|
Emmert's Law
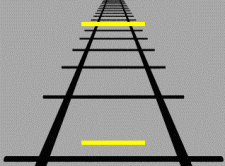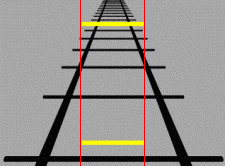
Emmert's law states that objects that generate retinal images of the same size will look different in physical size (linear size) if they appear to be located at different distances. Specifically, the ''perceived linear size'' of an object increases as its ''perceived'' distance from the observer increases. This makes intuitive sense: an object of constant size will project progressively smaller retinal images as its distance from the observer increases. Similarly, if the retinal images of two ''different'' objects at different distances are the same, the physical size of the object that is farther away must be larger than the one that is closer. Emil Emmert (1844–1911) first described the law in 1881. He noted that an afterimage appeared to increase in size when projected to a greater distance. Some authors thus take Emmert's law to refer strictly to the increase in the apparent size of an after-image when the distance between observer and projection plane is increased, as it d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which then processes that image within the retina and sends nerve impulses along the optic nerve to the visual cortex to create visual perception. The retina serves a function which is in many ways analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The primary light-sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells, which are of two types: rods and cones. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide monochromatic vision. Cones function in well-lit conditions and are responsible for the perception of colour through the use of a range of opsins, as well as high-acuity vision used for task ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil Emmert
Emil or Emile may refer to: Literature *''Emile, or On Education'' (1762), a treatise on education by Jean-Jacques Rousseau * ''Émile'' (novel) (1827), an autobiographical novel based on Émile de Girardin's early life *''Emil and the Detectives'' (1929), a children's novel *"Emil", nickname of the Kurt Maschler Award for integrated text and illustration (1982–1999) *''Emil i Lönneberga'', a series of children's novels by Astrid Lindgren Military *Emil (tank), a Swedish tank developed in the 1950s * Sturer Emil, a German tank destroyer People *Emil (given name), including a list of people with the given name ''Emil'' or ''Emile'' *Aquila Emil (died 2011), Papua New Guinean rugby league footballer Other * ''Emile'' (film), a Canadian film made in 2003 by Carl Bessai *Emil (river), in China and Kazakhstan See also * * *Aemilius (other) *Emilio (other) *Emílio (other) *Emilios (other) Emilios, or Aimilios, (Greek: Αιμίλιος) is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size Constancy
Subjective constancy or perceptual constancy is the perception of an object or quality as constant even though our sensation of the object changes. While the physical characteristics of an object may not change, in an attempt to deal with the external world, the human perceptual system has mechanisms that adjust to the stimulus. Visual There are several types of perceptual constancies in visual perception: * ''Size constancy'' is one type of visual subjective constancy. Within a certain range, people's perception of one particular object's size will not change, regardless of changes in distance or the video size change on the retina. The perception of image is still based upon the actual size of the perceptual characteristics. According to optical principles, for the same object, the size of the image on the retina changes as the distance from the object to the observer changes. The greater the distance, the smaller the image is sensed by the retina. When someone is observing an ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ames Room
An Ames room is a distorted room that creates an optical illusion. Likely influenced by the writings of Hermann Helmholtz, it was invented by American scientist Adelbert Ames Jr. in 1946, and constructed in the following year. Usage and effect An Ames room is viewed with one eye through a peephole. Through the peephole, the room appears to be an ordinary rectangular cuboid, with a back wall that is vertical and at right angles to the observer's line of sight, two vertical side walls parallel to each other, and a horizontal floor and ceiling. The observer will see that an adult standing in one corner of the room along the back wall appears to be a giant, while another adult standing in the other corner along the back wall appears to be a dwarf. And if an adult moves from one corner of the room to the other, they will appear to dramatically change in size. Explanation The true shape of the room is that of an irregular hexahedron: depending on the design of the room, all surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum reflected by objects in the environment. This is different from visual acuity, which refers to how clearly a person sees (for example "20/20 vision"). A person can have problems with visual perceptual processing even if they have 20/20 vision. The resulting perception is also known as vision, sight, or eyesight (adjectives ''visual'', ''optical'', and ''ocular'', respectively). The various physiological components involved in vision are referred to collectively as the visual system, and are the focus of much research in linguistics, psychology, cognitive science, neuroscience, and molecular biology, collectively referred to as vision science. Visual system In humans and a number of other mammals, light enters the eye through the cornea and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Illusion
Within visual perception, an optical illusion (also called a visual illusion) is an illusion caused by the visual system and characterized by a visual perception, percept that arguably appears to differ from reality. Illusions come in a wide variety; their categorization is difficult because the underlying cause is often not clear but a classification proposed by Richard Gregory is useful as an orientation. According to that, there are three main classes: physical, physiological, and cognitive illusions, and in each class there are four kinds: Ambiguities, distortions, paradoxes, and fictions. A classical example for a physical distortion would be the apparent bending of a stick half immerged in water; an example for a physiological paradox is the motion aftereffect (where, despite movement, position remains unchanged). An example for a physiological fiction is an afterimage. Three typical cognitive distortions are the Ponzo illusion, Ponzo, Poggendorff illusion, Poggendorff, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to: Perception Optical perception * Visual perception, the sense of sight * Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight * Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain understanding from digital images or videos * Machine vision, technology for imaging-based automatic inspection Perception of the future * Foresight (psychology), in business, the ability to envisage future market trends and plan accordingly * Goal, a desired result ** Vision statement, a declaration of objectives to guide decision-making Other perceptions * Vision (spirituality), a supernatural experience that conveys a revelation * Hallucination, a perception of something that does not exist Arts and media Events * Visions (convention), a science fiction event * Vision Festival, a New York City art festival Film and television * "The Vision", episode of '' Alcoa Presents: One Step Beyond'' * ''The Vision'' (film), 1998 British televisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Phenomena
Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter. All optics, optical phenomena coincide with Quantum mechanics, quantum phenomena. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of light from the sun or moon with the atmosphere, clouds, water, dust, and other particulates. One common example is the rainbow, when light from the sun is reflected and refracted by water droplets. Some phenomena, such as the green ray, are so rare they are sometimes thought to be mythical. Others, such as Fata Morgana (mirage), Fata Morganas, are commonplace in favored locations. Other phenomena are simply interesting aspects of optics, or optical effects. For instance, the colors generated by a dispersive prism, prism are often shown in classrooms. List Optical phenomena include those arising from the optical properties of the atmosphere; the rest of nature (other phenomena); of physical body, objects, whether natural or human-made (optic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |