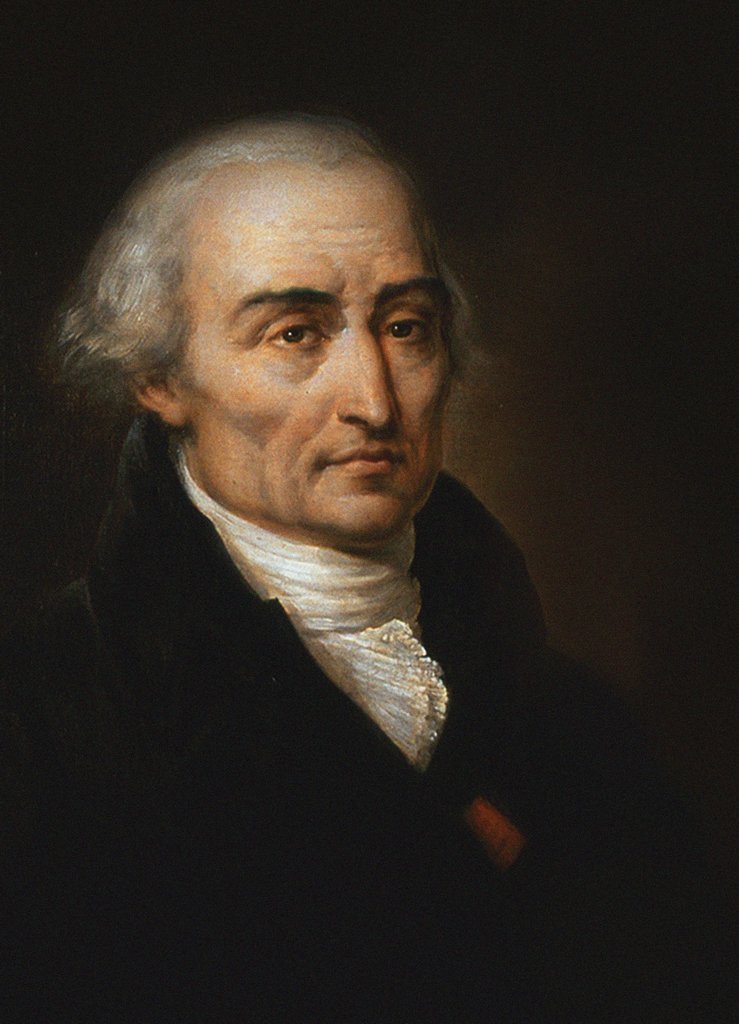|
Elements Of Algebra
''Elements of Algebra'' is an elementary mathematics textbook written by mathematician Leonhard Euler around 1765 in German. It was first published in Russian as "''Universal Arithmetic''" (''Универсальная арифметика''), two volumes appearing in 1768-9 and in 1770 was printed from the original text. ''Elements of Algebra'' is one of the earliest books to set out algebra in the modern form we would recognize today (another early book being ''Elements of Algebra'' by Nicholas Saunderson, published in 1740), and is one of Euler's few writings, along with ''Letters to a German Princess'', that are accessible to the general public. Written in numbered paragraphs as was common practice till the 19th century, ''Elements'' begins with the definition of mathematics and builds on the fundamental operations of arithmetic and number systems, and gradually moves towards more abstract topics. In 1771, Joseph-Louis Lagrange Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elements Of Algebra (IA Elementsofalgebr00eule)
''Elements of Algebra'' is an elementary mathematics textbook written by mathematician Leonhard Euler around 1765 in German. It was first published in Russian as "''Universal Arithmetic''" (''Универсальная арифметика''), two volumes appearing in 1768-9 and in 1770 was printed from the original text. ''Elements of Algebra'' is one of the earliest books to set out algebra in the modern form we would recognize today (another early book being ''Elements of Algebra'' by Nicholas Saunderson, published in 1740), and is one of Euler's few writings, along with '' Letters to a German Princess'', that are accessible to the general public. Written in numbered paragraphs as was common practice till the 19th century, ''Elements'' begins with the definition of mathematics and builds on the fundamental operations of arithmetic and number systems, and gradually moves towards more abstract topics. In 1771, Joseph-Louis Lagrange Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Mathematics
Elementary mathematics consists of mathematics topics frequently taught at the primary or secondary school levels. In the Canadian curriculum, there are six basic strands in Elementary Mathematics: Number, Algebra, Data, Spatial Sense, Financial Literacy, and Social emotional learning skills and math processes. These six strands are the focus of Mathematics education from grade 1 through grade 8. In secondary school, the main topics in elementary mathematics from grade nine until grade ten are: Number Sense and algebra, Linear Relations, Measurement and Geometry. Once students enter grade eleven and twelve students begin university and college preparation classes, which include: Functions, Calculus & Vectors, Advanced Functions, and Data Management. Strands of elementary mathematics Number Sense and Numeration Number Sense is an understanding of numbers and operations. In the 'Number Sense and Numeration' strand students develop an understanding of numbers by being taugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and Mathematical notation, notation, including the notion of a function (mathematics), mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Saunderson
Nicholas Saunderson (20 January 1682 – 19 April 1739) was a blind English scientist and mathematician. According to one historian of statistics, he may have been the earliest discoverer of Bayes' theorem. He worked as Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge University, a post also held by Isaac Newton, Charles Babbage and Stephen Hawking. Biography Saunderson was born at Thurlstone, Yorkshire, in January 1682. His parents were John and Ann Sanderson (or Saunderson), and his father made a living as an excise man. When he was about a year old, he lost his sight through smallpox; but this did not prevent him from learning arithmetic through assisting his father. As a child, he is also thought to have learnt to read by tracing the engravings on tombstones around St John the Baptist Church in Penistone with his fingers. His early education was at the free school, Penistone Grammar School where he learnt French, Latin and Greek. In 1700 a tutor taught him algebra and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letters To A German Princess
''Letters to a German Princess, On Different Subjects in Physics and Philosophy'' (French: ''Lettres à une princesse d'Allemagne sur divers sujets de physique et de philosophie'') were a series of 234 letters written by the mathematician Leonhard Euler between 1760 and 1762 addressed to Friederike Charlotte of Brandenburg-Schwedt and her younger sister Louise. Contents Euler started the first letter with an explanation of the concept of "size". Starting with the definition of a foot, he defined the mile and the diameter of the earth as a unit in terms of foot and then calculated the distance of the planets of the Solar System in terms of the diameter of the earth. Publication The first two volumes of the 234 letters originally written in French appeared in print in Saint Petersburg in 1768 and the third in Frankfurt in 1774. The letters were later reprinted in Paris with the first volume in 1787, the second in 1788 and the third in 1789. The publication of the book was suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an Italian and , later naturalized |
John Hewlett
John Hewlett (1762–13 April 1844) was a prominent biblical scholar in nineteenth-century England. Hewlett was born in Chetnole, Dorset to Timothy Hewlett. In his early 20s he established a school in Shacklewell, Hackney. During this period, he became acquainted with the young Mary Wollstonecraft, then running her own school at nearby Newington Green. Hewlett persuaded her to write her first book, ''Thoughts on the Education of Daughters'', and sold the yet-unwritten manuscript to the radical publisher Joseph Johnson. He also introduced her to the great lexicographer Samuel Johnson. In 1786 he was admitted as a sizar to Magdalene College, Cambridge. The Cambridge Alumni Database lists him as "a ten-year man", which the university defines as: "Under the 1570 statutes it was made possible for a man over the age of twenty-four to proceed to the degree of BD ten years after matriculation without first proceeding to the degrees of BA and MA . The privilege was not much used until s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Introductio In Analysin Infinitorum
''Introductio in analysin infinitorum'' (Latin: ''Introduction to the Analysis of the Infinite'') is a two-volume work by Leonhard Euler which lays the foundations of mathematical analysis. Written in Latin and published in 1748, the ''Introductio'' contains 18 chapters in the first part and 22 chapters in the second. It has Eneström numbers E101 and E102. Carl Boyer's lectures at the 1950 International Congress of Mathematicians compared the influence of Euler's ''Introductio'' to that of Euclid's '' Elements'', calling the ''Elements'' the foremost textbook of ancient times, and the ''Introductio'' "the foremost textbook of modern times". Boyer also wrote: :The analysis of Euler comes close to the modern orthodox discipline, the study of functions by means of infinite processes, especially through infinite series. :It is doubtful that any other essentially didactic work includes as large a portion of original material that survives in the college courses today...Can be read w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutiones Calculi Differentialis
''Institutiones calculi differentialis'' (''Foundations of differential calculus'') is a mathematical work written in 1748 by Leonhard Euler Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in ma ... and published in 1755 that lays the groundwork for the differential calculus. It consists of a single volume containing two internal books; there are 9 chapters in book I, and 18 in book II. writes that "this is the first textbook on the differential calculus which has any claim to be both complete and accurate, and it may be said that all modern treatises on the subject are based on it." See also * '' Institutiones calculi integralis'' * List of important publications in mathematics References * * External links Full textin Latin available from e-rara.ch. German translation''Vollständ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Textbooks
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |