|
English Coordinators
English coordinators (also known as coordinating conjunctions) are conjunctions that connect words, phrases, or clauses with equal syntactic importance. The primary coordinators in English are ''and'', ''but'', ''or'', and ''nor''. Syntactically, they appear between the elements they connect, and semantically, they express additive, contrastive, or alternative relationships between those elements. Terminology and membership Matthews defines ''coordinator'' as "a word, etc. which links syntactic units standing in a relation of coordination." Most dictionaries and many traditional grammar books use the term ''coordinating conjunction'' for this group of words. Central coordinators The primary coordinators include ''and'', ''but'', ''or'', and ''nor''. ''And'' ''And'' is a coordinator used to connect elements that have an additive relationship, such as ''I bought apples and oranges'' or ''He worked hard and achieved success''. ''But'' ''But'' is a coordinator used to c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunction (grammar)
In grammar, a conjunction (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated or ) is a part of speech that connects words, phrases, or clauses that are called the conjuncts of the conjunctions. That definition may overlap with that of other parts of speech and so what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each language. In English, a given word may have several word sense, senses and be either a preposition or a conjunction, depending on the syntax of the sentence. For example, ''after'' is a preposition in "he left after the fight" but is a conjunction in "he left after they fought". In general, a conjunction is an invariable (non-inflection, inflected) grammatical particle that may or may not stand between the items conjoined. The definition of conjunction may also be extended to idiomatic phrases that behave as a unit with the same function, "as well as", "provided that". A simple literary example of a conjunction is "the truth of nature, ''and'' the power of giving inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue (Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining trait of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation associated with dependency grammars; hence, phrase structure grammars are also known as constituency grammars. Any of several related theories for the parsing of natural language qualify as constituency grammars, and most of them have been develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Grammar
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, Sentence (linguistics), sentences, and whole texts. This article describes a generalized, present-day Standard English – a form of speech and writing used in public discourse, including broadcasting, education, entertainment, government, and news, over a range of Register (sociolinguistics), registers, from formal to informal. Divergences from the grammar described here occur in some historical, social, cultural, and regional List of dialects of the English language, varieties of English, although these are more minor than differences in English phonology, pronunciation and lexicon, vocabulary. Modern English has largely abandoned the inflectional grammatical case, case system of Indo-European in favor of analytic language, analytic constructions. The personal pronouns retain morphological case more strongly than any other word class (a remnant of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Prepositions
English prepositions are words – such as ''of'', ''in'', ''on'', ''at'', ''from'', etc. – that function as the head of a prepositional phrase, and most characteristically license a noun phrase object (e.g., ''in the water''). Semantically, they most typically denote relations in space and time. Morphologically, they are usually simple and do not inflect. They form a closed lexical category. Many of the most common of these are grammaticalized and correspond to case markings in languages such as Latin. For example, ''of'' typically corresponds to the genitive. History of the concept in English The history of the idea of prepositions inEnglish grammar writing can be seen as one of relative stagnation, only exceptionally interrupted by certain more influential authors... It was only in the second half of the twentieth century that the situation radically changed and since then, grammarians have introduced scientifically precise definitions and developed detailed and elab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subordination (linguistics)
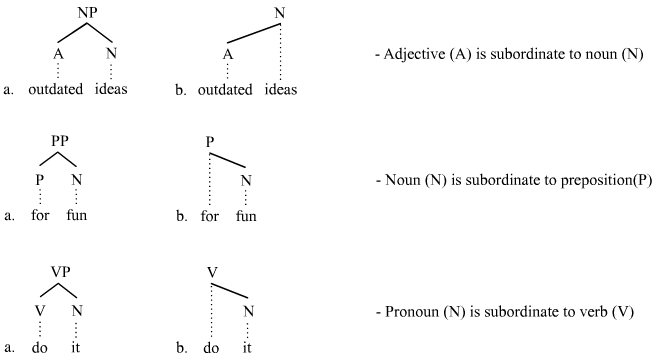
In linguistics, subordination (abbreviated variously , , or ) is a principle of the hierarchical organization of linguistic units. While the principle is applicable in semantics, morphology, and phonology, most work in linguistics employs the term "subordination" in the context of syntax, and that is the context in which it is considered here. The syntactic units of sentences are often either subordinate or coordinate to each other. Hence an understanding of subordination is promoted by an understanding of coordination, and vice versa. Subordinate clauses Subordination as a concept of syntactic organization is associated closely with the distinction between ''coordinate'' and ''subordinate'' clauses. One clause is subordinate to another if it depends on it. The dependent clause is called a ''subordinate clause'' and the independent clause is called the ''main clause'' (= matrix clause). Subordinate clauses are usually introduced by subordinators (= subordinate conjunctions) such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Subordinators
English subordinators (also known as subordinating conjunctions or complementizers) are words that mostly mark clauses as subordinate. The subordinators form a closed lexical category in English and include ''whether''; and, in some of their uses, ''if'', ''that'', ''for'', arguably ''to'', and marginally ''how''. Syntactically, they appear immediately before the subordinate element. Semantically, they tend to be empty. Terminology and membership Peter Matthews defines ''subordinator'' as "a word, etc. which marks a clause as subordinate." Most dictionaries and many traditional grammar books use the term ''subordinating conjunction'' and include a much larger set of words, most of them prepositions such as ''before'', ''when'', and ''though'' that take clausal complements. The generative grammar tradition uses the term ''complementizer'', a term which sometimes excludes the prepositions. Membership The subordinators are ''whether''; and, in some of their uses, '' if'', ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Adjectives
English adjectives form a large open category of words in English which, semantically, tend to denote properties such as size, colour, mood, quality, age, etc. with such members as ''other'', ''big'', ''new'', ''good'', ''different'', ''Cuban'', ''sure'', ''important'', and ''right''. Adjectives head adjective phrases, and the most typical members function as modifiers in noun phrases. Most adjectives either inflect for grade (e.g., ''big'', ''bigger'', ''biggest'') or combine with ''more'' and ''most'' to form comparatives (e.g., ''more interesting'') and superlatives (e.g., ''most interesting''). Huddleston, Rodney, Geoffrey K. Pullum, and Brett Reynolds. ''A Student's Introduction to English Grammar''. 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, 2022. p.157. They are characteristically modifiable by ''very'' (e.g., ''very small''). A large number of the most typical members combine with the suffix ''-ly'' to form adverbs (e.g., ''final'' + ''ly'': ''finally''). Most adjectives fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Grammar
Traditional grammar (also known as classical grammar) is a framework for the description of the structure of a language. The roots of traditional grammar are in the work of classical Greek and Latin philologists. The formal study of grammar based on these models became popular during the Renaissance. Traditional grammars may be contrasted with more modern theories of grammar in theoretical linguistics, which grew out of traditional descriptions. While traditional grammars seek to describe how particular languages are used, or to teach people to speak or read them, grammar frameworks in contemporary linguistics often seek to explain the nature of language knowledge and ability. Traditional grammar is often prescriptive, and may be regarded as unscientific by those working in linguistics. Traditional Western grammars classify words into parts of speech. They describe the patterns for word inflection, and the rules of syntax by which those words are combined into sentences. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an semantics, objective or pragmatics, practical semantics, meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no consensus among linguistics, linguists on its definition and numerous attempts to find specific criteria of the concept remain controversial. Different standards have been proposed, depending on the theoretical background and descriptive context; these do not converge on a single definition. Some specific definitions of the term "word" are employed to convey its different meanings at different levels of description, for example based on phonology, phonological, grammar, grammatical or orthography, orthographic basis. Others suggest that the concept is simply a convention used in everyday situations. The concept of "word" is distinguished from that of a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of language that has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination (linguistics)
In linguistics, coordination is a complex syntactic structure that links together two or more elements; these elements are called ''conjuncts'' or ''conjoins''. The presence of coordination is often signaled by the appearance of a coordinator (coordinating conjunction), e.g. ''and'', ''or'', ''but'' (in English). The totality of coordinator(s) and conjuncts forming an instance of coordination is called a coordinate structure. The unique properties of coordinate structures have motivated theoretical syntax to draw a broad distinction between coordination and subordination. It is also one of the many constituency tests in linguistics. Coordination is one of the most studied fields in theoretical syntax, but despite decades of intensive examination, theoretical accounts differ significantly and there is no consensus on the best analysis. Coordinators A ''coordinator'' or a coordinating conjunction, often appears between the conjuncts, usually at least between the penultimate and ult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantics
Semantics (from grc, σημαντικός ''sēmantikós'', "significant") is the study of reference, meaning, or truth. The term can be used to refer to subfields of several distinct disciplines, including philosophy Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ..., linguistics and computer science. History In English, the study of meaning in language has been known by many names that involve the Ancient Greek word (''sema'', "sign, mark, token"). In 1690, a Greek rendering of the term ''semiotics'', the interpretation of signs and symbols, finds an early allusion in John Locke's ''An Essay Concerning Human Understanding'': The third Branch may be called [''simeiotikí'', "semiotics"], or the Doctrine of Signs, the most usual whereof being words, it is aptly enough ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)


.jpg)
