|
Emancipation Of The Dissonance
The emancipation of the dissonance was a concept or goal put forth by composer Arnold Schoenberg and others, including his pupil Anton Webern. The phrase first appears in Schoenberg's 1926 essay "Opinion or Insight?" . It may be described as a metanarrative to justify atonality. Jim describes: Composers such as Charles Ives, Dane Rudhyar, Duke Ellington, and Lou Harrison connected the emancipation of the dissonance with the emancipation of society and humanity. Michael Broyles calls Ives tone-cluster-rich song "Majority" as "an incantation, a mystical statement of belief in the masses or the people" . Duke Ellington, after playing some of his pieces for a journalist, said, "That's the Negro's life ... Hear that chord! Dissonance is our way of life in America. We are something apart, yet an integral part" . Lou Harrison described Carl Ruggles's counterpoint as "a community of singing lines, living a life of its own, . . . careful not to get ahead or behind in its rhythmic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Ruggles
Carl Ruggles (born Charles Sprague Ruggles; March 11, 1876 – October 24, 1971) was an American composer, painter and teacher. His pieces employed " dissonant counterpoint", a term coined by fellow composer and musicologist Charles Seeger to describe Ruggles' music. His method of atonal counterpoint was based on a non- serial technique of avoiding repeating a pitch class until a generally fixed number of eight pitch classes intervened. He is considered a founder of the ultramodernist movement of American composers that included Henry Cowell and Ruth Crawford Seeger, among others. He had no formal musical education, yet was an extreme perfectionist — writing music at a painstakingly slow rate and leaving behind a very small output. Famous for his prickly personality, Ruggles was nonetheless close friends with Cowell, Seeger, Edgard Varèse, Charles Ives, and the painter Thomas Hart Benton. His students include the experimental composers James Tenney and Merton Brown. Condu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dika Newlin
Dika Newlin (November 22, 1923 – July 22, 2006) was a composer, pianist, professor, musicologist, and punk rock singer. She received a Ph.D. from Columbia University at the age of 22. She was one of the last living students of Arnold Schoenberg and was a Schoenberg scholar and a professor at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond from 1978 to 2004. She performed as an Elvis impersonator and played punk rock while in her seventies in Richmond, Virginia. She was featured in the documentary '' Dika: Murder City''. Early life Dika Newlin was born in Portland, Oregon. Her name was chosen by her mother and refers to an Amazon in one of Sappho's poems. Her parents were academics and her family moved to East Lansing, Michigan, so that her father could teach English at Michigan State University. Neither of her parents were musicians, but her grandmother was a piano teacher and her uncle a composer. Newlin was able to read the dictionary by age 3 and started piano lessons at age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Stein (musicologist)
Leonard David Stein (December 1, 1916 – June 24, 2004) was a musicologist, pianist, conductor, university teacher, and influential in promoting contemporary music on the American West Coast. He was for years Arnold Schoenberg's assistant, music director of the Schoenberg Institute at USC, and among the foremost authorities on Schoenberg's music. He was also an influential teacher in the lives of many younger composers, such as the influential minimalist La Monte Young. Life Stein studied piano under the Busoni disciple Richard Buhlig at Los Angeles City College, and composition and theory under Schoenberg at University of Southern California (1935–36) and University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) (BA: 1939, MM: 1941, MA: 1942).(July 01, 2004).Leonard Stein, Pianist and Music Scholar, 87, ''USC News'' (archive from October 26, 2011; accessed June 24, 2019). Stein was an assistant to Schoenberg at UCLA from 1939 until Schoenberg's retirement in 1942. Thereafter until Schoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Chailley
Jacques Chailley (24 March 1910 – 21 January 1999) was a French musicologist and composer.Alain Lompech, "Jacques Chailley, musicologue-praticien et infatigable chercheur", ''Consociatio internationalis musicæ sacræ, Musicæ sacræ ministerium'', Anno XXXIV-XXXVI (1997 - 1999), Rome, p. 146 - 147 Biography His mother was the pianist Céliny Chailley-Richez (1884–1973), his father the cellist Marcel Chailley (1881–1936). Adolescent, he was a boarder at the Fontgombault Abbey (Indre) where he learned to play the organ and learned about choir directing. At the age of 14, he composed a four-voice ''Domine non sum dignus''. He received a classical and musical teaching of high quality, studying harmony with Nadia Boulanger, counterpoint and fugue with Claude Delvincourt, musicology with Yvonne Rokseth who gave him insight into medieval music. At the Conservatoire de Paris, he followed Maurice Emmanuel's class of music history and studied music composition with Henri Büsser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overtone Series And Western Music Development
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental is the lowest pitch. While the fundamental is usually heard most prominently, overtones are actually present in any pitch except a true sine wave. The relative volume or amplitude of various overtone partials is one of the key identifying features of timbre, or the individual characteristic of a sound. Using the model of Fourier analysis, the fundamental and the overtones together are called partials. Harmonics, or more precisely, harmonic partials, are partials whose frequencies are numerical integer multiples of the fundamental (including the fundamental, which is 1 times itself). These overlapping terms are variously used when discussing the acoustic behavior of musical instruments. Alexander J. Ellis (translating Hermann von Helmholtz) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
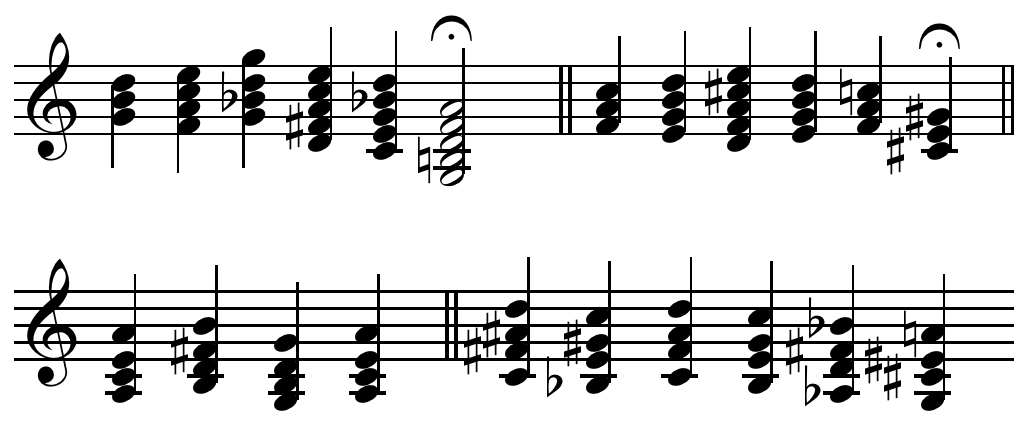
Chailley Harmonic Series Emancipationt
Chailley () is a commune in the Yonne department in Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in north-central France. See also *Communes of the Yonne department The following is a list of the 423 communes of the Yonne Yonne () is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in France. It is named after the river Yonne, which flows through it, in the country's north-central part. One of Bourgo ... References Communes of Yonne {{Yonne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Cowell
Henry Dixon Cowell (; March 11, 1897 – December 10, 1965) was an American composer, writer, pianist, publisher and teacher. Marchioni, Tonimarie (2012)"Henry Cowell: A Life Stranger Than Fiction" ''The Juilliard Journal''. Retrieved 19 June 2022.Campbell, Brett (2014)"Liberating Henry Cowell's Music at San Quentin" ''San Francisco Classical Voice''. Retrieved 19 June 2022. Earning a reputation as an extremely controversial performer and eccentric composer, Cowell became a leading figure of American avant-garde music for the first half of the 20th century — his writings and music serving as a great influence to similar artists at the time, including Lou Harrison, George Antheil, and John Cage, among others.Swed, Mark (2010)"Critic's notebook: Revelatory Henry Cowell revival at Lincoln Center" ''The Los Angeles Times''. Retrieved 19 June 2022. He is considered one of America's most important and influential composers. Cowell was mostly self-taught and developed a unique musical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (music)
A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of pitches/frequencies consisting of multiple notes (also called "pitches") that are heard as if sounding simultaneously. For many practical and theoretical purposes, arpeggios and broken chords (in which the notes of the chord are sounded one after the other, rather than simultaneously), or sequences of chord tones, may also be considered as chords in the right musical context. In tonal Western classical music (music with a tonic key or "home key"), the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: the root note, and intervals of a third and a fifth above the root note. Chords with more than three notes include added tone chords, extended chords and tone clusters, which are used in contemporary classical music, jazz and almost any other genre. A series of chords is called a chord progression. One example of a widely used chord progression in Western traditional music and blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord. In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Intervals between successive notes of a scale are also known as scale steps. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales. Some of the very smallest ones are called commas, and describe small discrepancies, observed in some tuning systems, between enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and D. Intervals can be arbitrarily small, and even imperceptible to the human ear. In physical terms, an interval is the ratio between two sonic freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Series (music)
A harmonic series (also overtone series) is the sequence of harmonics, musical tones, or pure tones whose frequency is an integer multiple of a ''fundamental frequency''. Pitched musical instruments are often based on an acoustic resonator such as a string or a column of air, which oscillates at numerous modes simultaneously. At the frequencies of each vibrating mode, waves travel in both directions along the string or air column, reinforcing and canceling each other to form standing waves. Interaction with the surrounding air causes audible sound waves, which travel away from the instrument. Because of the typical spacing of the resonances, these frequencies are mostly limited to integer multiples, or harmonics, of the lowest frequency, and such multiples form the harmonic series. The musical pitch of a note is usually perceived as the lowest partial present (the fundamental frequency), which may be the one created by vibration over the full length of the string or air co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |