|
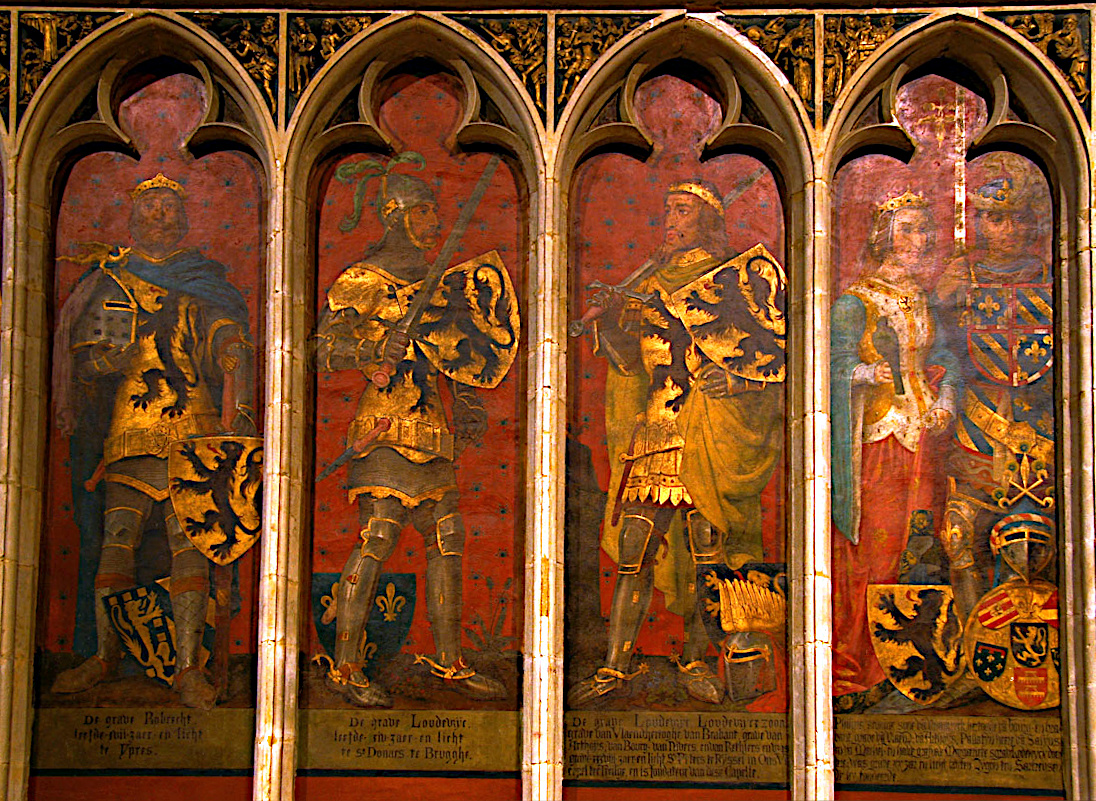
Enguerrand IV, Lord Of Coucy
Enguerrand IV, Lord of Coucy (c. 1236 – 1311) was the son of Enguerrand III, Lord of Coucy and Marie de Montmirail. He succeeded his older brother Raoul II, Lord of Coucy, serving as the Sire de Coucy from his brother's death in 1250 until his own in 1311. Biography Enguerrand IV succeeded to the large fief established by his father, Enguerrand the Great, due to his elder brother's death on crusade. Enguerrand IV's rule was notable for his crimes and cruelty. Setting an important medieval legal precedent, King Louis IX of France refused to allow him trial by combat for the hanging of three Flemish squires found on his land, and imprisoned him instead. In the end, Enguerrand escaped with a fine, and through his wealth remained important to the King, lending him 15,000 livres in 1265 to purchase a piece of the True Cross. He was married twice: his first wife was Margaret of Guelders, and his second wife was Jeanne of Flanders, daughter of Robert III, Count of Flanders Rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of Coucy
The Lords of Coucy (french: sires de Coucy or ''seigneurs de Coucy''), also spelt Couci, were a medieval lordship based on the barony of Coucy located in the current commune of Coucy-le-Château-Auffrique, Picardy. The château de Coucy was founded by Hervé, archbishop of Rheims, and remained under the fluctuating control of these archbishops for some time until probably the later part of the 10th century. The exact status of Coucy becomes obscure for nearly a century before the emergence of Lord Aubrey, Earl of Northumbria. Though the Lords of Coucy were entitled to the title of baron, they preferred the rarer ''Sire''. The lords of Coucy became, especially in the 13th century, one of the most powerful sub-comital magnates in western Europe and forged links with royal families, such as those of France, England, Scotland and Austria. The title was eventually absorbed at the end of the 14th century by Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans. List of known lords of Coucy * 1059: Aubrey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raoul II, Lord Of Coucy
Raoul II, Lord of Coucy (died 1250) was a son of Enguerrand III and his wife Maria of Oisy. In 1246 he succeeded his father as lord of Coucy. Raoul died at the Battle of Mansurah in Egypt during the Seventh Crusade. Raoul married Elisabeth, daughter of Walter III of Châtillon, and later remarried to Philippe of Dammartin Philippe of Dammartin (Philippa de Dammartin) was a 13th-century noble woman. Philippe was the daughter of Simon of Dammartin, Count of Aumâle and his wife Marie of Ponthieu. She was the sister of Joan, Countess of Ponthieu, wife of Ferdinand III ..., daughter of Simon of Dammartin. References Sources * * * 1250 deaths Christians of the Sixth Crusade Christians of the Seventh Crusade Lords of Coucy Year of birth unknown {{France-noble-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enguerrand V, Lord Of Coucy
Enguerrand V, Lord of Coucy (-after 1321) inherited the title of Lord of Coucy and castle from his maternal uncle, Enguerrand IV in 1311. He was also lord of Oisy and Montmirail. Biography Enguerrand was the second son of Arnould III, Count of Guînes and Alix de Coucy, daughter of Enguerrand III, Lord of Coucy. His father, Arnould, sold the county of Guines to King Louis IX of France, forcing Enguerrand to find his fortune abroad. After arriving in Scotland, he married Christiana Lindsay in Scotland. Christiana was the daughter of William Lindsay and Ada Balliol, sister of John Balliol. Their wedding was arranged by their mutual cousin, King Alexander III of Scotland. Enguerrand was present at the recognition of Margaret as Alexander III's heir and the Treaty of Birgham in 1290. On 28 May 1283, Enguerrand pledged his service to King Edward I of England Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enguerrand III, Lord Of Coucy
Enguerrand III de Boves, Lord of Coucy (c. 1182 – 1242) was a medieval French nobleman. The eldest son and successor of Ralph I, Lord of Coucy (c. 1134 – 1191) and Alix de Dreux,M. A. Pollock, ''Scotland, England and France After the Loss of Normandy, 1204-1296: Auld Amitie''. Boydell & Brewer, 2015. pg. 145. he succeeded as Lord of Coucy (''sieur de Couci'') in 1191, and held it until his death; he was also lord of Marle and Boves. Biography Enguerrand III was born in Marle, Picardy, France. He became one of the most ambitious and powerful of all the French nobles, called by one historian "the greatest baron in all Picardy", and earning himself his epithet, ''Enguerrand le Grand'', or Enguerrand "the Great". Enguerrand had an illustrious military career, helping King Philip II of France reduce the French territories of the King of England. Enguerrand campaigned in Anjou in 1205, and in 1214, fought in the French victory over an Anglo-German alliance at the Battle of Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lords Of Coucy
The Lords of Coucy (french: sires de Coucy or ''seigneurs de Coucy''), also spelt Couci, were a medieval lordship based on the barony of Coucy located in the current commune of Coucy-le-Château-Auffrique, Picardy. The château de Coucy was founded by Hervé, archbishop of Rheims, and remained under the fluctuating control of these archbishops for some time until probably the later part of the 10th century. The exact status of Coucy becomes obscure for nearly a century before the emergence of Aubrey de Coucy, Lord Aubrey, Earl of Northumbria. Though the Lords of Coucy were entitled to the title of baron, they preferred the rarer ''Sire''. The lords of Coucy became, especially in the 13th century, one of the most powerful sub-comital magnates in western Europe and forged links with royal families, such as those of France, England, Scotland and Austria. The title was eventually absorbed at the end of the 14th century by Louis I, Duke of Orléans, Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans. Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Precedent
A precedent is a principle or rule established in a previous legal case that is either binding on or persuasive for a court or other tribunal when deciding subsequent cases with similar issues or facts. Common-law legal systems place great value on deciding cases according to consistent principled rules, so that similar facts will yield similar and predictable outcomes, and observance of precedent is the mechanism by which that goal is attained. The principle by which judges are bound to precedents is known as ''stare decisis'' (a Latin phrase with the literal meaning of "to stand in the-things-that-have-been-decided"). Common-law precedent is a third kind of law, on equal footing with statutory law (that is, statutes and codes enacted by legislative bodies) and subordinate legislation (that is, regulations promulgated by executive branch agencies, in the form of delegated legislation) in UK parlance – or regulatory law (in US parlance). Case law, in common-law jurisdictions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IX Of France
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the Direct Capetians. He was crowned in Reims at the age of 12, following the death of his father Louis VIII Louis VIII (5 September 1187 – 8 November 1226), nicknamed The Lion (french: Le Lion), was King of France from 1223 to 1226. As prince, he invaded England on 21 May 1216 and was excommunicated by a papal legate on 29 May 1216. On 2 June 1216 .... His mother, Blanche of Castile, ruled the kingdom as regent until he reached maturity, and then remained his valued adviser until her death. During Louis' childhood, Blanche dealt with the opposition of rebellious vassals and secured Capetian success in the Albigensian Crusade, which had started 20 years earlier. As an adult, Louis IX faced recurring conflicts with some of his realm's most powerful nobles, such as Hugh X of Lusignan and Peter of Dreux. Simult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trial By Combat
Trial by combat (also wager of battle, trial by battle or judicial duel) was a method of Germanic law to settle accusations in the absence of witnesses or a confession in which two parties in dispute fought in single combat; the winner of the fight was proclaimed to be right. In essence, it was a judicially sanctioned duel. It remained in use throughout the European Middle Ages, gradually disappearing in the course of the 16th century. History Origins Unlike trial by ordeal in general, which is known to many cultures worldwide, trial by combat is known primarily from the customs of the Germanic peoples. The practice was "almost universal in Europe" according to medievalist Eric Jager. It was in use among the ancient Burgundians, Ripuarian Franks, Alamans, Lombards, and Swedes. It was unknown in Anglo-Saxon law and Roman law and it does not figure in the traditions of Middle Eastern antiquity such as the code of Hammurabi or the Torah. However, it is recorded in the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livres
The (; ; abbreviation: ₶.) was one of numerous currencies used in medieval France, and a unit of account (i.e., a monetary unit used in accounting) used in Early Modern France. The 1262 monetary reform established the as 20 , or 80.88 grams of fine silver. The was a gold coin of one minted in large numbers from 1360. In 1549, the was decreed a unit of account, and in 1667 it officially replaced the . In 1720, the was redefined as 0.31 grams of pure gold, and in 1726, in a devaluation under Louis XV, as 4.50516 grams of fine silver. It was the basis of the revolutionary French franc of 1795, defined as 4.5 grams of fine silver exactly. Circulating currency In France, the was worth 240 deniers (the "Tours penny"). The latter were initially minted by the abbey of Saint Martin in the Touraine region of France. Soon after Philip II of France seized the counties of Anjou and Touraine in 1203 and standardized the use of the there, the began to supersede the (Paris pou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert III, Count Of Flanders
Robert III (1249 – 17 September 1322), also called Robert of Béthune and nicknamed The Lion of Flanders (''De Leeuw van Vlaanderen''), was the Count of Nevers from 1273 and Count of Flanders from 1305 until his death. History Robert was the oldest son of Guy of Dampierre from his first marriage with Matilda of Béthune. His father essentially transferred the reign of Flanders to him in November 1299, during his war with Philip IV of France. Both father and son were taken into captivity in May 1300, and Robert was not released until 1305. Robert of Béthune gained military fame in Italy, when he fought at the side of his father-in-law, Charles I of Sicily (1265–1268) against the last Hohenstaufens, Manfred and Conradin. Together with his father he took part in 1270 in the Eighth Crusade, led by Saint Louis. After his return from the Crusade he continued to be a loyal aid for his father, politically and militarily, in the fight against the attempts of the French King Philip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulletin De La Commission Royale D'Histoire
The Commission royale d'Histoire (in French) or Koninklijke Commissie voor Geschiedenis (in Dutch) is the Belgian Royal Historical Commission. It was founded by royal decree on 22 July 1834. They initially published their proceedings under the title ''Compte-rendu des séances de la commission royale d'histoire'' and since 1845 have published a journal, the ''Bulletin de la Commission royale d'Histoire / Handelingen van de Koninklijke Commissie voor Geschiedenis''. Members Victor Coremans Victor Amédée Jacques Marie Coremans (5 October 1802 – 23 October 1872) was a Belgian archivist, journalist, historian, and political activist. He supported the Flemish Movement, advocating nationhood for Flanders. Life and career Victor wa ... was appointed to the Commission in 1836. References History organisations based in Belgium Heritage organizations {{Belgium-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |