|
Elastic Pendulum
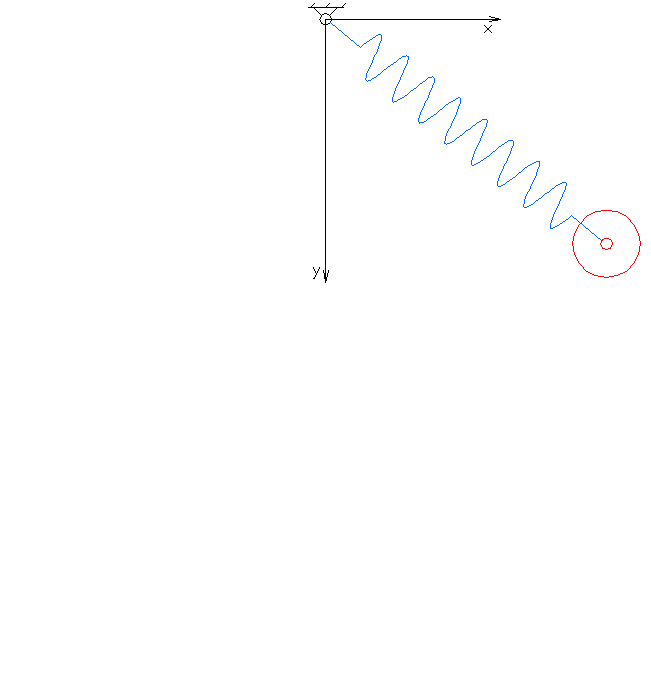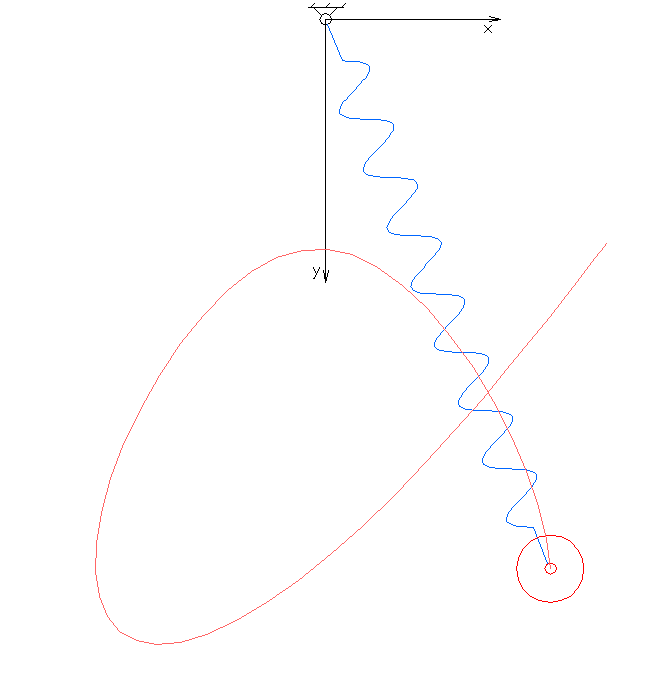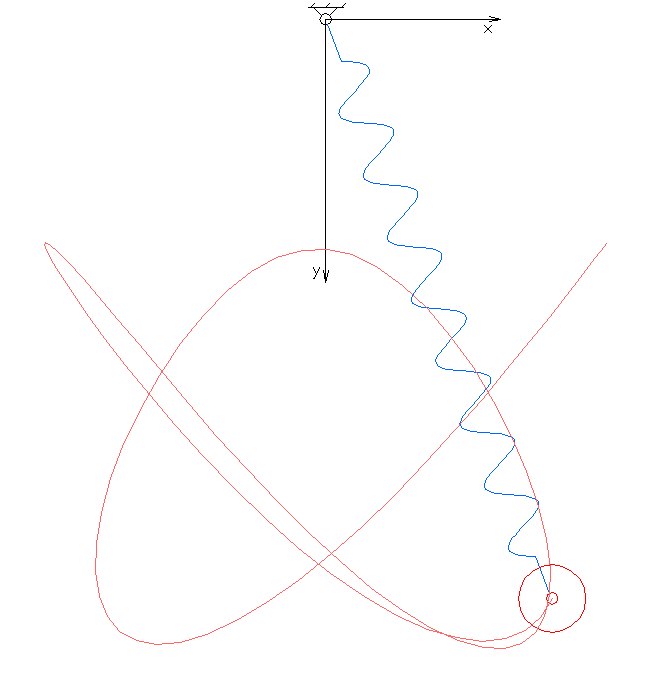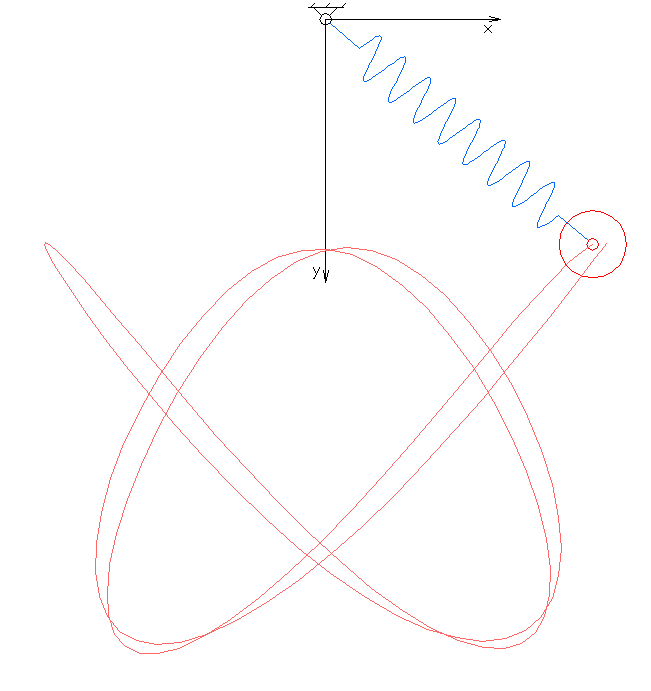
In physics and mathematics, in the area of dynamical systems, an elastic pendulum (also called spring pendulum or swinging spring) is a physical system where a piece of mass is connected to a spring so that the resulting motion contains elements of both a simple pendulum and a one-dimensional spring-mass system. The system exhibits chaotic behaviour and is sensitive to initial conditions. The motion of an elastic pendulum is governed by a set of coupled ordinary differential equations. Analysis and interpretation The system is much more complex than a simple pendulum, as the properties of the spring add an extra dimension of freedom to the system. For example, when the spring compresses, the shorter radius causes the spring to move faster due to the conservation of angular momentum. It is also possible that the spring has a range that is overtaken by the motion of the pendulum, making it practically neutral to the motion of the pendulum. Lagrangian The spring has the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring-mass System
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive coefficient, constant. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force (Damping ratio, damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction coefficient, the system can: * Oscillate with a frequency lower than in the Damping ratio, undamped case, and an amplitude decreasing with time (Damping ratio, underdamped oscillator). * Decay to the equilibrium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian (field Theory)
Lagrangian may refer to: Mathematics * Lagrangian function, used to solve constrained minimization problems in optimization theory; see Lagrange multiplier ** Lagrangian relaxation, the method of approximating a difficult constrained problem with an easier problem having an enlarged feasible set ** Lagrangian dual problem, the problem of maximizing the value of the Lagrangian function, in terms of the Lagrange-multiplier variable; See Dual problem * Lagrangian, a functional whose extrema are to be determined in the calculus of variations * Lagrangian submanifold, a class of submanifolds in symplectic geometry * Lagrangian system, a pair consisting of a smooth fiber bundle and a Lagrangian density Physics * Lagrangian mechanics, a reformulation of classical mechanics * Lagrangian (field theory), a formalism in classical field theory * Lagrangian point, a position in an orbital configuration of two large bodies * Lagrangian coordinates, a way of describing the motions of particles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaotic Maps
Chaotic was originally a Danish trading card game. It expanded to an online game in America which then became a television program based on the game. The program was able to be seen on 4Kids TV (Fox affiliates, nationwide), Jetix, The CW4Kids, Cartoon Network and Disney XD. It was brought over to the United States from Denmark by Bryan C. Gannon and Chaotic USA Entertainment Group, and produced by Chaotic USA Entertainment Group, 4Kids Productions and Bardel Entertainment. The trading card game came out 6 September 2006 in the U.S. and Canada. Each card comes with a unique code which the owner can upload onto the Chaotic website. This allows the owner to trade and play online using their own card collection. The game was well known to be the only game with a TV show, an online game, and a TCG that were all integrated. However, the online game is currently closed. History Chaotic started out as a trading card game known as "Grolls and Gorks" and an idea for a cartoon se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring-mass System
In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force ''F'' Proportionality (mathematics), proportional to the displacement ''x'': \vec F = -k \vec x, where ''k'' is a positive coefficient, constant. If ''F'' is the only force acting on the system, the system is called a simple harmonic oscillator, and it undergoes simple harmonic motion: sinusoidal oscillations about the equilibrium point, with a constant amplitude and a constant frequency (which does not depend on the amplitude). If a frictional force (Damping ratio, damping) proportional to the velocity is also present, the harmonic oscillator is described as a damped oscillator. Depending on the friction coefficient, the system can: * Oscillate with a frequency lower than in the Damping ratio, undamped case, and an amplitude decreasing with time (Damping ratio, underdamped oscillator). * Decay to the equilibrium p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
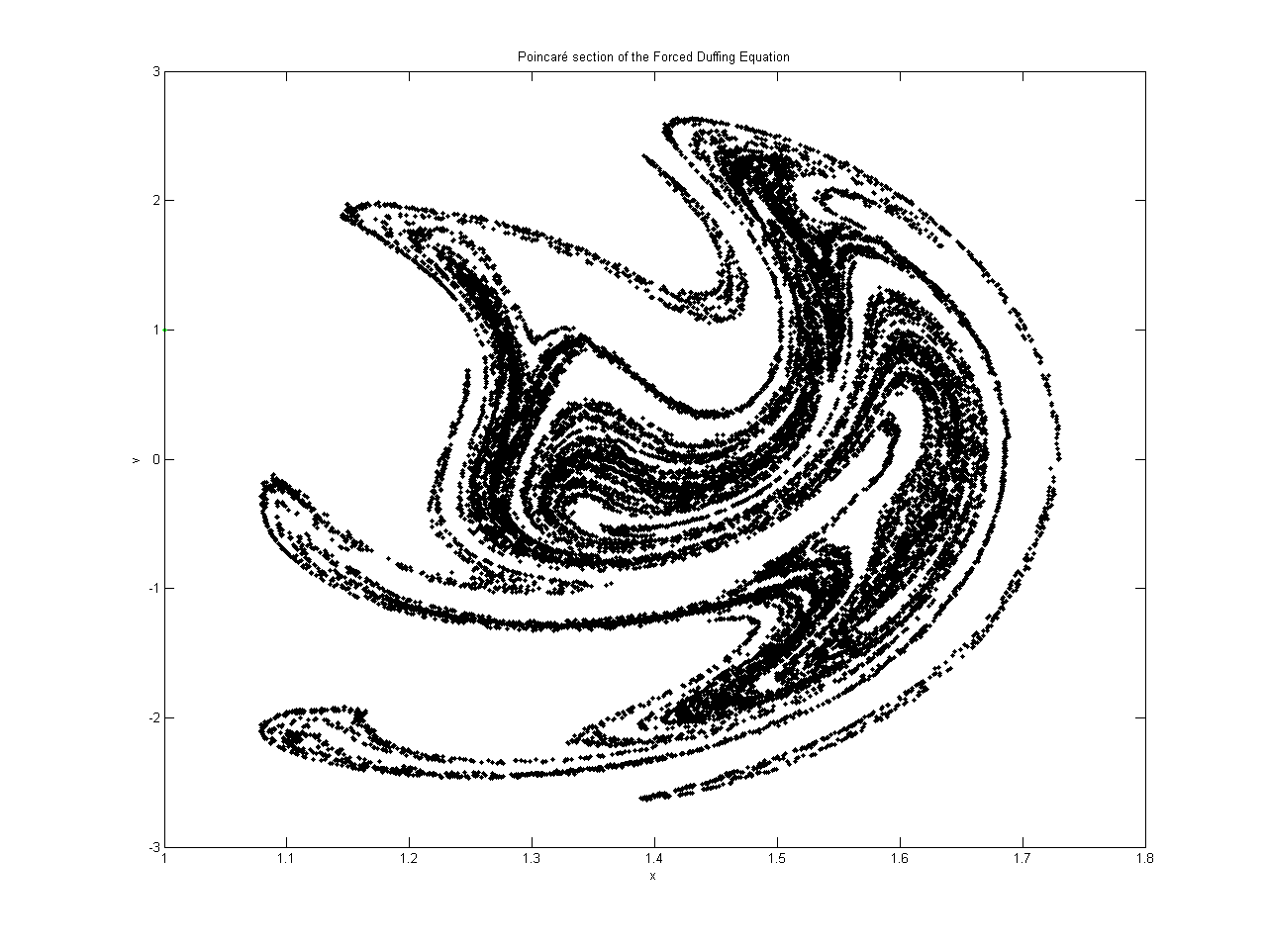
Duffing Oscillator
The Duffing equation (or Duffing oscillator), named after Georg Duffing (1861–1944), is a non-linear second-order differential equation used to model certain damped and driven oscillators. The equation is given by :\ddot + \delta \dot + \alpha x + \beta x^3 = \gamma \cos (\omega t), where the (unknown) function x=x(t) is the displacement at time t, \dot is the first derivative of x with respect to time, i.e. velocity, and \ddot is the second time-derivative of x, i.e. acceleration. The numbers \delta, \alpha, \beta, \gamma and \omega are given constants. The equation describes the motion of a damped oscillator with a more complex potential than in simple harmonic motion (which corresponds to the case \beta=\delta=0); in physical terms, it models, for example, an elastic pendulum whose spring's stiffness does not exactly obey Hooke's law. The Duffing equation is an example of a dynamical system that exhibits chaotic behavior. Moreover, the Duffing system presents in the fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic computation, symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods that attempt at finding approximate solutions of problems rather than the exact ones. Numerical analysis finds application in all fields of engineering and the physical sciences, and in the 21st century also the life and social sciences, medicine, business and even the arts. Current growth in computing power has enabled the use of more complex numerical analysis, providing detailed and realistic mathematical models in science and engineering. Examples of numerical analysis include: ordinary differential equations as found in celestial mechanics (predicting the motions of planets, stars and galaxies), numerical linear algebra in data analysis, and stochastic differential equations and Markov chains for simulating living ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ordinary Differential Equations
In mathematics, an ordinary differential equation (ODE) is a differential equation whose unknown(s) consists of one (or more) function(s) of one variable and involves the derivatives of those functions. The term ''ordinary'' is used in contrast with the term partial differential equation which may be with respect to ''more than'' one independent variable. Differential equations A linear differential equation is a differential equation that is defined by a linear polynomial in the unknown function and its derivatives, that is an equation of the form :a_0(x)y +a_1(x)y' + a_2(x)y'' +\cdots +a_n(x)y^+b(x)=0, where , ..., and are arbitrary differentiable functions that do not need to be linear, and are the successive derivatives of the unknown function of the variable . Among ordinary differential equations, linear differential equations play a prominent role for several reasons. Most elementary and special functions that are encountered in physics and applied mathematics are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degrees Of Freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or other physical processes are possible. This relates to the philosophical concept to the extent that people may be considered to have as much freedom as they are physically able to exercise. Applications Statistics In statistics, degrees of freedom refers to the number of variables in a statistic calculation that can vary. It can be calculated by subtracting the number of estimated parameters from the total number of values in the sample. For example, a sample variance calculation based on n samples will have n-1 degrees of freedom, because sample variance is calculated using the sample mean as an estimate of the actual mean. Mathematics In mathematics, this notion is formalized as the dimension of a manifold or an algebraic variety. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity; both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value (magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI (metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Constant velocity vs acceleration To have a ''constant velocity'', an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant direction cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry. At a fixed point on the surface, the magnitude of Earth's gravity results from combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation. At different points on Earth's surface, the free fall acceleration ranges from , depending on altitude, latitude, and longitude. A conventional standard value is defined exactly as . Locations of significant variation from this value are known as gravity anomalies. This does not take into account other effects, such as buoyancy or drag. Relation to the Universal Law Newton's law of universal gravitation states that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it determines the motion of planets, stars, galaxies, and even light. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the Moon's gravity is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of plants through the process of gravitropism and influencing the circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |