|
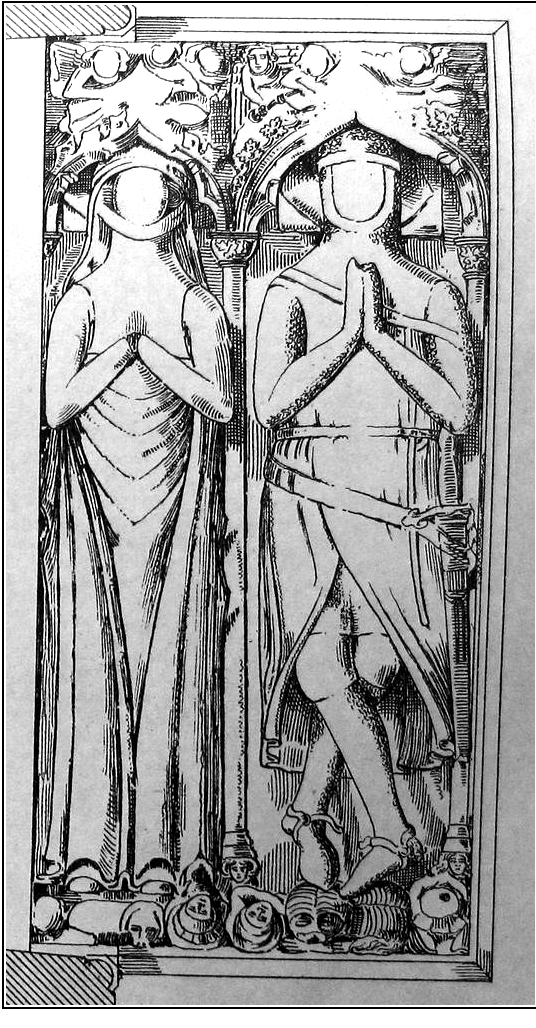
Elizabeth De Comyn
Elizabeth de Comyn (1 November 1299 – 20 November 1372) was a medieval noblewoman and heiress, notable for being kidnapped by the Despenser family towards the end of the reign of King Edward II. Background Elizabeth was born to John III Comyn, Lord of Badenoch, also known as the "Red Comyn", a powerful Scottish nobleman related to the Scottish crown, and Joan de Valence, the daughter of the French knight William de Valence, 1st Earl of Pembroke. She was the youngest of three children, with an elder sister, Joan de Comyn, and brother, John de Comyn. Her father was stabbed to death in 1306 by Robert the Bruce and Elizabeth and her siblings were sent south to England for their own safety. Joan married David II Strathbogie, the earl of Atholl, whilst her brother John later died at the Battle of Bannockburn in 1314, fighting Robert. Inheritance and kidnap In 1324 Elizabeth's uncle on her father's side, Aymer de Valence, the earl of Pembroke, died. Since he had no surviving ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Talbot, 2nd Baron Talbot
Richard Talbot, 2nd Baron Talbot (c. 1306 – 23 October 1356) was an English nobleman and soldier. As the husband of the heiress Elizabeth de Comyn, he played a role in the Second War of Scottish Independence. Family Talbot was the son and heir of Gilbert Talbot and Anne Boteler. His father had been raised to the peerage as the first Baron Talbot in 1331. The Talbots had been part of the Herefordshire gentry since the time of Henry II,Robinson, Charles John"A History of the Castles of Herefordshire and Their Lords pp. 52-3 and also had blood ties to the Welsh elite through a daughter of Rhys Mechyll, whose arms they had assumed. He inherited the title of Baron Talbot on his father's death in 1346. Nicolas, Nicholas Harris"A Synopsis of the Peerage of England" pp. 633-4 Talbot married Elizabeth Comyn, the daughter of John de Comyn and Joan de Valence. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John De Bousser
John de Bourchier (alias Boussier, etc., d. c. 1329) was an English Judge of the Common Pleas and the earliest ancestor, about whose life substantial details are known, of the noble and prolific Bourchier family, which in its various branches later held the titles Barons Bourchier, Counts of Eu, Viscounts Bourchier, Earls of Essex, Barons Berners, Barons FitzWarin and Earls of Bath. Origins There is no evidence which confirms this family to have originated in France, and it was possibly of ancient English origin. Its name was however Latinised by scribes to ''de Burgo Caro'', "from the costly town", from a Gallicisation of the name to ''le Bourg Cher''. Early career Bouchier is first mentioned as deputed by Robert de Vere, 6th Earl of Oxford (1257–1331) to represent him in the parliament summoned in 1306 for the purpose of granting an aid on the occasion of the Prince of Wales (the future King Edward II (1307–1327)) receiving knighthood. In 1312 he was permitted to po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Women Landowners
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century English Landowners
As a means of recording the passage of time, the 14th century was a century lasting from 1 January 1301 ( MCCCI), to 31 December 1400 ( MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of Charles IV, King of France led to a claim to the French throne by Edward III, King of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century English Women
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resiste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13th-century English People
The 13th century was the century which lasted from January 1, 1201 ( MCCI) through December 31, 1300 ( MCCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan, which stretched from Eastern Asia to Eastern Europe. The conquests of Hulagu Khan and other Mongol invasions changed the course of the Muslim world, most notably the Siege of Baghdad (1258), the destruction of the House of Wisdom and the weakening of the Mamluks and Rums which, according to historians, caused the decline of the Islamic Golden Age. Other Muslim powers such as the Mali Empire and Delhi Sultanate conquered large parts of West Africa and the Indian subcontinent, while Buddhism witnessed a decline through the conquest led by Bakhtiyar Khilji. The Southern Song dynasty would begin the century as a prosperous kingdom but would eventually be invaded and annexed into the Yuan dynasty of the Mongols. The Kamakura Shogunate of Japan would be invaded by the Mongols. Goryeo resist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talbot Family
Talbot was an automobile marque introduced in 1902 by English-French company Clément-Talbot. The founders, Charles Chetwynd-Talbot, 20th Earl of Shrewsbury and Adolphe Clément-Bayard, reduced their financial interests in their Clément-Talbot business during the First World War. Soon after the end of the war, Clément-Talbot was brought into a combine named STD Motors. Shortly afterward, STD Motors' French products were renamed Talbot instead of Darracq. In the mid-1930s, with the collapse of STD Motors, Rootes bought the London Talbot factory and Antonio Lago bought the Paris Talbot factory, Lago producing vehicles under the marques Talbot and Talbot-Lago. Rootes renamed Clément-Talbot Sunbeam-Talbot in 1938, and stopped using the brand name Talbot in the mid-1950s. The Paris factory closed a few years later. Ownership of the marque came by a series of takeovers to Peugeot, which revived use of the Talbot name from 1978 until 1994. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1372 Deaths
{{numberdis ...
137 may refer to: *137 (number) *137 BC *AD 137 *137 (album), an album by The Pineapple Thief *137 (MBTA bus) *137 (New Jersey bus) 137 may refer to: *137 (number) *137 BC *AD 137 *137 (album), an album by The Pineapple Thief *137 (MBTA bus) The Massachusetts Bay Transportation Authority bus division operates bus routes in the Boston, Massachusetts metropolitan area. All ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1299 Births
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Tombleson
William Tombleson (1795 - c. 1846) was an English topographical and architecture artist, illustrator, copper and steel engraver, writer and printmaker, based in London.William Tombleson (German Wikipedia). Life and works In the 1830s, his topographical drawings of the upper and middle River Rhine in Germany, and of the rivers Thames and Medway in England were published as engraved prints and books (see bibliography). For volume 1 of "Views of the Rhine etc." he provided 69 illustrations - the book was also published in French and German editions. Engravers who worked on Tombleson's drawings included Thomas Clark, John Cleghorn, T. Cox, R. Harris, W. Hood, J. Howe, W. Lacey, O. Smith, Shenfield, J. Stokes, D. Thompson, W. Tombleson, W. Watts, R. Wilson, H. Winkles and others. Selected bibliography Illustrated by Tombleson: *Fearnside, William Gray. ''Tombleson's Views of the Rhine from Cologne to Mainz'(London: George Virtue, 1832) - French edition. *Fearnside, William Gray. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward William Brayley
Edward William Brayley FRS (1801 – 1 February 1870) was an English geographer, librarian, and science author. Early life Brayley was born in London, the son of Edward Wedlake Brayley, a notable antiquary, and his wife Anne (''c.'' 1771–1850). His early schooling, in the company of his brothers Henry and Horatio was private and sheltered. His upbringing was austere with little contact with other children or the world outside his home. He later studied at the London Institution and the Royal Institution under William Thomas Brande.Hays (2004) Brayley abandoned an early inclination to follow his father's interests for science. He published on diverse topics in several scientific journals including the ''Philosophical Magazine'', for which he became an editorial assistant between 1823 and 1844. In 1829 and 1830, Brayley was employed by Rowland Hill to lecture on the physical sciences at his schools as Hazelwood, Edgbaston, Birmingham and Bruce Castle, Tottenham, London. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charge (heraldry)
In heraldry, a charge is any emblem or device occupying the field of an '' escutcheon'' (shield). That may be a geometric design (sometimes called an '' ordinary'') or a symbolic representation of a person, animal, plant, object, building, or other device. In French blazon, the ordinaries are called ''pièces'', and other charges are called ''meubles'' (" hemobile nes). The term ''charge'' can also be used as a verb; for example, if an escutcheon depicts three lions, it is said to be ''charged with three lions''; similarly, a crest or even a charge itself may be "charged", such as a pair of eagle wings ''charged with trefoils'' (as on the coat of arms of Brandenburg). It is important to distinguish between the ordinaries and divisions of the field, as that typically follow similar patterns, such as a shield ''divided'' "per chevron", as distinct from being ''charged with'' a chevron. While thousands of objects found in religion, nature, mythology, or technology have appeared in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |