|
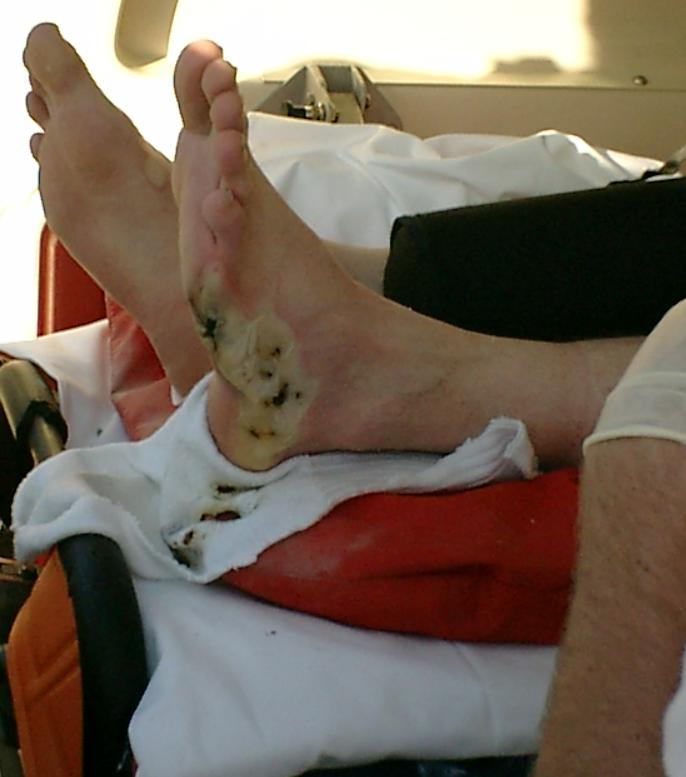
Electrical Shocks
Electrical injury is a physiological reaction caused by electric current passing through the body. The injury depends on the density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or produce a light tingling sensation. A shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. Stronger currents may cause some degree of discomfort or pain, while more intense currents may induce involuntary muscle contractions, preventing the person from breaking free of the source of electricity. Still larger currents result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. Consequences of injury from electricity may include amputations, bone fractures and orthopedic and musculoskeletal injuries. If death results from an electric shock the cause of death is generally referred to as electrocution. Electric injury occurs upon contact of a body part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightning Injury
Lightning injuries are injury, injuries caused by a lightning strike. Initial symptoms may include heart asystole and respiratory arrest. While the asystole may resolve spontaneously fairly rapidly, the respiratory arrest is typically more prolonged. Other symptoms may include burns and blunt injuries. Of those who survive, about 75% have ongoing health problems as a result, such as cataracts and hearing loss. If death occurs it is typically from either an arrhythmia, abnormal heart rhythm or respiratory failure. Lightning injuries are divided into direct strikes, side splash, contact injury, and ground current. Ground current make up about half of cases and occurs when the lightning strikes nearby and travels to the person through the ground. Side splash makes up about a third of cases and occurs when lightning strikes nearby and jumps through the air to the person. Contact injury occurs when the person is touching the object that is hit. Direct strikes make up about 5% of injur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle is the performance of the human heart from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. It consists of two periods: one during which the heart muscle relaxes and refills with blood, called diastole, following a period of robust contraction and pumping of blood, called systole. After emptying, the heart immediately relaxes and expands to receive another influx of blood returning from the lungs and other systems of the body, before again contracting to pump blood to the lungs and those systems. A normally performing heart must be fully expanded before it can efficiently pump again. Assuming a healthy heart and a typical rate of 70 to 75 beats per minute, each cardiac cycle, or heartbeat, takes about 0.8 second to complete the cycle. There are two atrial and two ventricle chambers of the heart; they are paired as the left heart and the right heart—that is, the left atrium with the left ventricle, the right atrium with the right ventricle—and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Action Potential
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage ( membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms (called ions) between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins called ion channels. The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such as nerves. Action potentials also vary within the heart; this is due to the presence of different ion channels in different cells. Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells known as pacemaker cells, that have automatic action potential generation capability. In healthy hearts, these cells form the cardiac pacemaker and are found in the sinoatrial node in the right atrium. They produce roughly 60–100 action potentials every minute. The action potential passes along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiac Muscle
Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle, myocardium, cardiomyocytes and cardiac myocytes) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. It is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the wall of the heart. The cardiac muscle (myocardium) forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the pericardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium), with blood supplied via the coronary circulation. It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined by intercalated discs, and encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar manner to skeletal muscle, although with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from the cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defibrillation
Defibrillation is a treatment for life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, specifically ventricular fibrillation (V-Fib) and non-perfusing ventricular tachycardia (V-Tach). A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current (often called a ''counter-shock'') to the heart. Although not fully understood, this process depolarizes a large amount of the heart muscle, ending the arrhythmia. Subsequently, the body's natural pacemaker in the sinoatrial node of the heart is able to re-establish normal sinus rhythm. A heart which is in asystole (flatline) cannot be restarted by a defibrillator, but would be treated by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). In contrast to defibrillation, synchronized electrical cardioversion is an electrical shock delivered in synchrony to the cardiac cycle. Although the person may still be critically ill, cardioversion normally aims to end poorly perfusing cardiac arrhythmias, such as supraventricular tachycardia. Defibrillators can be external, transve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery. The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery made was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes separated by brine-soaked paper disks. Due to fluctuation in the voltage provided by the voltaic cell it wasn't very practical. The first practical battery was invented in 1839 and named the Daniell cell after John Frederic Daniell. Still making use of the zinc–copper electrode combination. Since then many more batteries have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are manufactured for specific applications, such as cardiovascular, urological, gastrointestinal, neurovascular and ophthalmic procedures. The process of inserting a catheter is ''catheterization''. In most uses, a catheter is a thin, flexible tube (''soft'' catheter) though catheters are available in varying levels of stiffness depending on the application. A catheter left inside the body, either temporarily or permanently, may be referred to as an "indwelling catheter" (for example, a peripherally inserted central catheter). A permanently inserted catheter may be referred to as a "permcath" (originally a trademark). Catheters can be inserted into a body cavity, duct, or vessel, brain, skin or adipose tissue. Functionally, they all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. A common source of DC power is a battery cell in a flashlight. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa. In certain applications, like guitar amplifiers, different waveforms are used, such as triangular waves or square waves. Audio a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burn
A burn is an injury to skin, or other tissues, caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction, or ultraviolet radiation (like sunburn). Most burns are due to heat from hot liquids (called scalding), solids, or fire. Burns occur mainly in the home or the workplace. In the home, risks are associated with domestic kitchens, including stoves, flames, and hot liquids. In the workplace, risks are associated with fire and chemical and electric burns. Alcoholism and smoking are other risk factors. Burns can also occur as a result of self-harm or violence between people (assault). Burns that affect only the superficial skin layers are known as superficial or first-degree burns. They appear red without blisters and pain typically lasts around three days. When the injury extends into some of the underlying skin layer, it is a partial-thickness or second-degree burn. Blisters are frequently present and they are often very painful. Healing can require up to eight weeks and scarri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather than intens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |