|
Elections In Pakistan
Since establishment in 1947, Pakistan has had a non-symmetric federal government and is a federal parliamentary democratic republic. At the national level, the people of Pakistan elect a bicameral legislature, the Parliament of Pakistan. The parliament consists of a lower house, the National Assembly, elected directly via first-past-the-post voting, and an upper house, the Senate, whose members are chosen by elected provincial legislators. The head of government, the Prime Minister, is elected by the majority members of the National Assembly and the head of state (and figurehead), the President, is elected by the Electoral College, which consists of both houses of Parliament together with the four provincial assemblies. In addition to the national and provincial assemblies, Pakistan has over five thousand elected local governments. The Election Commission of Pakistan is a constitutionally-established institution chaired by an appointed and designated Chief Election Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of State
A head of state is the public persona of a sovereign state.#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "[The head of state] being an embodiment of the State itself or representative of its international persona." The name given to the office of head of state depends on the country's form of government and any separation of powers; the powers of the office in each country range from being also the head of government to being little more than a ceremonial figurehead. In a parliamentary system, such as Politics of India, India or the Politics of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom, the head of state usually has mostly ceremonial powers, with a separate head of government. However, in some parliamentary systems, like Politics of South Africa, South Africa, there is an executive president that is both head of state and head of government. Likewise, in some parliamentary systems the head of state is not the head of government, but still has significant powers, for example Politics of Morocco, Moro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
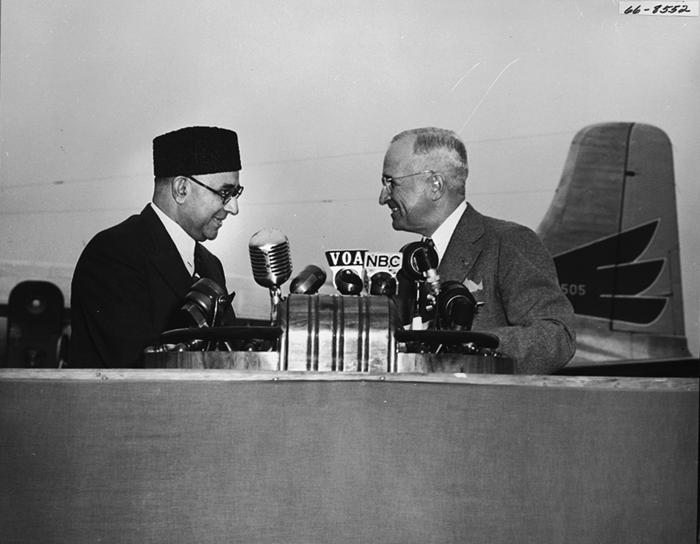
Liaquat Ali Khan
Liaquat Ali Khan (1 October 189516 October 1951) was a Pakistani lawyer, politician and statesman who served as the first prime minister of Pakistan The prime minister of Pakistan (, Roman Urdu, romanized: Wazīr ē Aʿẓam , ) is the head of government of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Executive authority is vested in the prime minister and his chosen Cabinet of Pakistan, cabinet, desp ... from 1947 until Assassination of Liaquat Ali Khan, his assassination in 1951. He was as pivotal to the consolidation of Pakistan as the Quaid-i-Azam, Muhammad Ali Jinnah, was central to the creation of Pakistan. He was one of the leading figures of the Pakistan Movement and is revered as Quaid-e-Millat ("Leader of the Nation") and later on as "Shaheed e Millat" ("Martyr of the Nation"). Khan was born in Karnal, Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province to a wealthy family. His grandfather, Nawab Ahmad Ali, provided significant support to the British during the Indian Rebellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All-India Muslim League
The All-India Muslim League (AIML) was a political party founded in 1906 in Dhaka, British India with the goal of securing Muslims, Muslim interests in South Asia. Although initially espousing a united India with interfaith unity, the Muslim League later led the Pakistan Movement, calling for a Two-nation theory, separate Muslim homeland after the British exit from India. The party arose out of the need for the political representation of Muslims in British Raj, British India, especially during the Indian National Congress-sponsored Swadeshi movement, massive Hindu opposition to the 1905 partition of Bengal. During the 1906 annual meeting of the All India Muslim Education Conference held in Ahsan Manzil, Israt Manzil Palace, Dhaka, the Nawab of Dhaka, Khwaja Salimullah, forwarded a proposal to create a political party which would protect the interests of Muslims in British India. He suggested the political party be named the 'All-India Muslim League'. The motion was unanimously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1947 Pakistani Constituent Assembly Election
Before the independence of Pakistan in 1947, members of the first term of the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan were selected through an indirect election held after June by the votes of the British Indian members of the provincial legislative assemblies. Background In 1946, after the provincial elections were held in British India, the British government sent a Cabinet Mission to the colony. The mission proposed the formation of an Indian confederacy, where autonomous states would have the authority to frame their own constitutions in unitary groups. Following the Constituent Assembly election later that year, the Constituent Assembly of India was formed. Indian National Congress, the largest member party, initially accepted the mission's proposal but later the party's leader Jawaharlal Nehru rejected it. As a result, the Muslim nationalist All-India Muslim League boycotted the assembly sessions, and its leader Muhammad Ali Jinnah refused to participate in the assembly. On 3 Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-party System
In political science, a multi-party system is a political system where more than two meaningfully-distinct political parties regularly run for office and win elections. Multi-party systems tend to be more common in countries using proportional representation compared to those using winner-take-all elections, a result known as Duverger's law. In these countries, usually no single party has a parliamentary majority by itself ( hung parliaments). Instead, multiple political parties must negotiate to form a coalition with a majority of the vote, in order to make substantial changes. Comparisons with other party systems Unlike a one-party system (or a dominant-party system), a multi-party system encourages the general constituency to form multiple distinct, officially recognized groups, generally called political parties. Each party competes for votes from the enfranchised constituents (those allowed to vote). A multi-party system prevents the leadership of a single party fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amendments To The Constitution Of Pakistan
This is a list of all the amendments to the Constitution of Pakistan The Constitution of Pakistan ( ; ISO 15919, ISO: '' Āīn-ē-Pākistān''), also known as the 1973 Constitution, is the supreme law of Pakistan. The document guides Pakistan's law, political culture, and system. It sets out the state's outlin .... References External links The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan {{Constitution of Pakistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Election Commissioner Of Pakistan
The Chief Election Commissioner is the authority and the appointed chair of the Election Commission of Pakistan— an institution constitutionally empowered to conduct free and fair elections to the national and provincial legislatures. Before 1973, appointment of the commissioner only restricted to the civil services and appointments came from the President. After the promulgation of much and thoroughly reformed constitution in 1973 in shape of 18th Amendment, the constitutional provisions made mandatory and compulsory that the only appointments would come from the judicature branch's judges who were eligible to become Chief Election Commissioner, however later on an amendment to the Constitution allowed civil servants to be appointed to the post as well. The Constitution (or President on different occasions) lays the appointment and oath administered by the Chief Justice of Pakistan. Appointment of the Chief Election Commissioner The President of Pakistan appoints the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of Pakistan
The Constitution of Pakistan ( ; ISO 15919, ISO: '' Āīn-ē-Pākistān''), also known as the 1973 Constitution, is the supreme law of Pakistan. The document guides Pakistan's law, political culture, and system. It sets out the state's outline, the fundamental rights of the population, the state's law and orders, and also the structure and establishment of the institutions and the armed forces. Drafted by the government of Zulfikar Ali Bhutto, with additional assistance from the country's Pakistani political parties, opposition parties, it was unanimously approved by the Parliament of Pakistan, 5th Parliament on 10 April and ratified on 14 August 1973. The first three chapters establish the rules, mandate, and Separation of powers, separate powers of the three branches of the government: a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature; an executive branch governed by the Prime Minister of Pakistan, Prime Minister as chief executive; and an apex federal judiciary headed by Supreme Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election Commission Of Pakistan
The Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP) is an independent, autonomous, permanent and constitutionally established federal body responsible for organizing and conducting elections to the national parliament, provincial legislatures, local governments, and the office of president of Pakistan, as well as the delimitation of constituencies and preparation of electoral rolls. As per the principles outlined in the Constitution of Pakistan, the Commission makes such arrangements as needed to ensure that the election is conducted honestly, justly, fairly and in accordance with law, and guard against corrupt practices. The Election Commission was formed on 23 March 1956. The Chief Election Commissioner and four Members, each from one of the four provinces (Punjab, Sindh, Balochistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa) of the country, form the five-member panel of the Election Commission. The current Chief Election Commissioner of Pakistan iSikandar Sultan Raja The General Elections 2018 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government In Pakistan
Pakistan is a federal republic with three tiers of government: national, provincial and local. Local government is protected by the constitution in Articles 32 and 140-A, and each province also has its own local-government-enabling legislation and ministries responsible for implementation. District councils and metropolitan corporations are respectively the highest rural and urban tiers of local government in the provinces. Both urban and rural local government have two or three tiers in all provinces except Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, where councils are not identified as either urban or rural. There are 129 district councils across the four provinces, 619 urban councils made up of one city district, four metropolitan corporations, 13 municipal corporations, 96 municipal committees, 148 town councils, 360 urban union committees, and 1,925 rural councils. Additionally there are 3339 neighbourhood, ‘tehsil’ and village councils in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Legislation In response to the fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
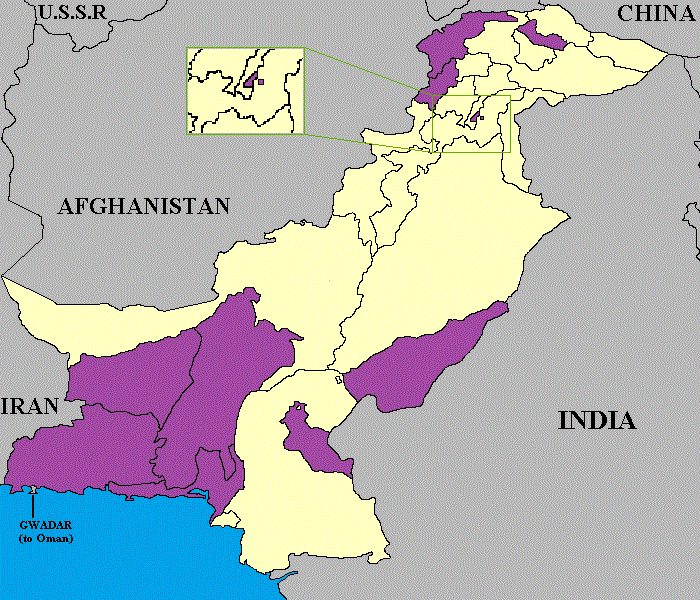
Administrative Units Of Pakistan
The administrative units of Pakistan comprise four provinces, one federal territory, and two territorial dispute, disputed territories: the provinces of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab, Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan; the Islamabad Capital Territory; and the administrative territories of Azad Kashmir, Azad Jammu and Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit–Baltistan. As part of the Kashmir conflict with neighbouring India, Pakistan has also claimed sovereignty over the Indian-controlled territories of Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh since the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947–1948, First Kashmir War of 1947–1948. It also has a territorial dispute with India over Junagadh State, Junagadh, but has never exercised administrative authority over either regions. All of Pakistan's provinces and territories are subdivided into divisions of Pakistan, divisions, which are further subdivided into districts of Pakistan, districts, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |