative impact on the environment. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Substance
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contaminant
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, wiktionary:Workplace, workplace, etc. Types of contamination Within the sciences, the word "contamination" can take on a variety of subtle differences in meaning, whether the contaminant is a solid or a liquid, as well as the variance of environment the contaminant is found to be in. A contaminant may even be more abstract, as in the case of an unwanted energy source that may interfere with a process. The following represent examples of different types of contamination based on these and other variances. Chemical contamination In chemistry, the term "contamination" usually describes a single constituent, but in specialized fields the term can also mean chemical mixtures, even up to the level of cellular materials. All chemicals contain some level of impurity. Contamination may be recognized or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative inorganic analysis, Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while Quantitative analysis (chemistry), quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemistry, wet chemical methods and modern analytical techniques. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as Precipitation (chemistry), precipitation, Extraction (chemistry), extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling (statistics)
In this statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is the selection of a subset or a statistical sample (termed sample for short) of individuals from within a population (statistics), statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. The subset is meant to reflect the whole population, and statisticians attempt to collect samples that are representative of the population. Sampling has lower costs and faster data collection compared to recording data from the entire population (in many cases, collecting the whole population is impossible, like getting sizes of all stars in the universe), and thus, it can provide insights in cases where it is infeasible to measure an entire population. Each observation measures one or more properties (such as weight, location, colour or mass) of independent objects or individuals. In survey sampling, weights can be applied to the data to adjust for the sample design, particularly in stratified samplin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude (mathematics), magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of System of measurement, systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution (chemistry)
In chemistry, a solution is defined by IUPAC as "A liquid or solid phase containing more than one substance, when for convenience one (or more) substance, which is called the solvent, is treated differently from the other substances, which are called solutes. When, as is often but not necessarily the case, the sum of the mole fractions of solutes is small compared with unity, the solution is called a dilute solution. A superscript attached to the ∞ symbol for a property of a solution denotes the property in the limit of infinite dilution." One important parameter of a solution is the concentration, which is a measure of the amount of solute in a given amount of solution or solvent. The term " aqueous solution" is used when one of the solvents is water. Types ''Homogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture form a single phase. ''Heterogeneous'' means that the components of the mixture are of different phase. The properties of the mixture (such as concentration, temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |