|
Eltonian Niche
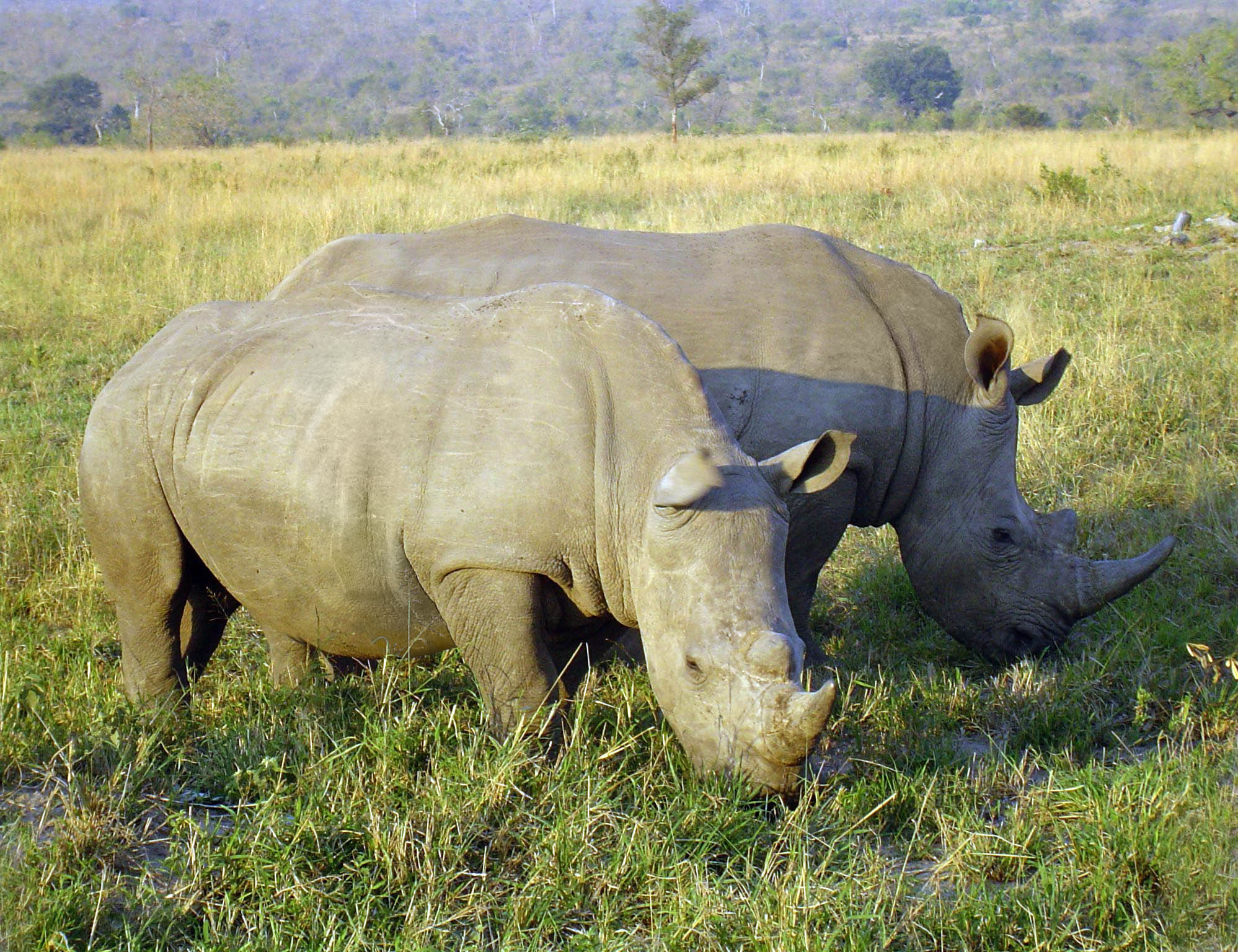
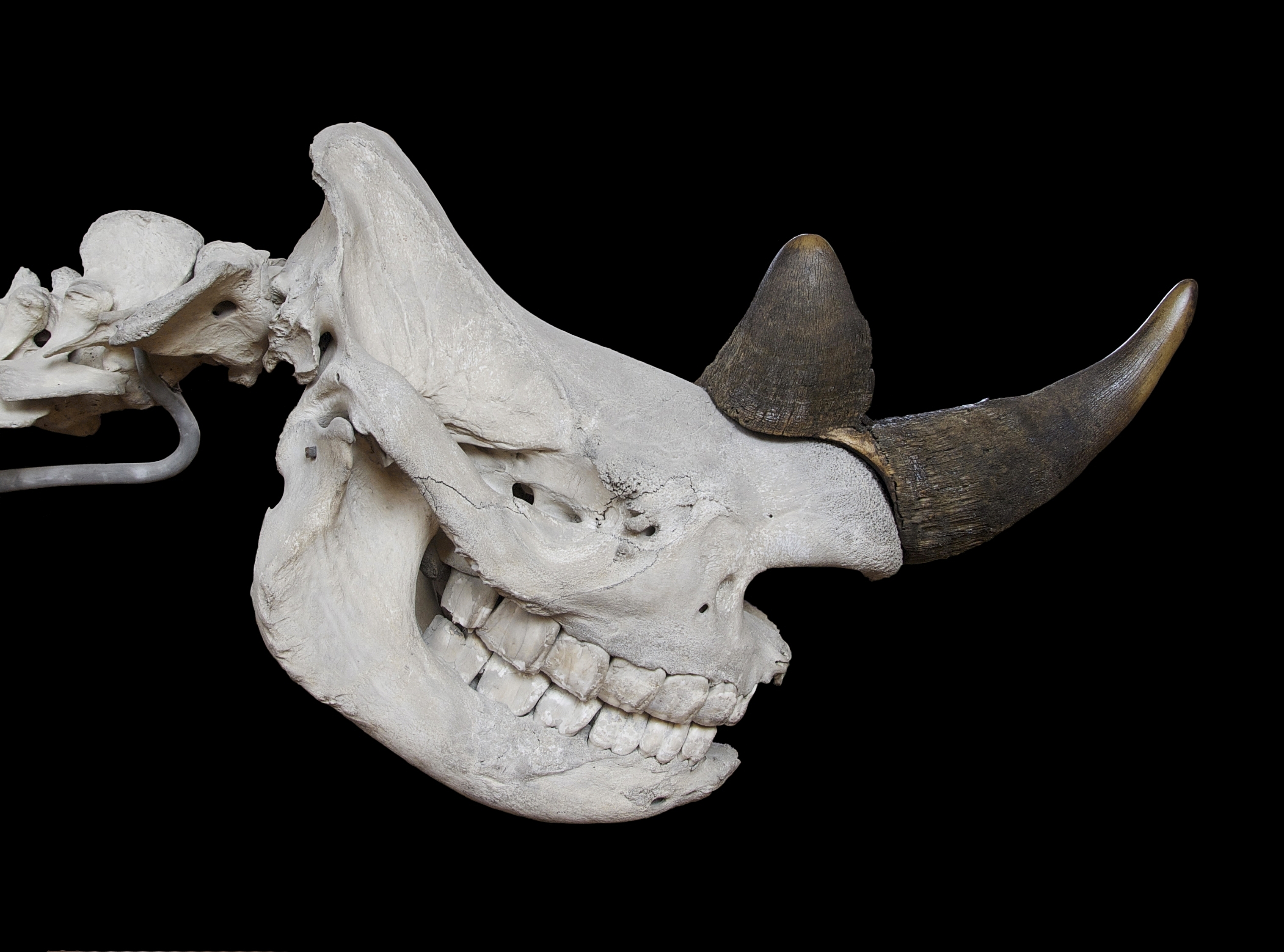
The Eltonian niche is an ecological niche that emphasizes the functional attributes of animals and their corresponding trophic position. This was the definition Eugene Odum popularized in his analogy of the niche of a species with its profession in the ecosystem as opposed to the habitat being its address. The definition is attributed to Charles Elton in his 1927 now classic book ''Animal Ecology''.Elton, C.(1927) Animal Ecology. Sidgwick and Jackson, London. Reprinted several times, e.g. 2001 by The University of Chicago Press, Elton used the two African Rhinoceros species to exemplify the definition. The White Rhinoceros has broad (wide, hence its name A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A personal ...) mouthparts, which are efficient in harvesting grass, while the Black Rh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition. Three variants of ecological niche are described by It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for example, by growing when resources are abundant, and when predators, parasites and pathogens are scarce) and how it in turn alters those same factors (for example, limiting access to resources by other organisms, acting as a food source for predators and a consumer of prey). "The type and number of variables comprising the dimensions of an environmental niche vary from one species to another ndthe relative importance of particular environmental variables for a species may vary according to the geographic and biotic contexts". See also Chapter 2: Concepts of niches, pp. 7 ''ff'' A Grinnellian niche is determined by the habitat in which a species lives and its accompanying behavioral adaptations. An Eltonian niche emphasizes that a spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trophic Level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. A food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the number of steps it is from the start of the chain. A food web starts at trophic level 1 with primary producers such as plants, can move to herbivores at level 2, carnivores at level 3 or higher, and typically finish with apex predators at level 4 or 5. The path along the chain can form either a one-way flow or a food "web". Ecological communities with higher biodiversity form more complex trophic paths. The word ''trophic'' derives from the Greek τροφή (trophē) referring to food or nourishment. History The concept of trophic level was developed by Raymond Lindeman (1942), based on the terminology of August Thienemann (1926): "producers", "consumers" and "reducers" (modified to "decomposers" by Lindeman). Overview The three basic ways in which org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eugene Odum
Eugene Pleasants Odum (September 17, 1913 – August 10, 2002) was an American biologist at the University of Georgia known for his pioneering work on ecosystem ecology. He and his brother Howard T. Odum wrote the popular ecology textbook, ''Fundamentals of Ecology'' (1953). The Odum School of Ecology is named in his honor. Biography Son of the sociologist Howard W. Odum, and older brother of the ecologist Howard T. Odum, E.P. Odum credited his father for imparting a holistic approach to exploring subjects. When contemplating where to conduct his advanced graduate work, he rejected both the University of Michigan and Cornell University, as he did not feel that this holism was embodied in their approach to their biology departments. Instead, he chose the Graduate Department of Zoology at the University of Illinois, where he earned his doctorate degree. There Odum was a student of Victor Shelford, whose efforts led to the establishment of The Nature Conservancy.Smith, S. & Mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat (ecology)
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ecological niche. Thus "habitat" is a species-specific term, fundamentally different from concepts such as environment or vegetation assemblages, for which the term "habitat-type" is more appropriate. The physical factors may include (for example): soil, moisture, range of temperature, and light intensity. Biotic factors will include the availability of food and the presence or absence of predators. Every species has particular habitat requirements, with habitat generalist species able to thrive in a wide array of environmental conditions while habitat specialist species requiring a very limited set of factors to survive. The habitat of a species is not necessarily found in a geographical area, it can be the interior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Sutherland Elton
Charles Sutherland Elton (29 March 1900 – 1 May 1991) was an English zoologist and animal ecologist. He is associated with the development of population and community ecology, including studies of invasive organisms. Personal life Charles Sutherland Elton was born in Manchester, a son of the literary scholar Oliver Elton and the children's writer Letitia Maynard Elton (''née'' MacColl). He had an older brother, Geoffrey Elton, who died at 33, and to whom Charles Elton in many of his writings attributes his interest in scientific natural history. Charles Elton married the English poet Edith Joy Scovell in 1937, a first five-year marriage to Rose Montague having ended in amicable divorce. Charles and Joy had two children, Catherine Ingrid Buffonge MBE and Robert Elton. Professional life Charles Elton was educated at Liverpool College and Oxford University, from which he graduated in zoology in 1922, with a first in his field research project and a third in the exams, and whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young population make Afr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct species of the superfamily Rhinocerotoidea.) Two of the extant species are native to Africa, and three to South and Southeast Asia. Rhinoceroses are some of the largest remaining megafauna: all weigh at least one tonne in adulthood. They have a herbivorous diet, small brains (400–600 g) for mammals of their size, one or two horns, and a thick (1.5–5 cm), protective skin formed from layers of collagen positioned in a lattice structure. They generally eat leafy material, although their ability to ferment food in their hindgut allows them to subsist on more fibrous plant matter when necessary. Unlike other perissodactyls, the two African species of rhinoceros lack teeth at the front of their mouths; they rely instead on their lips to pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing (behaviour), grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists of two subspecies: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 19,682–21,077 wild-living animals in the year 2015, and the much rarer northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies has very few remaining individuals, with only two confirmed left in 2018 (two females: Fatu, 18 and Najin, 29), both in captivity. Sudan (rhinoceros), Sudan, the world's last known male Northern white rhinoceros, died in Kenya on 19 March 2018 at age 45. Naming A popular albeit widely discredited theory of the origins of the name "white rhinoceros" is a mistranslation from Dutch to English. The English word "white" is said to have been derived by mistranslation of the Dutch word "wijd", which means "wide" in English. The word " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Rhinoceros
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing (behaviour), grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists of two subspecies: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 19,682–21,077 wild-living animals in the year 2015, and the much rarer northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies has very few remaining individuals, with only two confirmed left in 2018 (two females: Fatu, 18 and Najin, 29), both in captivity. Sudan (rhinoceros), Sudan, the world's last known male Northern white rhinoceros, died in Kenya on 19 March 2018 at age 45. Naming A popular albeit widely discredited theory of the origins of the name "white rhinoceros" is a mistranslation from Dutch to English. The English word "white" is said to have been derived by mistranslation of the Dutch word "wijd", which means "wide" in English. The word " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Rhinoceros
The black rhinoceros, black rhino or hook-lipped rhinoceros (''Diceros bicornis'') is a species of rhinoceros, native to eastern and southern Africa including Angola, Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Eswatini, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. Although the rhinoceros is referred to as ''black'', its colours vary from brown to grey. The other African rhinoceros is the white rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''). The word "white" in the name "white rhinoceros" is often said to be a misinterpretation of the Afrikaans word ' (Dutch ') meaning wide, referring to its square upper lip, as opposed to the pointed or hooked lip of the black rhinoceros. These species are now sometimes referred to as the square-lipped (for white) or hook-lipped (for black) rhinoceros. The species overall is classified as critically endangered (even though the south-western black rhinoceros is classified as near threatened). Three subspecies have been declared extinct, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)