|
Electromagnetically Induced Grating
Electromagnetically induced grating (EIG) is an optical Interference (wave propagation), interference phenomenon where an interference pattern is used to build a dynamic spatial diffraction grating in matter. EIGs are dynamically created by light interference on optically resonant materials and rely on population inversion and/or optical coherence (physics), coherence properties of the material. They were first demonstrated with population gratings on atoms. EIGs can be used for purposes of atomic/molecular velocimetry, to probe the material optical properties such as coherence and population life-times, and switching and routing of light. Related but different effects are thermally induced gratings and photolithographic, photolithography gratings. Writing, reading and phase-matching conditions for EIG diffraction Figure 1 shows a possible beam configuration to write and read an EIG. The period of the grating is controlled by the angle \theta. The writing and reading frequencies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference (wave Propagation)
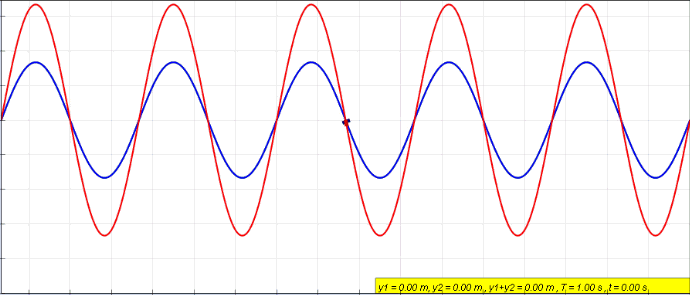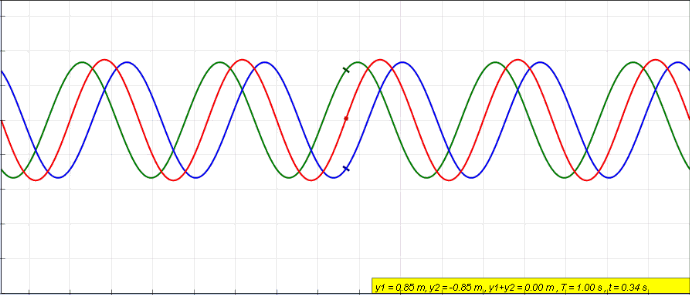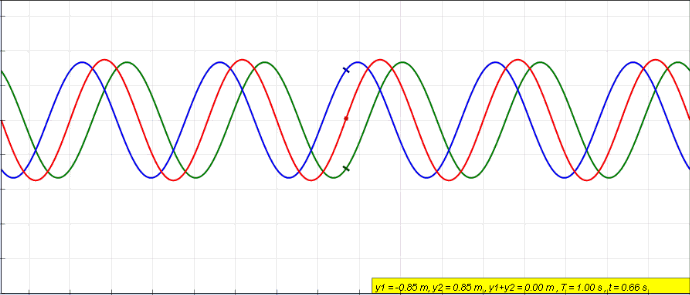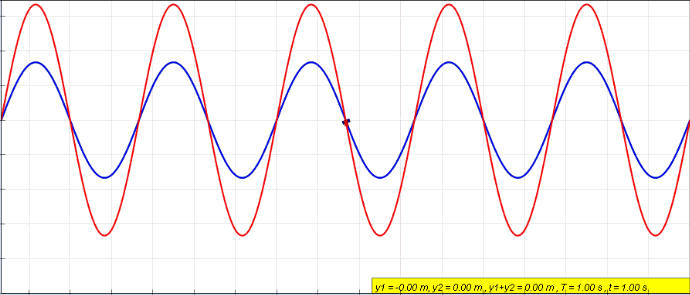
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow frequency spectrum, spectru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Mechanics
Wave mechanics may refer to: * the mechanics of waves * the ''wave equation'' in quantum physics, see Schrödinger equation See also * Quantum mechanics * Wave equation The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves or standing wave fields — as they occur in classical physics — such as mechanical waves (e.g. water waves, sound waves and s ... {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulated Raman Spectroscopy
Stimulated Raman spectroscopy, also referred to as stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) is a form of spectroscopy employed in physics, chemistry, biology, and other fields. The basic mechanism resembles that of spontaneous Raman spectroscopy: a pump photon, of the angular frequency \omega_p, which is scattered by a molecule has some small probability of inducing some vibrational (or rotational) transition, as opposed to inducing a simple Rayleigh transition. This makes the molecule emit a photon at a shifted frequency. However, SRS, as opposed to spontaneous Raman spectroscopy, is a third-order non-linear phenomenon involving a second photon—the Stokes photon of angular frequency \omega_S—which stimulates a specific transition. When the difference in frequency between both photons (\omega_p-\omega_S) resembles that of a specific vibrational (or rotational) transition (\omega_\nu) the occurrence of this transition is resonantly enhanced. In SRS, the signal is equivalent to changes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerr Effect
The Kerr effect, also called the quadratic electro-optic (QEO) effect, is a change in the refractive index of a material in response to an applied electric field. The Kerr effect is distinct from the Pockels effect in that the induced index change is directly proportional to the ''square'' of the electric field instead of varying linearly with it. All materials show a Kerr effect, but certain liquids display it more strongly than others. The Kerr effect was discovered in 1875 by Scottish physicist John Kerr. Two special cases of the Kerr effect are normally considered, these being the Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, and the optical Kerr effect, or AC Kerr effect. Kerr electro-optic effect The Kerr electro-optic effect, or DC Kerr effect, is the special case in which a slowly varying external electric field is applied by, for instance, a voltage on electrodes across the sample material. Under this influence, the sample becomes birefringent, with different indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Hole Burning
Spectral hole burning is the frequency-selective bleaching of the absorption spectrum of a material, which leads to an increased transmission (a "spectral hole") at the selected frequency. Two basic requirements must be met for the phenomenon to be observed: # The spectrum is inhomogeneously broadened # The material undergoes, subsequent to light absorption, a modification which changes its absorption spectrum. Typical materials include dye molecules dissolved in suitable host matrices; the frequency-selective irradiation is usually realized by a narrow-band laser. Particular case Most molecules and atoms always return from the excited state to the initial ground state. In some situations, however, this may not happen. For example, some organic dye molecules can undergo a photochemical reaction, which alters the whole chemical structure of the molecule. If such a photochemically active molecule absorbs light, then with a probability of a few percent it will not return to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Lattice
An optical lattice is formed by the interference of counter-propagating laser beams, creating a spatially periodic polarization pattern. The resulting periodic potential may trap neutral atoms via the Stark shift. Atoms are cooled and congregate at the potential extrema (at maxima for blue-detuned lattices, and minima for red-detuned lattices). The resulting arrangement of trapped atoms resembles a crystal lattice and can be used for quantum simulation. Atoms trapped in the optical lattice may move due to quantum tunneling, even if the potential well depth of the lattice points exceeds the kinetic energy of the atoms, which is similar to the electrons in a conductor. However, a superfluid– Mott insulator transition may occur, if the interaction energy between the atoms becomes larger than the hopping energy when the well depth is very large. In the Mott insulator phase, atoms will be trapped in the potential minima and cannot move freely, which is similar to the electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bragg's Law
In physics and chemistry , Bragg's law, Wulff–Bragg's condition or Laue–Bragg interference, a special case of Laue diffraction, gives the angles for coherent scattering of waves from a crystal lattice. It encompasses the superposition of wave fronts scattered by lattice planes, leading to a strict relation between wavelength and scattering angle, or else to the wavevector transfer with respect to the crystal lattice. Such law had initially been formulated for X-rays upon crystals. However, It applies to all sorts of quantum beams, including neutron and electron waves at atomic distances, as well as visible light at artificial periodic microscale lattices. History Bragg diffraction (also referred to as the Bragg formulation of X-ray diffraction) was first proposed by Lawrence Bragg and his father, William Henry Bragg, in 1913 in response to their discovery that crystalline solids produced surprising patterns of reflected X-rays (in contrast to that of, say, a liquid). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetically Induced Transparency
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) is a coherent optical nonlinearity which renders a medium transparent within a narrow spectral range around an absorption line. Extreme dispersion is also created within this transparency "window" which leads to "slow light", described below. It is in essence a quantum interference effect that permits the propagation of light through an otherwise opaque atomic medium. Observation of EIT involves two optical fields (highly coherent light sources, such as lasers) which are tuned to interact with three quantum states of a material. The "probe" field is tuned near resonance between two of the states and measures the absorption spectrum of the transition. A much stronger "coupling" field is tuned near resonance at a different transition. If the states are selected properly, the presence of the coupling field will create a spectral "window" of transparency which will be detected by the probe. The coupling laser is sometimes referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Coherence
Atomic may refer to: * Of or relating to the atom, the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains its chemical properties * Atomic physics, the study of the atom * Atomic Age, also known as the "Atomic Era" * Atomic scale, distances comparable to the dimensions of an atom * Atom (order theory), in mathematics * Atomic (cocktail), a champagne cocktail * ''Atomic'' (magazine), an Australian computing and technology magazine * Atomic Skis, an Austrian ski producer Music * Atomic (band), a Norwegian jazz quintet * ''Atomic'' (Lit album), 2001 * ''Atomic'' (Mogwai album), 2016 * ''Atomic'', an album by Rockets, 1982 * ''Atomic'' (EP), by , 2013 * "Atomic" (song), by Blondie, 1979 * "Atomic", a song by Tiger Army from '' Tiger Army III: Ghost Tigers Rise'' See also * * * Atom (other) * Atomicity (database systems) * Nuclear (other) * Atomism, philosophy about the basic building blocks of reality * Atomic City (other) * Atomic formula, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetically Induced Transparency
Electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT) is a coherent optical nonlinearity which renders a medium transparent within a narrow spectral range around an absorption line. Extreme dispersion is also created within this transparency "window" which leads to "slow light", described below. It is in essence a quantum interference effect that permits the propagation of light through an otherwise opaque atomic medium. Observation of EIT involves two optical fields (highly coherent light sources, such as lasers) which are tuned to interact with three quantum states of a material. The "probe" field is tuned near resonance between two of the states and measures the absorption spectrum of the transition. A much stronger "coupling" field is tuned near resonance at a different transition. If the states are selected properly, the presence of the coupling field will create a spectral "window" of transparency which will be detected by the probe. The coupling laser is sometimes referr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interference Pattern
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |